- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 42(3); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy and safety of our 4-week caregiver-mediated exercise (CME) in improving trunk control capacity, gait, and balance and in decreasing concerns about post-stroke falls when there is an increase in its efficacy.
Methods
Acute or subacute stroke survivors were assigned to either the trial group (n=35) or the control group (n=37). Changes in Modified Barthel Index (MBI), Functional Ambulation Categories (FAC), Berg Balance Scale (BBS), and Trunk Impairment Scale (TIS) scores at 4 weeks from baseline served as primary outcome measures. Correlations of primary outcome measures with changes in Fall Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) scores at 4 weeks from baseline in the trial group served as secondary outcome measures. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) served as safety outcome measures.
Results
There were significant differences in changes in MBI, FAC, BBS, TIS-T, TIS-D, TIS-C, and FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups (all p<0.0001). There were no significant (p=0.0755) differences in changes in TIS-S scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups. MBI, FAC, BBS, and TIS scores showed significantly inverse correlations with FES-I scores in patients receiving CME. There were no TEAEs in our series.
Stroke survivors often experience a variety of physical and cognitive dysfunctions. Of these, balance and gait disturbances are the most common problems that they encounter. Decreased mobility is one of their major concerns [1]. In addition, they often have impaired proprioception, causing them to depend on visual sense both greatly and incorrectly. This can eventually lead to sensory integration disorder, abnormal compensatory strategies, inappropriate body response to interference, inability to maintain stability, and decline in motor control skills. They are therefore vulnerable to post-stroke falls as well as poor quality of life (QOL) [2-4]. Post-stroke falls are one of the most common complications that place patients in danger during post-stroke rehabilitation [5]. Their prevalence in Western countries ranges between 8.9/1000 and 15.9/1000 in patients/day [6,7]. A higher risk of post-stroke falls is closely associated with a variety of factors, including age of ≥60 years, female gender, poor balance, gait disorders, wheelchair confinement, confusion, attacks of syncope, symptoms of visuospatial hemineglect and dyspraxia, postural hypotension, and medication usage [8-10].
Both trunk movement and balance ability are key factors that are closely associated with the degree of functional independence in stroke survivors [11]. That is, trunk muscles are involved in the stabilization of proximal body segments during several balancing activities [12]. However, stroke survivors are characterized by impairments in trunk control that is needed for weightshifting capacity and equilibrium function [13]. In other words, they lack the ability to maintain even weight distribution on both feet due to their weakness of trunk muscles and impairments in trunk control [14]. Moreover, they are unable to perform functional activities due to decreased balance capacity [15]. Improvement in trunk control may therefore lead to improved balance capacity and better degree of activities of daily living (ADL) [12].
With increased demands on post-stroke rehabilitation and decreased length of hospital stay, new approaches are warranted to improve health-related quality of life (HRQOL) outcomes [16]. However, shorter length of hospital stay is associated with less access to post-stroke rehabilitation, potentially less recovery, and more burden to the caregiver and family. It is therefore imperative that novel, more efficient, and cost-effective post-stroke rehabilitation strategies should be established [17]. Active involvement of caregivers as a co-therapist termed as caregiver-mediated exercise (CME) is one of various methods for increasing the intensity of exercise therapy for post-stroke rehabilitation [18]. The concept of CME is not novel. In fact, it is common practice in pediatric neurological rehabilitation [19]. There is no denying that stroke survivors are psychologically burdened with poststroke outcomes on their caregivers’ role and functions. It has been suggested that caregivers are willing to be involved in post-stroke rehabilitation [20].
Given the above background, we developed a CME protocol as a way to improve trunk control capacity, gait, and balance. The objective of this study was to assess its efficacy and safety in a single-institution setting. We also examined whether our CME protocol might be effective in diminishing concerns about post-stroke falls when there was an increase in its efficacy.
