- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 42(2); 2018 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
To identify the pressure relieving effect of adding a pelvic well pad, a firm pad that is cut in the ischial area, to a wheelchair cushion on the ischium.
Methods
Medical records of 77 individuals with SCI, who underwent interface pressure mapping of the buttock-thigh area, were retrospectively reviewed. The pelvic well pad is a 2.5-cm thick firm pad and has a cut in the ischial area. Expecting additional pressure relief, it can be inserted under a wheelchair cushion. Subjects underwent interface pressure mapping in the subject's wheelchair utilizing the subject's pre-existing pressure relieving cushion and subsequently on a combination of a pelvic well pad and the cushion. The average pressure, peak pressure, and contact area of the buttock-thigh were evaluated.
Results
Adding a pelvic well pad, under the pressure relieving cushion, resulted in a decrease in the average and peak pressures and increase in the contact area of the buttock-thigh area when compared with applying only pressure relieving cushions (p<0.05). The mean of the average pressure decreased from 46.10┬▒10.26 to 44.09┬▒9.92 mmHg and peak pressure decreased from 155.03┬▒48.02 to 131.42┬▒45.86 mmHg when adding a pelvic well pad. The mean of the contact area increased from 1,136.44┬▒262.46 to 1,216.99┬▒255.29 cm2.
Conclusion
When a pelvic well pad was applied, in addition to a pre-existing pressure relieving cushion, the average and peak pressures of the buttock-thigh area decreased and the contact area increased. These results suggest that adding a pelvic well pad to wheelchair cushion may be effective in preventing a pressure ulcer of the buttock area.
Pressure ulcers (PU) are one of the most common complications in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI) [1]. Tetraplegic and paraplegic SCI individuals rely on wheelchairs for mobility and thus despite the use of a pressure relieving cushion, the sacrum and ischium are the most common sites of PUs [2,3,4,5].
Prolonged exposure to pressure and shear force are the major causes of PU [3]. Many methods of relieving pressure and shear force have been devised to prevent a PU at the ischium. Educations of posture in bed and wheelchair [6,7], the use of various kinds of pressure relieving cushions [8,9], and the application of tilt and recline systems on the wheelchair [10,11,12,13] are methods utilized to reduce pressure and shear force. Among the many pressure relieving methods, the use of pressure relieving cushions is essential. And many types of pressure relieving cushions are in use. However, a cushion alone cannot prevent PU sufficiently.
In 2012, World Health Organization (WHO) proposed a ŌĆśfoam type pressure relief cushionŌĆÖ as a wheelchair cushion [14]. The cushion consists of a firm base layer and a soft top layer, and fabric wrapping them. The base layer is a firm pad cut in the ischial area. The firm base layer has two main components. First, a ŌĆśwellŌĆÖ under the ischial bones reduces pressure on the buttock area. Second, a ŌĆśshelfŌĆÖ in front of the ischial bones keeps the pelvis more upright and prevents it from sliding forward. If more pressure relief is required, an additional layer, called a ŌĆśliftŌĆÖ, can be added between the base and the top [15].
In Korea, however, most of the SCI individuals use ready-made air cushions. Air-cell-based cushions have good pressure relieving abilities. However, PUs occur occasionally, in spite of the prior use of pressure relieving cushions. In these cases, an additional pressure relieving method is to provide a pad like the ŌĆśliftŌĆÖ under the pre-existing cushion which can be effective. This is more costeffective and convenient than purchasing a new cushion.
Despite existing recommendations made by the WHO on such relief cushion bases, there have not been any objective evidence regarding its effects. The pad, with a cut in the ischial area, can be used as an add on approach in combination with the SCI individual's pre-existing pressure relieving cushion, allowing additional pressure relief. The purpose of the current study was to objectively identify the pressure relieving effects of adding a pad to the wheelchair cushion on the ischium.
Medical records of 77 individuals with SCI, who were admitted to the SCI health medical screening program of the National Rehabilitation Center in Korea between September 2014 to June 2015 and who underwent interface pressure mapping were retrospectively analyzed. The SCI health medical screening program includes community dwelling individuals who come for annual routine health screening. All SCI individuals using a manual or electric wheelchair underwent interface pressure mapping of the buttock-thigh area. However, individuals who had pressure ulcers on their buttock-thigh area or who refused to undergo interface pressure mapping were not analyzed. Individuals with deformities of the pelvis or femur and neurological injuries other than SCI were not included in the study. There also was no limit on age for this analysis. The study was approved by the National Rehabilitation Center Institutional Review Board (No. NRC-2018-03-016).
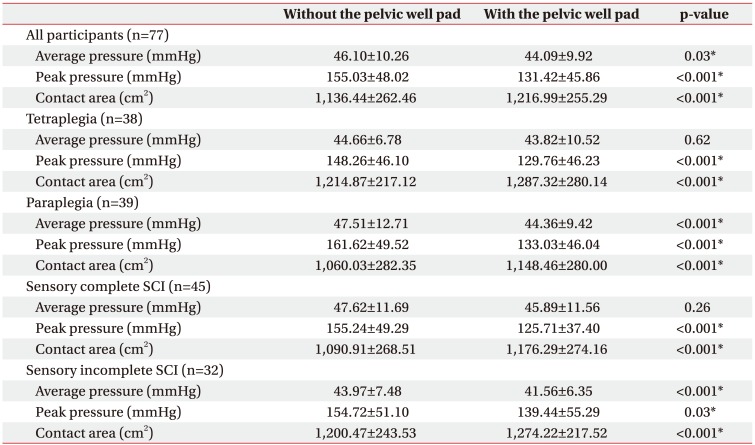
