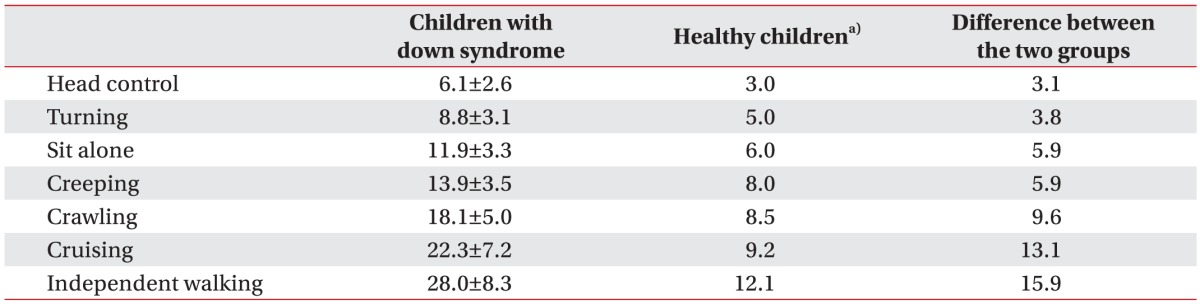
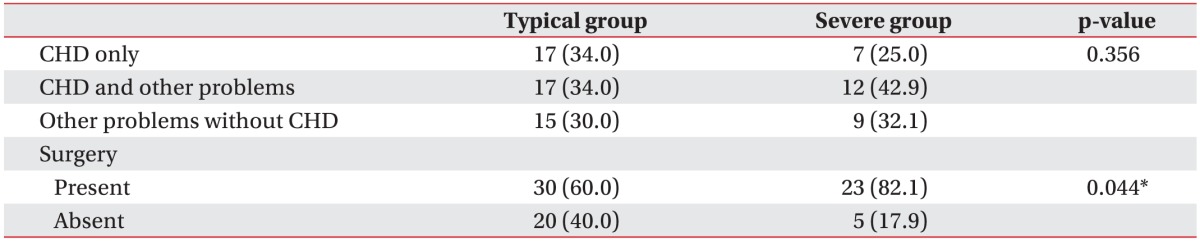
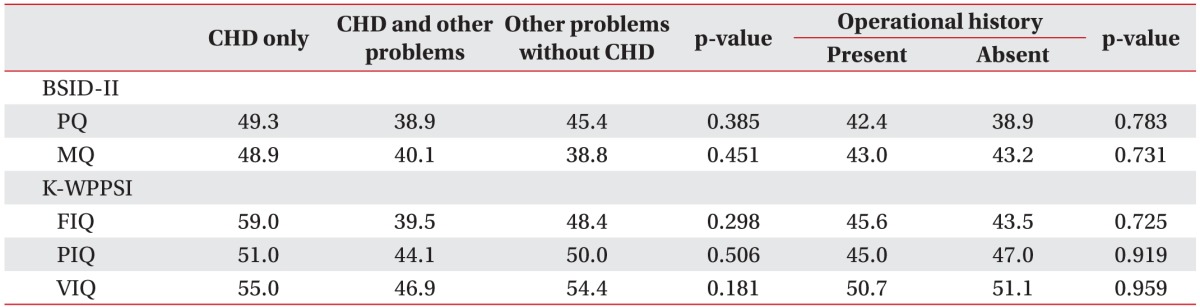
1. Frank K, Esbensen AJ. Fine motor and self-care milestones for individuals with Down syndrome using a Retrospective Chart Review. J Intellect Disabil Res 2015;59:719-729. PMID:
25533735.


2. Parker SE, Mai CT, Canfield MA, Rickard R, Wang Y, Meyer RE, et al. Updated National Birth Prevalence estimates for selected birth defects in the United States, 2004-2006. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol 2010;88:1008-1016. PMID:
20878909.


3. Weijerman ME, de Winter JP. Clinical practice: the care of children with Down syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 2010;169:1445-1452. PMID:
20632187.



4. Pangalos C, Avramopoulos D, Blouin JL, Raoul O, deBlois MC, Prieur M, et al. Understanding the mechanism(s) of mosaic trisomy 21 by using DNA polymorphism analysis. Am J Hum Genet 1994;54:473-481. PMID:
8116616.


5. Ulrich DA, Lloyd MC, Tiernan CW, Looper JE, Angulo-Barroso RM. Effects of intensity of treadmill training on developmental outcomes and stepping in infants with Down syndrome: a randomized trial. Phys Ther 2008;88:114-122. PMID:
17940103.


6. Palisano RJ, Walter SD, Russell DJ, Rosenbaum PL, Gemus M, Galuppi BE, et al. Gross motor function of children with down syndrome: creation of motor growth curves. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2001;82:494-500. PMID:
11295010.


7. Malak R, Kotwicka M, Krawczyk-Wasielewska A, Mojs E, Samborski W. Motor skills, cognitive development and balance functions of children with Down syndrome. Ann Agric Environ Med 2013;20:803-806. PMID:
24364457.

8. Edgin JO. Cognition in Down syndrome: a developmental cognitive neuroscience perspective. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci 2013;4:307-317. PMID:
26304208.


9. Martin K. Effects of supramalleolar orthoses on postural stability in children with Down syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol 2004;46:406-411. PMID:
15174532.


10. Mauerberg-deCastro E, Angulo-Kinzler RM. Locomotor patterns of individuals with Down syndrome: effects of environmental and task constraints. In: Weeks DJ, Chua R, Elliott D, editors. Perceptual-motor behavior in Down syndrome. Champaign: Human Kinetics; 2000. p.71-98.
11. de Campos AC, Rocha NA, Savelsbergh GJ. Development of reaching and grasping skills in infants with Down syndrome. Res Dev Disabil 2010;31:70-80. PMID:
19713074.