The current single-center, prospective, randomized, observer-blind, controlled study was conducted in a total of 80 acute or subacute stroke survivors who were referred to us after treatment of acute hemiplegia at the Department of Neurology or Neurosurgery between January 2016 and February 2017.
Inclusion criteria for these patients were as follows: (1) patients aged 18 years or older, (2) patients with first-ever stroke, (3) patients who experienced a single ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke in the cerebral hemisphere as confirmed by computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, (4) patients with poststroke duration <2 months, (5) patients with post-stroke hemiplegia with decreased stability of the trunk or lower limb, (6) patients with the Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) scores ≥24 points, (7) patients who were able to keep static sitting balance for more than 2 minutes, (8) patients who were able to keep standing posture when receiving mild-to-moderate assistance.
Inclusion criteria for caregivers were as follows: (1) caregivers who were able to understand instructions on CME, (2) caregivers who were motivated for CME, (3) caregivers who were medically stable, (4) caregivers who were physically able to perform exercises together with the patients.
Exclusion criteria for patients were as follows: (1) those with poor visual acuity, (2) those with severe aphasia, (3) those with neurological deficits due to causes other than cerebral infarction (e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, fractures, or congestive heart failure), (4) those who had serious underlying medical conditions that might affect mobility training (e.g., unstable blood pressure), (5) those who had severe unilateral neglect, (6) those who had abnormalities of the vestibular system, (7) those who had musculoskeletal disorders that might affect motor performance, (8) those who underwent amputation or joint replacement surgery within 6 months prior to the study participation, (9) those who used a cardiac pacemaker or a defibrillator, (10) those who received a nasogastric tube feeding, (11) those who used a urine or tracheal tube, (12) those who were uncooperative or unable to comply with instructions on CME, (13) those who were deemed to be ineligible for study participation according to our judgment.
Exclusion criteria for caregivers were as follows: (1) those with serious comorbidities, (2) those who were not able to walk 100 m, stand, and/or keep their balance.
We therefore enrolled a total of 72 patients in the current analysis. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Konkuk University Chungju Hospital (No. KUCH-2017-04-009). All patients submitted a written informed consent for study participation. The current study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
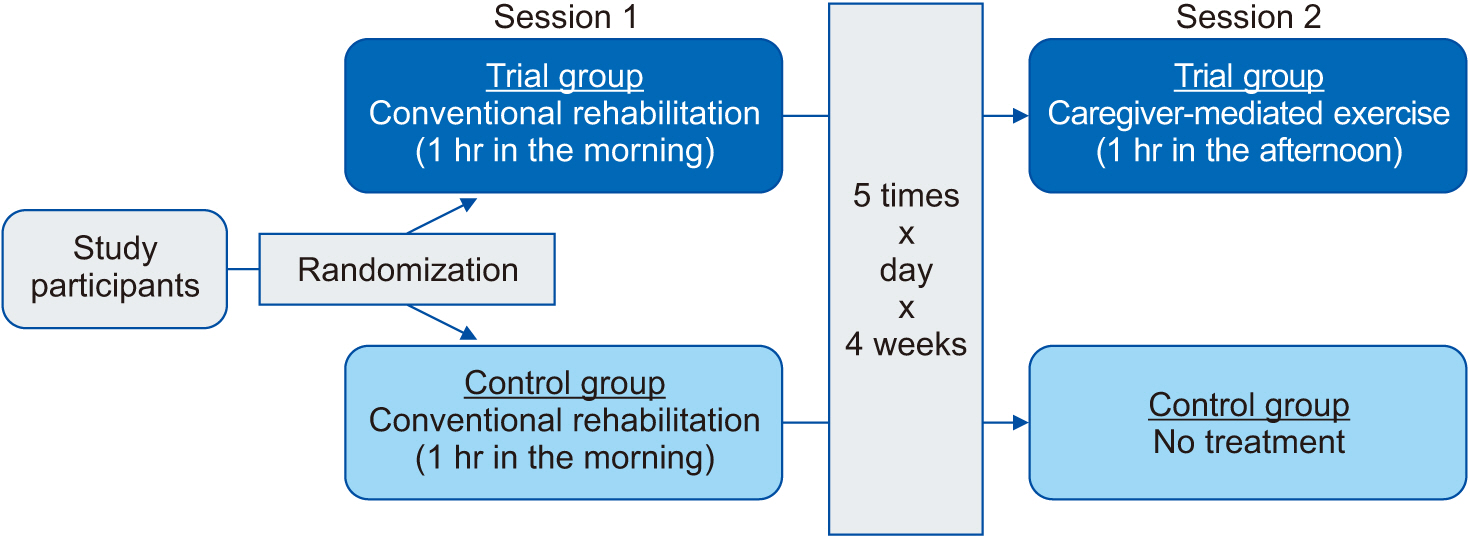
Depending on the type of post-stroke rehabilitation, patients were randomly assigned to either the trial group (n=35) or the control group (n=37) using a permuted block design. This was done by a study personnel who was blinded to details of the current study. In addition, CME was done by a physical therapist under the supervision of a physician who was not involved in the current study. In more detail, patients of the trial group received a 1-hour conventional post-stroke rehabilitation in the morning and did a 1-hour CME for 2 hr/day, 5 times a week for 4 weeks. Patients of the control group solely received a 1-hour conventional post-stroke rehabilitation in the morning at 1 hr/day, 5 times a week for 4 weeks. The conventional post-stroke rehabilitation was a multi-disciplinary, patient-specific intervention that was composed of physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and nursing care. It also included neuropsychological and speech therapy if needed. Various neurological treatment elements were combined, for which motor re-learning strategies as well as neuro-developmental recovery were considered as priority. CME was gradually performed. The frequency of its repetition was determined according to patients’ performance. Finally, compliance was monitored using a self-reported diary during CME.
At baseline, patients received baseline assessment. They were evaluated for baseline characteristics and outcome measures prior to a 4-week post-stroke rehabilitation program. At 4 weeks, they were evaluated for changes in outcome measures from baseline. Differences in changes of outcome measures at 4 weeks from baseline were compared between the two groups (Fig. 1). They were also evaluated for the safety of our rehabilitation program.
At both baseline and at 4 weeks, patients were evaluated using the following scales.