Expecting additional pressure relief, we created a pad that can be inserted under a wheelchair cushion. We named the pad as a ŌĆśpelvic well padŌĆÖ. Pelvic well pad, is a firm pad, made from ethylene vinyl acetate foam. It is 2.5 cm thick and has a cut in the ischial area. It was placed on the seat of a wheelchair, and a pressure relieving cushion was placed over it (Fig. 1A). The objective was to relieve pressure in the ischial area and to redistribute pressure towards the thighs. The pelvic well pads were cut so the relief area would be 3 cm in front of the anterior tip of the ischial tuberosity and 2.5 cm from the lateral borders of the ischial tuberosity (Fig. 1B).
As in many prior studies, we used a high-resolution pressure mapping system, X3 PRO (XSENSOR Technology Corporation, Calgary, Canada) to measure the pressure between the cushion and the buttock-thigh [16,17,18] (Fig. 2). XSENSOR X3 system includes a thin, flexible mat-like pressure sensor with a 1,296 cell matrix (36├Ś36), which covered a 45├Ś45 cm2 sensing area. The sensor was placed under the buttock-thigh area of subjects to measure pressure in the corresponding area. Pressure distribution is displayed in color on a monitor. High pressure areas are shown in red, low pressure areas in blue. Average pressure, peak pressure and contact area are calculated and the graphical displays of pressure distribution are shown.
In order to confirm the pressure relieving effects of the pelvic well pad, the patients underwent interface pressure mapping with the XSENSOR X3 system in the subject's wheelchair utilizing the subject's pre-existing pressure relieving cushion and subsequently on a combination of the customized pelvic well pad and the preexisting pressure relieving cushion. The average pressure, peak pressure, and the contact area of the buttock-thigh were evaluated. The results were recorded prospectively.
Exams were conducted in the following order. First, the subject's pre-existing cushion was applied to one's wheelchair seat. Pressure sensor of the XSENSOR X3 system was placed over the cushion and the subject was carefully seated using an electric lift onto the wheelchair. The average pressure, the peak pressure, and the contact area of the buttock-thigh area were evaluated while the subject sat quietly. To reflect the subject's daily posture, the pressures and the contact area were evaluated after the patient was seated in the wheelchair for 5 minutes.
Second, a pelvic well pad was added and evaluated. To add the pelvic well pad, the subject was taken out of the wheelchair. The pelvic well pad was placed between the wheelchair seat and the cushion. Then the pressures and the contact area were evaluated as before.
All exams were performed by an occupational therapist specialized in seating assessment and who had more than 5 years of experience in seating of SCI individuals.
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). A paired t-test was used to analyze the differences between the average pressure, the peak pressure, and the contact area of the buttock-thigh area before and after the pelvic well pad applied. We considered p<0.05 significant.
Seventy-seven subjects were retrospectively reviewed. The average age was 42.55┬▒13.89 years with a range between of ages from 16 to 72 years. Fifty-seven (74%) were male, 20 (26%) were female. Thirty-eight (49.4%) were tetraplegic and 39 (50.6%) were paraplegic. According to the American Spinal Injury Association impairment scale (AIS), 45 (58.4%) were AIS-A, 15 (19.5%) were B, 13 (16.9%) were C, 4 (5.2%) were D (Table 1).
The types of subject's pre-existing pressure relieving cushions were as follows: thirty-one (40%) subjects used 5 cm air-cell-based cushion, 13 (17%) used 8 cm air-cellbased cushion, 5 (6%) used 10 cm air-cell-based cushion, 1 (1%) used ROHO Hybrid Elite cushion, and 21 (27%) used low priced air cushion. The types of cushions used by the 6 (8%) subjects were not known.
Adding a pelvic well pad to the pressure relieving cushion resulted in a statistically significant reduction in average and peak pressure and increase in contact area of the buttock-thigh area, as compared with applying only pressure relieving cushions (p<0.05). The mean of the average pressure decreased from 46.10 to 44.09 mmHg (p=0.03) and the peak pressure decreased from 155.03 to 131.42 mmHg (p<0.001), when adding a pelvic well pad. The mean of the contact area increased from 1,136.44 to 1,216.99 cm2 (p<0.001) (Table 2).
Fig. 3 are views of the screen of XSENSOR of the buttock- thigh area. As displayed in Fig. 3, pressures of the ischial area decreased and the contact area of the thigh area increased when a pelvic well pad was added. This is suspected to occur because the pelvic well pad redistributes pressure from the ischial area to the thigh.
Both tetraplegic and paraplegic SCI groups revealed decreased average and peak pressure and increased contact area of the buttock-thigh area when the pelvic well pad was added. In tetraplegics, the mean of the average pressure decreased from 44.66 to 43.82 mmHg (p=0.62), the peak pressure decreased from 148.26 to 129.76 mmHg (p<0.001), and the contact area increased from 1,214.87 to 1,287.32 cm2 (p<0.001). In paraplegics, the mean of the average pressure decreased from 47.51 to 44.36 mmHg (p<0.001), the peak pressure decreased from 161.62 to 133.03 mmHg (p<0.001), and the contact area increased from 1,060.03 to 1,148.46 cm2 (p<0.001). All changes, except the contact area of the tetraplegic group, were statistically significant (p<0.05) (Table 2).
