- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 35(4); 2011 > Article |
Abstract
Epilepsy is an intractable disease, though many treatment modalities have been developed. Recently, noninvasive transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), which can change brain excitability, was introduced and has been applied for therapeutic purposes regarding epilepsy. A suppression of seizures was experienced by cathodal tDCS in a medication refractory pediatric epileptic patient. The patient was an 11-year-old female who had focal cortical dysplasia of the cerebral hemisphere. The patient was treated with antiepileptic drugs but the mean seizure frequency was still eight episodes per month. The tDCS cathode was placed at the midpoint of P4 and T4 in the 10-20 EEG system where the abnormal wave was observed on a sleep EEG. Two mA of tDCS was applied 20 minutes a day, five days a week for two weeks. During a two-month period after treatment termination, only six seizure attacks occurred, and the duration of each seizure episode also decreased. tDCS was applied under the same conditions for another two weeks. For two months after the second treatment session, only one seizure attack occurred, and it showed great improvement compared to the eight seizure attacks per month before the tDCS treatment. The medications were not changed, and there were no notable side effects that were caused by tDCS.
Epilepsy is a chronic neurologic disorder that manifests in diverse ways. The two hallmarks of seizure generation are hyperexcitability of neurons and hypersynchrony of neural circuits.1 Treatment of epilepsy is focused on inactivation of the excitative brain cortex, including antiepileptic drugs and surgery. However, epilepsy is intractable in some patients.2,3 Recently, noninvasive techniques, such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) that can change brain excitability, were introduced.4 These techniques have been applied for therapeutic purposes in epilepsy, but there have been no reports on tDCS being applied on epileptic patients in Korea. Suppression of seizure by cathodal tDCS in a medication refractory epileptic patient was observed.
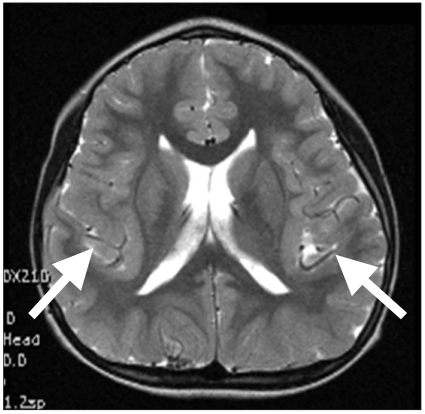
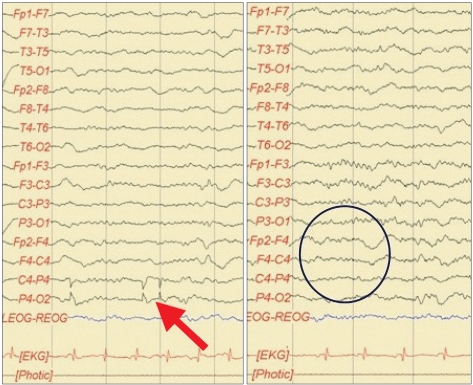
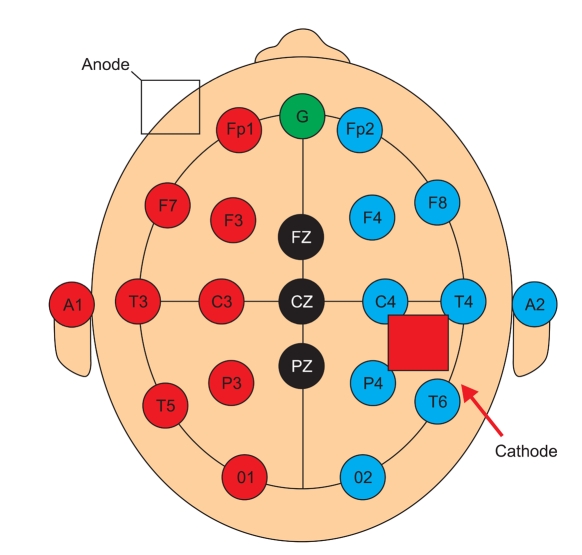
An 11-year-old female patient suffering from epileptic seizures visited our clinic. The patient born by was a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery at 39 weeks/3.08 kg, and she was the second child of two siblings. The patient presented her first seizure attack at the age of four. A brain magnetic resonance image revealed cortical dysplasia of both sylvian areas. The patient was diagnosed with congenital bilateral perisylvian syndrome (Fig. 1). Electroencephalography (EEG) revealed diffuse slow waves on the right hemisphere and intermittent spikes on the temporoparietal area (Fig. 2). A chromosomal study showed 46, XX, inversion 9. The patient also was diagnosed with mental retardation and microcephaly. The patient presented seizure attacks an average of eight times a month. In spite of prescribing Topamax® (topiramate, 10 mg/day) and Trilpetal® (oxycarbazepine, 600 mg/day), the seizure frequency and durations were constant. Cathodal tDCS was applied on the right temporo-parietal area that showed abnormal findings in an EEG. Phoresor® II Auto Model PM850 (IOMED®, Salt Lake City, USA) was used as a direct current generator. The electrodes attached to the scalp were 5×5 cm (area 25 cm2) sponge electrodes. The anode was attached on the area above the left orbit and the cathode between P4 and T4 of the international 10-20 system of electrode placement (Fig. 3). tDCS was performed for 20 minutes using 2 mA, 5 times a week for 2 weeks.
The patient did not present seizures during the intervention period. For two months after the intervention period, the patient suffered seizure attacks six times. This was half as frequent as before the intervention, which was eight times a month. The duration of each seizure was less than 30 seconds after the intervention compared to 30 seconds to 1 minute before the intervention. Two months after the first intervention session, a second intervention session with the same methods was conducted for two weeks. After the second intervention session, the patient had a seizure attack just once over two months.
Non-invasive brain stimulation techniques such as rTMS and tDCS have been investigated for suppression of epilepsy. Though several studies have suggested rTMS reduces epilepsy, there is little evidence on suppression of epilepsy by tDCS.4
tDCS causes excitation of excitatory glutamatergic cortical pathways and suppression of intracortical inhibitory pathways.5 This is based on findings that a surface-positive current enhances neuronal firing and increases the size of evoked potentials while a surface-negative current has the opposite effect.6 Liebetanz, et al.7 reported anticonvulsive effects induced by cathodal tDCS in rats.
Generally, antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) and surgery are treatments for epilepsy. The recurrence rates were about 30% after treatment with AEDs and about 30-50% after treatment with surgery.2,3 Recently, noninvasive techniques, such as rTMS and tDCS, were introduced as therapeutic options for intractable epilepsy.4 Fregni et al. showed that nineteen patients (mean age=24) with refractory epilepsy underwent one session of active tDCS (20 minutes, 1 mA). Fregni et al.8 showed a significant reduction in the number of epileptiform discharges and decrease in seizure frequency compared with sham tDCS, and the effects lasted for one month. The results in this study also showed that treatment for two weeks, five days a week tDCS (20 minutes, 2 mA) reduced epileptic seizures. As several authors have demonstrated in humans, cathodal stimulation decreased cortical excitability. In this study, the findings suggest that cathodal tDCS reduced cortical excitability, thus suppressing epileptic activity. This can be evidence of tDCS as a therapeutic option for treatment of seizures. Further studies regarding the correct attachment sites of reference electrodes, tDCS intensity, duration, and frequency are needed.
References
1. Stafstrom CE. Epilepsy: a review of selected clinical syndromes and advances in basic science. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2006;26:983-1004. PMID: 16437061.