A measure of ADL, Modified Barthel Index (MBI) represents the degree of independence of stroke survivors from any assistance. Its functional domains are composed of bowel control, bladder control, as well as help with grooming, toilet use, feeding, transfers, walking, dressing, climbing stairs, and bathing [21].
Functional Ambulation Categories (FAC) is commonly used to assess the ambulation status of stroke survivors based on a 6-point scale by measuring the degree of support they require during walking irrespective of the use of an orthosis [22].
Berg Balance Scale (BBS) is a measure of static and dynamic balance of patients with stroke [23].
Trunk Impairment Scale (TIS) is a measure of the trunk function of stroke survivors. It is composed of three subscales with a total possible score (TIS-T) of 23 points: static sitting balance (TIS-S; 3 questions with a total possible score of 7 points), dynamic sitting balance (TIS-D; 10 questions with a total possible score of 10 points), and coordination (TIS-C; 4 questions with a total possible score of 6 points), with higher TIS score indicating higher degree of trunk balance [24].
Fall Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) is a measure of fear of falling (FOF). FOF is defined as an ongoing concern about falling, thus restricting ADL. Its scores range between 16 and 64 points, with higher FES-I score indicating higher degree of FOF [25].
Changes in MBI, FAC, BBS, and TIS scores at 4 weeks from baseline served as primary outcome measures. Correlations of primary outcome measures with changes in FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline in the trial group served as secondary outcome measures. For efficacy assessment, we compared differences in changes in efficacy outcome measures at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups. We also performed intent-to-treat (ITT) and per-protocol (PP) analyses.
The ITT set comprised all enrolled patients who were given randomization number except the following patients: (1) those who did not meet inclusion/exclusion criteria at screening visit, (2) those who did not receive treatment, and (3) those who did not receive efficacy analysis.
The PP set comprised all ITT patients who completed the current study without seriously violating the study protocol except the following patients: (1) those who did not submit a written informed consent, (2) those who were not evaluated for the efficacy at 4 weeks, (3) those who underwent procedures or treatments that might affect results of the efficacy analysis (including prohibited concomitant medications) during the study period, and (4) those who seriously violated the study protocol according to our judgment.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) served as safety outcome measures. The safety set comprised all patients who were enrolled in the current study and received safety analysis after the treatment.
Our CME protocol consisted of three phases: exercise in lying, sitting, and standing positions.
Lying in bed and looking at the ceiling, patients placed a balance pad underneath the pelvis to bend both knees and to touch the sole on the bed. Then they spontaneously place both hands on the chest and perform weight transfer by alternating left and right hands for 3 seconds. Lying in bed and looking at the ceiling, patients bent both knees and placed both soles on the balance pad. Then they spontaneously place both arms straight beside the body. They lifted the hip with both hip joints extended. They kept this posture for 3 seconds.
A balance pad was placed on the bed for patients to sit on it. To make sure that both soles completely touch the ground, they had the height of the bed adjusted. Lifting both arms straight and having them softly held by a caregiver, they kept the posture for 3 seconds while performing weight transfer to left, right, and posterior directions. Patients perched on the bed. After placing a balance pad on the ground, patients completely touched both soles on it. After lifting both arms and then straightening them side by side, they had them softly held by a caregiver. Stepping on the pad slowly and keeping their balance, they performed complete standing exercise followed by slow sitting.
Stepping on the pad, patients straightened both arms side by side and had them softly held by a caregiver. With eyes closed, they kept their balance on the pad. For safety reasons, however, they performed exercise beside the bed. They could immediately sit on the bed whenever their posture became unstable. Stepping on the pad, patients straightened both arms side by side and had them softly held by a caregiver. Then they bent or extended both knees slowly. They were not allowed to precede their knee to the tip of the foot. For safety reasons, they performed the exercise beside the bed. They could immediately sit on the bed whenever their posture became unstable.