According to AIS, 45 (58.4%) were sensory complete (AIS A) SCI and 32 (41.6%) were sensory incomplete (AIS B/C/D) SCI. Both groups revealed decreased average and peak pressure and increased contact area of the buttock-thigh area when a pelvic well pad was added. In sensory complete SCI group, the mean of the average pressure decreased from 47.62 to 45.89 mmHg (p=0.26), the peak pressure decreased from 155.24 to 125.71 mmHg (p<0.001), the contact area increased from 1,090.91 to 1,176.29 cm2 (p<0.001). In sensory incomplete SCI group, the mean of the average pressure decreased from 43.97 to 41.56 mmHg (p<0.001), peak pressure decreased from 154.72 to 139.44 mmHg (p=0.03), and the contact area increased from 1,200.47 to 1,274.22 cm2 (p<0.001). All changes, except the contact area of the sensory complete SCI group, were statistically significant (p<0.05) (Table 2).
Lowering the pressure on the buttock area reduces the risk of PUs on wheelchair users. Many methods of relieving pressure of the buttock area have been devised [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,18,19,20,21]. However, despite the use of pressure relieving cushions, many of them have pressure ulcers in the buttock area. Gil-Agudo et al. [8] studied the interface pressure of the buttock area with various types of cushions. According to his study, the average of the peak pressures was 105.5 mmHg with dual-compartment air cushions and with a ranged between 180.5 mmHg and 207.5 mmHg using other types of cushions (low-profile air, high-profile air, gel and firm foam cushions). These results suggest that interface pressures vary depending on the pressure cushion types and these pressures may not be adequate to prevent PU occurrence. According to this study, the pelvic well pad increases the contact area between the buttock-thigh area and the cushion. Addition it decreases the average and the peak pressure of the area when applied additionally to a pressure relieving cushion. Using the pelvic well pad, the peak pressures of the cushions seen in the study of Gil-Agudo et al. [8] might be decreased.
In individuals with tetraplegia and sensory complete SCI, average pressure reduction with a pelvic well pad was not statically significant. However peak pressures were significantly reduced and the contact area redistribution was significantly increased. PUs typically occur in the areas of focally concentrated pressures and thus an addition of pelvic well pad to the pre-existing cushion may be an option when prior pressure relieving methods fail.
Pelvic well pad, which is a 2.5-cm thick and cut 3 cm in front of the anterior tip and 2.5 cm from the lateral borders of the ischial tuberosity, were used in this study (Fig. 1). However, due to different subcutaneous fat or muscle thickness depending on body weight or body mass index, the optimal dimensions of the pelvic well pad may vary depending individual variables.
We evaluated the pressures and the contact areas after the patient was seated in the wheelchair for 5 minutes to reflect the subject's daily posture. According to Kim et al. [22], the peak and the average interface pressure of buttock in SCI patients increased significantly when sitting on 5 cm air-filled cushion during 0 to 25 minutes. They also reported there were no significant changes of the interface pressure after 25 minutes. Therefore, they recommended 25 minutes for sitting time prior to interface pressure recording. It is not known at this time how the pressures of the buttock-thigh area will change when the pelvic well pad is added to a pressure relieving cushion.
Our study has limitations. In that it is retrospective and a single-center study. Only one occupational therapist covered interface pressure mapping in National Rehabilitation Center and thus a rater bias may have been introduced. This study does not confirm a direct correlation between the PU occurrence and the addition of the pelvic well pad.
This study only analyzed the pressure relief effects of pelvic well pad by ŌĆśwellŌĆÖ component. Theoretically, a pelvic well pad can also reduce the shear force by the effect of the ŌĆśshelfŌĆÖ, preventing forward sliding of the wheelchair user [14]. Therefore, the pelvic well pad may be able to prevent PUs beyond the pressure relieving effects observed in this study.
This is the first study to show the effects of adding a pelvic well pad to wheelchair cushion for improving the interface pressure in people with SCI. A decreased average and peak pressure and increased contact area of the buttock-thigh area was noticed when a pelvic well pad was added to a pre-existing pressure relieving cushion. Utilizing a pelvic well pad in combination with pressure relieving cushions decreases the pressure of the buttocks more effectively than using only the cushion. The pelvic well pad may be a good option when repetitive PUs occur, despite the use of pre-existing pressure relief cushions.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Javadi M, Hafezi-Nejad N, Vaccaro AR, Rahimi-Movaghar V. Medical complications and patient outcomes in Iranian veterans with spinal cord injury. Adv Clin Exp Med 2014;23:269-275. PMID: 24913118.