2. Schiller Y, Najjar Y. Quantifying the response to antiepileptic drugs: effect of past treatment history. Neurology 2008;70:54-65. PMID: 18166707.


3. Spencer S, Huh L. Outcomes of epilepsy surgery in adults and children. Lancet Neurol 2008;7:525-537. PMID: 18485316.


4. Nitsche MA, Paulus W. Noninvasive brain stimulation protocols in the treatment of epilepsy: current state and perspectives. Neurotherapeutics 2009;6:244-250. PMID: 19332316.



5. Liebetanz D, Nitsche MA, Tergau F, Paulus W. Pharmacological approach to the mechanisms of transcranial DC-stimulation-induced after-effects of human motor cortex excitability. Brain 2002;125:2238-2247. PMID: 12244081.



6. Bindman LJ, Lippold OCJ, Redfearn JWT. The action of brief polarizing currents on the cerebral cortex of the rat (1) during current flow and (2) in the production of long-lasting after-effects. J Physiol 1964;172:369-382. PMID: 14199369.



7. Liebetanz D, Klinker F, Hering D, Koch R, Nitsche MA, Potschka H, Loscher W, Paulus W, Tergau F. Anti convulsant effects of transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat cortical ramp model of focal epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006;47:1216-1224. PMID: 16886986.


8. Fregni F, Thome-Souza S, Nitsche MA, Freedman SD, Valente KD, Pascual-Leone A. A controlled clinical trial of cathodal DC polarization in patients with refractory epilepsy. Epilepsia 2006;47:335-342. PMID: 16499758.


-
METRICS

-
- 70 Crossref
- Scopus
- 5,972 View
- 68 Download
- Related articles in ARM