We estimated the sample size using PASS version 12 (NCSS, Kaysville, UT, USA) as previously described [26]. We hypothesized that the degree of changes in the TIS at 4 weeks from baseline would be 3.37 in the trial group and 1.25 in the control group. In addition, we hypothesized that the standard deviation would be 3 based on its maximum value (=2.76). Considering a significance level of 5%, a statistical power of 80%, and a drop-out rate of 30%, we estimated the sample size to be 42 per group.
All data are expressed as mean±standard deviation. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS version 18.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Differences in changes of efficacy outcome measures at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups were analyzed using unpaired t-test. We also performed linear regression analysis to identify correlations of primary outcome measures with changes in FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
The 80 recruited patients were initially assigned to the trial group (n=40) and the control group (n=40). Of these patients in the trial group, 2 and 3 discontinued the study because of discharge and non-compliance, respectively. Of patients in the control group, 3 discontinued the study because of discharge. Therefore, 35 and 37 patients were assigned to the trial group and the control group, respectively. The study flow chart is shown in Fig. 2.
Our clinical series of patients consist of 39 men and 33 women whose mean age was 59.7±6.3 years old. They had a mRS score of 3.6±0.5, an NIHSS score of 4.8±2.4 points, a time from the onset of stroke to CME of 10.8 days, and a K-MMSE score of 26.6±1.3 points. Baseline characteristics of these patients are represented in Table 1.
As shown in Table 2, there were differences in changes in outcome measures at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups. There were significant differences in changes in MBI, FAC, BBS, TIS-T, TIS-D, TIS-C, and FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups (all p<0.0001). There was no significant (p=0.0755) difference in changes in TIS-S scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups.
In the trial group, primary outcome measures had significant inverse correlations with changes in FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline (Fig. 3).
The goal of post-stroke rehabilitation is to raise the degree of independence of ADL. Risk factors of post-stroke falls and standing balance are important predictors of functional recovery and gait capacity. They play a key role in determining ADL [27,28]. According to a review of previous published studies in this series, approximately 75% of stroke survivors achieved a recovery of independent standing-balance capacity. However, they persistently presented with weight-bearing imbalance and increased postural sway as well as impaired weight-shifting capacity. Therefore, the key goal of post-stroke rehabilitation is to improve balance capacity, for which a variety of exercise interventions have been used [29].
In our trial, we found that changes in MBI, FAC, BBS, TIS-T, TIS-D, TIS-C, and FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline showed significant differences between the two groups (all p<0.0001). However, there was no significant (p=0.0755) difference in changes in TIS-S scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups. This might be because we enrolled patients who were able to keep static sitting balance for more than 2 minutes.
Caregivers are involved in ADL of stroke survivors. According to current clinical practice guidelines, caregivers are recommended to be actively involved in post-stroke rehabilitation for the promotion of their functional recovery [30,31].
It has been shown that CME is both efficacious and cost-effective in improving functional recovery of stroke survivors [32]. Prospective, randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the efficacy of CME in stroke survivors. Vloothuis et al. [1] have conducted an observerblind, randomized controlled trial to assess the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of an 8-week CARE4STROKE program in a total of 66 stroke survivors, showing that the intensity of CME is increased through e-health support. These authors have suggested that CME would be effective in improving functional outcomes, providing early supported discharge, and reducing the cost [1]. Wang et al. [33] have also conducted a single-blind, randomized, controlled trial to assess the efficacy of a 12-week caregiver-mediated, home-based intervention in improving physical functions and social participation in a total of 51 patients with chronic stroke, showing that it is an effective modality. Caregivers are relatively more intensively involved in CME. This might have increased caregiver burden. There are also contradictory reports showing that CME does not increase the caregiver burden [33,34]. Wang et al. [33] have analyzed caregiver burden using the Caregiver Burden Scale, showing that CME does not have significant effects on caregiver burden at endpoint. This might be due to caregivers’ high levels of knowledge about patients’ physical performances. These authors have also found that caregiver burden is closely associated with caregivers’ psychological distress, the amount of exercise rehabilitation, and the degree of patients’ physical impairment [33].