2. New PW, Rawicki HB, Bailey MJ. Nontraumatic spinal cord injury rehabilitation: pressure ulcer patterns, prediction, and impact. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004;85:87-93. PMID: 14970974.


4. Rabadi MH, Vincent AS. Do vascular risk factors contribute to the prevalence of pressure ulcer in veterans with spinal cord injury? J Spinal Cord Med 2011;34:46-51. PMID: 21528626.



5. Kim YC, Park CI, Shin JC, Kim SW, Yoo WK. Epidemiology of pressure sore in spinal cord injured patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2010;22:552-558.
6. Stinson M, Schofield R, Gillan C, Morton J, Gardner E, Sprigle S, et al. Spinal cord injury and pressure ulcer prevention: using functional activity in pressure relief. Nurs Res Pract 2013;2013:860396PMID: 23691301.




7. Groah SL, Schladen M, Pineda CG, Hsieh CH. Prevention of pressure ulcers among people with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. PM R 2015;7:613-636. PMID: 25529614.


8. Gil-Agudo A, De la Pena-Gonzalez A, Del Ama-Espinosa A, Perez-Rizo E, Diaz-Dominguez E, Sanchez-Ramos A. Comparative study of pressure distribution at the user-cushion interface with different cushions in a population with spinal cord injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2009;24:558-563.