12. Charlton JL, Ihsen E, Oxley J. Kinematic characteristics of reaching in children with Down syndrome. Hum Mov Sci 1996;15:727-743.

13. Frank K, Esbensen AJ. Fine motor and self-care milestones for individuals with Down syndrome using a Retrospective Chart Review. J Intellect Disabil Res 2015;59:719-729. PMID:
25533735.


14. Polastri PF, Barela JA. Perception-action coupling in infants with Down syndrome: effects of experience and practice. Adapt Phys Activ Q 2005;22:39-56.

15. Polastri PF, Barela JA. Visual information and trunk sway coupling in infants with Down syndrome. J Sport Exerc Psychol 2002;24:104.
16. Cicchetti D, Beeghly M. Children with Down syndrome: a developmental perspective. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1990. p.280-313.
17. WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Motor Development Study: windows of achievement for six gross motor development milestones. Acta Paediatr Suppl 2006;450:86-95. PMID:
16817682.


18. Alexander MA, Matthews DJ, Murphy KP. Pediatric rehabilitation: principles and practice. 5th ed. New York: Demos Medical Publishing; 2015.
19. Melyn MA, White DT. Mental and developmental milestones of noninstitutionalized Down's syndrome children. Pediatrics 1973;52:542-545. PMID:
4270249.



20. Fishler K, Share J, Koch R. Adaptation of Gesell developmental scales for evaluation of development in children with Down's syndrome (Mongolism). Am J Ment Defic 1964;68:642-646. PMID:
14131888.

21. Centerwall SA, Centerwall WR. A study of children with mongolism reared in the home compared to those reared away from the home. Pediatrics 1960;25:678-685. PMID:
13808797.



22. Kugel RB, Reque D. A comparison of mongoloid children. JAMA 1961;175:959-961. PMID:
13754934.


23. Jobling AA, Virji-Babul N. Motor development in Down syndrome: play, move and grow. Burnaby: Down syndrome Research Foundation; 2004. p.15-22.
24. Babb JG. Gross motor skills in children with Down syndrome. J Dev Behav Pediatr 2000;21:155-156.

25. Tudella E, Pereira K, Basso RP, Savelsbergh GJ. Description of the motor development of 3-12 month old infants with Down syndrome: the influence of the postural body position. Res Dev Disabil 2011;32:1514-1520. PMID:
21367575.


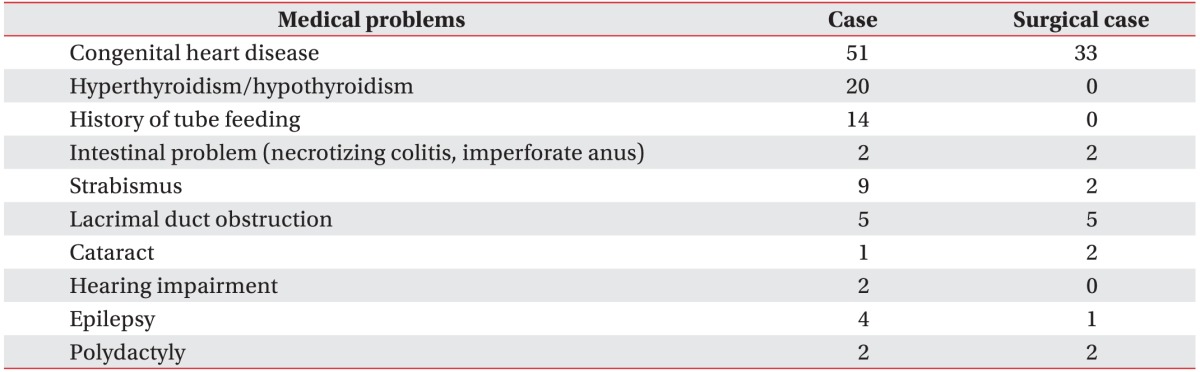
26. Alsaied T, Marino BS, Esbensen AJ, Anixt JS, Epstein JN, Cnota JF. Does congenital heart disease affect neurodevelopmental outcomes in children with Down syndrome? Congenit Heart Dis 2016;11:26-33. PMID:
26914309.


28. Gallagher A, Dagenais L, Doussau A, Décarie JC, Materassi M, Gagnon K, et al. Significant motor improvement in an infant with congenital heart disease and a rolandic stroke: the impact of early intervention. Dev Neurorehabil 2016;2 18 [Epub]. PMID:
10.3109/17518423.2015.1132280.

29. van Trotsenburg AS, Heymans HS, Tijssen JG, de Vijlder JJ, Vulsma T. Comorbidity, hospitalization, and medication use and their influence on mental and motor development of young infants with Down syndrome. Pediatrics 2006;118:1633-1639. PMID:
17015556.


30. Gibson D. Down's syndrome: the psychology of mongolism. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1978.
31. Tsao R, Kindelberger C. Variability of cognitive development in children with Down syndrome: relevance of good reasons for using the cluster procedure. Res Dev Disabil 2009;30:426-432. PMID:
19036558.


32. Perron-Borelli M, Perron R. Differential Scales of Intellectual Efficiency [Echelles differentielles d'efficiences intellectuelles]. Paris: Ets d'Applications Psychotechniques; 1996.
33. Seitz J, Jenni OG, Molinari L, Caflisch J, Largo RH, Latal Hajnal B. Correlations between motor performance and cognitive functions in children born <1250 g at school age. Neuropediatrics 2006;37:6-12. PMID:
16541362.



34. Joo JW, Choi JY, Rha DW, Kwak EH, Park ES. Neuropsychological outcomes of preterm birth in children with no major neurodevelopmental impairments in early life. Ann Rehabil Med 2015;39:676-685. PMID:
26605165.