Limitations of the current study are as follows: (1) we evaluated a small series of patients; (2) we conducted the current study with short periods of time; (3) we only evaluated patients who were hospitalized at a single, tertiary medical institution. We could not therefore completely rule out the possibility of selection bias. (4) We failed to consider NIHSS or mRS scores when assessing the efficacy of our CME protocol. A phase I or II clinical trial needs to be conducted to clarify mechanisms of a certain intervention. A phase III trial is also needed to assess its efficacy considering NIHSS or mRS scores in the assessment of treatment effect to determine indications of our CME protocol. (5) We failed to consider risk factors of post-stroke falls in enrolled patients. (6) We failed to completely assess treatment compliance. Stroke survivors are more likely to practice motor activities during supervised exercise [35]. In the current study, the additional CME was delivered in the evening outside of routine physiotherapy hours. This enabled stroke survivors to participate in their routine rehabilitation program during the day and their caregivers to continue with their daily working schedule. Moreover, effects of CME on caregivers deserve special attention, including their anxiety, depression, QOL, fatigue, and self-efficacy. (7) There was a difference in the treatment dose between the two groups. There might be a dose-response relationship between CME and outcome measures which has been supported by previous published studies [36-39]. Currently, there is limited evidence supporting the dose-response relationship in post-stroke CME [1]. This deserves further studies.
To summarize, our results are as follows: (1) there were significant differences in changes in MBI, FAC, BBS, TIS-T, TIS-D, TIS-C, and FES-I scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups (all p<0.0001). (2) There was no significant (p=0.0755) difference in changes of TIS-S scores at 4 weeks from baseline between the two groups. (3) MBI, FAC, BBS, and TIS scores had significantly inverse correlations with FES-I scores in patients receiving CME. (4) There were no TEAEs in our series.
In conclusion, our results indicate that our CME protocol is an effective and safe modality in improving the degree of independence, ambulation status, dynamic and static balance, trunk function, and concerns about poststroke falls in stroke survivors. Our results also showed that there was a decrease in FES-I scores when there was an increase in MBI, FAC, BBS, and TIS scored. Thus, multi-disciplinary approaches are needed to develop an algorithm to minimize risks of post-stroke falls. Further large-scale, long-term, multi-center studies are warranted to confirm our results.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Fig. 3.
Correlations of MBI, BBS, FAC, and TIS scores with FES-I scores. Linear relation (A) between MBI and FES-I scores, (B) between BBS and FES-I scores, (C) between FAC and FES-I scores, and (D) between TIS and FES-I scores. MBI, Modified Barthel Index; BBS, Berg Balance Scale; FAC, Functional Ambulation Category; TIS, Trunk Impairment Scale; FES-I, Fall Efficacy Scale-International.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients
Table 2.
Efficacy outcomes
|
Trial group (n=35) |
Control group (n=37) |
p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 4 weeks | Baseline | 4 weeks | ||
| MBI | 35.5±4.6 | 63.3±6.3 | 36.2±5.3 | 58±7.0 | <0.0001* |
| FAC | 1.2±0.4 | 2.7±0.5 | 1.3±0.5 | 2.3±0.5 | <0.0001* |
| BBS | 12.5±2.8 | 29.1±3.6 | 13.8±2.8 | 25.8±3.3 | <0.0001* |
| TIS-T | 13.5±1.8 | 17.4±1.9 | 13.7±1.9 | 15.8±1.8 | <0.0001* |
| TIS-S | 5.5±0.5 | 6.4±0.5 | 5.6±0.5 | 6.2±0.4 | 0.0755 |
| TIS-D | 5.4±0.8 | 7.0±0.7 | 5.5±0.8 | 6.3±0.7 | <0.0001* |
| TIS-C | 2.5±0.6 | 4.0±0.8 | 2.6±0.6 | 3.3±0.7 | <0.0001* |
| FES-I | 52.2±3.0 | 35.4±5.5 | 51.4±3.8 | 41.3±6.1 | <0.0001* |
REFERENCES
1. Vloothuis J, Mulder M, Nijland RH, Konijnenbelt M, Mulder H, Hertogh CM, et al. Caregiver-mediated exercises with e-health support for early supported discharge after stroke (CARE4STROKE): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Neurol 2015;15:193.