9. Levy A, Kopplin K, Gefen A. An air-cell-based cushion for pressure ulcer protection remarkably reduces tissue stresses in the seated buttocks with respect to foams: finite element studies. J Tissue Viability 2014;23:13-23. PMID: 24405723.


10. Jan YK, Crane BA, Liao F, Woods JA, Ennis WJ. Comparison of muscle and skin perfusion over the ischial tuberosities in response to wheelchair tilt-in-space and recline angles in people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013;94:1990-1996. PMID: 23602880.



11. Jan YK, Crane BA. Wheelchair tilt-in-space and recline does not reduce sacral skin perfusion as changing from the upright to the tilted and reclined position in people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013;94:1207-1210. PMID: 23313352.



12. Jan YK, Liao F, Jones MA, Rice LA, Tisdell T. Effect of durations of wheelchair tilt-in-space and recline on skin perfusion over the ischial tuberosity in people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013;94:667-672. PMID: 23178540.


13. Sprigle S, Maurer C, Soneblum SE. Load redistribution in variable position wheelchairs in people with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2010;33:58-64. PMID: 20397444.



14. Khasnabis C, Mines K. Wheelchair service training package: reference manual for participants: basic level. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
15. Khasnabis C, Mines K. Wheelchair service training package: trainer's manual: basic level. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
16. Peterson MJ, Gravenstein N, Schwab WK, van Oostrom JH, Caruso LJ. Patient repositioning and pressure ulcer risk: monitoring interface pressures of at-risk patients. J Rehabil Res Dev 2013;50:477-488. PMID: 23934869.


17. Yuen HK, Garrett D. Comparison of three wheelchair cushions for effectiveness of pressure relief. Am J Occup Ther 2001;55:470-475. PMID: 11723993.


18. Makhsous M, Rowles DM, Rymer WZ, Bankard J, Nam EK, Chen D, et al. Periodically relieving ischial sitting load to decrease the risk of pressure ulcers. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007;88:862-870. PMID: 17601466.



19. Sonenblum SE, Vonk TE, Janssen TW, Sprigle SH. Effects of wheelchair cushions and pressure relief maneuvers on ischial interface pressure and blood flow in people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2014;95:1350-1357. PMID: 24480336.


20. Previnaire JG, Fontet P, Opsomer C, Simon M, Ducrocq T. Lipofilling (fat grafting) in the secondary prevention of ischial tuberosity and pelvic pressure ulcers. Spinal Cord 2016;54:39-45. PMID: 26481707.



21. Yusmido YA, Hisamud-Din N, Mazlan M. Elective proximal lower limb amputation in spinal cord injury patients with chronic pressure ulcers: improve quality of life, function, and shorten hospital stay: case report. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2014;50:557-560. PMID: 24694951.

22. Kim DA, Yi SH, Lee BS, Lim MH, Ryh BJ, Kim HC, et al. Impact of sitting time on seat-interface pressure of spinal cord injured patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2009;33:614-618.
Fig.┬Ā1
(A) A three-dimensional image of the pelvic well pad (blue). It is 2.5 cm thick and has a cut in the ischial area. A ready-made air cushion (translucent grey) is placed over it. (B) A schematic view from below of the pelvic well pad. The pelvic well pad is expressed as a translucent blue figure. The pelvic well pads were cut so that the relief area would be 3 cm in front of the anterior tip of the ischial tuberosity and 2.5 cm from the lateral borders of the ischial tuberosity.
Fig.┬Ā2
The XSENSOR X3 system. Interface pressure distribution between the seat cushion and the buttock-thigh area is displayed in color on a monitor.

Fig.┬Ā3
Pictures on the screen of XSENSOR X3 system presenting a graphical image of a subject's interface pressure of the buttockthigh area. Left side of each picture reflects the pressure of the buttock area, and right side reflects thigh area. (A) Image with application of only pressure relieving cushion. (B) Image with and additional pelvic well pad applied beneath the cushion.

- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ARM
-
Effect of Clonidine on Spasticity in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury.1999 December;23(6)