2. Belgen B, Beninato M, Sullivan PE, Narielwalla K. The association of balance capacity and falls self-efficacy with history of falling in community-dwelling people with chronic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2006;87:554-61.


3. Zijlstra GA, van Haastregt JC, van Rossum E, van Eijk JT, Yardley L, Kempen GI. Interventions to reduce fear of falling in community-living older people: a systematic review. J Am Geriatr Soc 2007;55:603-15.


4. Pajala S, Era P, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Tormakangas T, Rantanen T. Force platform balance measures as predictors of indoor and outdoor falls in communitydwelling women aged 63-76 years. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2008;63:171-8.



5. Kosse NM, de Groot MH, Vuillerme N, Hortobagyi T, Lamoth CJ. Factors related to the high fall rate in longterm care residents with dementia. Int Psychogeriatr 2015;27:803-14.


6. Forster A, Young J. Incidence and consequences of falls due to stroke: a systematic inquiry. BMJ 1995;311:83-6.



7. Nyberg L, Gustafson Y. Patient falls in stroke rehabilitation: a challenge to rehabilitation strategies. Stroke 1995;26:838-42.


8. Vlahov D, Myers AH, Al-Ibrahim MS. Epidemiology of falls among patients in a rehabilitation hospital. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1990;71:8-12.

9. Teasell R, McRae M, Foley N, Bhardwaj A. The incidence and consequences of falls in stroke patients during inpatient rehabilitation: factors associated with high risk. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2002;83:329-33.


10. Di Monaco M, Trucco M, Di Monaco R, Tappero R, Cavanna A. The relationship between initial trunk control or postural balance and inpatient rehabilitation outcome after stroke: a prospective comparative study. Clin Rehabil 2010;24:543-54.


11. Verheyden G, Vereeck L, Truijen S, Troch M, Herregodts I, Lafosse C, et al. Trunk performance after stroke and the relationship with balance, gait and functional ability. Clin Rehabil 2006;20:451-8.


12. Dault MC, de Haart M, Geurts AC, Arts IM, Nienhuis B. Effects of visual center of pressure feedback on postural control in young and elderly healthy adults and in stroke patients. Hum Mov Sci 2003;22:221-36.


13. Chou SW, Wong AM, Leong CP, Hong WS, Tang FT, Lin TH. Postural control during sit-to stand and gait in stroke patients. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2003;82:42-7.


14. Mehrholz J, Pohl M, Elsner B. Treadmill training and body weight support for walking after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014;(1):CD002840.

15. Verheyden G, Vereeck L, Truijen S, Troch M, Lafosse C, Saeys W, et al. Additional exercises improve trunk performance after stroke: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2009;23:281-6.


16. English C, Shields N, Brusco NK, Taylor NF, Watts JJ, Peiris C, et al. Additional weekend therapy may reduce length of rehabilitation stay after stroke: a metaanalysis of individual patient data. J Physiother 2016;62:124-9.


17. Vloothuis JD, Mulder M, Veerbeek JM, Konijnenbelt M, Visser-Meily JM, Ket JC, et al. Caregiver-mediated exercises for improving outcomes after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016;12:CD011058.


18. Visser-Meily A, Post M, Gorter JW, Berlekom SB, Van Den Bos T, Lindeman E. Rehabilitation of stroke patients needs a family-centred approach. Disabil Rehabil 2006;28:1557-61.


19. Galvin R, Cusack T, Stokes E. To what extent are family members and friends involved in physiotherapy and the delivery of exercises to people with stroke? Disabil Rehabil 2009;31:898-905.


20. Cobley CS, Fisher RJ, Chouliara N, Kerr M, Walker MF. A qualitative study exploring patients’ and carers’ experiences of Early Supported Discharge services after stroke. Clin Rehabil 2013;27:750-7.


21. Scherer MJ, Craddock G, Mackeogh T. The relationship of personal factors and subjective well-being to the use of assistive technology devices. Disabil Rehabil 2011;33:811-7.


22. Liao CD, Liou TH, Huang YY, Huang YC. Effects of balance training on functional outcome after total knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil 2013;27:697-709.


23. Verheyden G, Nieuwboer A, Mertin J, Preger R, Kiekens C, De Weerdt W. The Trunk Impairment Scale: a new tool to measure motor impairment of the trunk after stroke. Clin Rehabil 2004;18:326-34.


24. Morgan MT, Friscia LA, Whitney SL, Furman JM, Sparto PJ. Reliability and validity of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) in individuals with dizziness and imbalance. Otol Neurotol 2013;34:1104-8.



26. van de Port IG, Kwakkel G, Schepers VP, Lindeman E. Predicting mobility outcome one year after stroke: a prospective cohort study. J Rehabil Med 2006;38:218-23.


27. Kollen B, van de Port I, Lindeman E, Twisk J, Kwakkel G. Predicting improvement in gait after stroke: a longitudinal prospective study. Stroke 2005;36:2676-80.


28. Dobkin BH, Nadeau SE, Behrman AL, Wu SS, Rose DK, Bowden M, et al. Prediction of responders for outcome measures of Locomotor Experience Applied Post Stroke trial. J Rehabil Res Dev 2014;51:39-50.



29. Scholte op Reimer WJ, de Haan RJ, Rijnders PT, Limburg M, van den Bos GA. The burden of caregiving in partners of long-term stroke survivors. Stroke 1998;29:1605-11.


30. Duncan PW, Zorowitz R, Bates B, Choi JY, Glasberg JJ, Graham GD, et al. Management of adult stroke rehabilitation care: a clinical practice guideline. Stroke 2005;36:e100. -43.


31. Miller EL, Murray L, Richards L, Zorowitz RD, Bakas T, Clark P, et al. Comprehensive overview of nursing and interdisciplinary rehabilitation care of the stroke patient: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke 2010;41:2402-48.


32. Kalra L, Evans A, Perez I, Melbourn A, Patel A, Knapp M, et al. Training carers of stroke patients: randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2004;328:1099.



33. Wang TC, Tsai AC, Wang JY, Lin YT, Lin KL, Chen JJ, et al. Caregiver-mediated intervention can improve physical functional recovery of patients with chronic stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2015;29:3-12.


34. Galvin R, Cusack T, O’Grady E, Murphy TB, Stokes E. Family-mediated exercise intervention (FAME): evaluation of a novel form of exercise delivery after stroke. Stroke 2011;42:681-6.


35. Blennerhassett J, Dite W. Additional task-related practice improves mobility and upper limb function early after stroke: a randomised controlled trial. Aust J Physiother 2004;50:219-24.


36. Galvin R, Murphy B, Cusack T, Stokes E. The impact of increased duration of exercise therapy on functional recovery following stroke: what is the evidence? Top Stroke Rehabil 2008;15:365-77.


37. Kwakkel G, van Peppen R, Wagenaar RC, Wood Dauphinee S, Richards C, Ashburn A, et al. Effects of augmented exercise therapy time after stroke: a metaanalysis. Stroke 2004;35:2529-39.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ARM
-
Depression and Anxiety of Caregivers of Stroke Patient.2001 December;25(6)
Long-term Effects of Day Hospital Program in Stroke Rehabilitation.2005 February;29(1)
Effect and Safety of Cardiac Rehabilitation Program in Heart Failure.2005 February;29(1)
The Effects of Arm Ergometry Exercise in Acute Stroke Patients.2007 December;31(6)
Effect of a Caregiver's Education Program on Stroke Rehabilitation2017 February;41(1)