- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 41(4); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Methods
Motor nerve branches to the abductor hallucis muscles were examined in eight Korean cadaver feet. The motor point was defined as the site where the intramuscular nerve penetrates the muscle belly. The reference line connects the metatarsal base of the hallux (H) to the medial tubercle of the calcaneus (C). The x coordinate was the horizontal distance from the motor point to the point where the perpendicular line from the navicular tuberosity crossed the reference line. The y coordinate was the perpendicular distance from the motor point to the navicular tuberosity.
Results
Most of the medial plantar nerves to the abductor hallucis muscles divide into multiple branches before entering the muscles. One, two, and three motor branches were observed in 37.5%, 37.5%, and 25% of the feet, respectively. The ratios of the main motor point from the H with respect to the H-C line were: main motor point, 68.79%±5.69%; second motor point, 73.45%±3.25%. The mean x coordinate value from the main motor point was 0.65±0.49 cm. The mean value of the y coordinate was 1.43±0.35 cm. All of the motor points of the abductor hallucis were consistently found inferior and posterior to the navicular tuberosity.
Electrodiagnostic studies are powerful tools to use with patients who have neuromuscular disorders. Since electrophysiological studies are sensitive tests that are susceptible to subtle changes, imprecisely recorded compound muscle action potential (CMAP) can lead to incorrect diagnoses. The tibial motor-nerve conduction to the abductor hallucis muscle is commonly studied in electrophysiology. However, there is still a lack of consensus among the textbooks on where an active electrode (E1) should be placed on the navicular tuberosity in tibial motor conduction studies. All the authors recommended placing E1 below the navicular tuberosity, but some proposed placing it anterior to the navicular tuberosity [1,2], and others suggested placing it posterior to the navicular tuberosity [3,4]. This disagreement might have confused electromyographers.
False motor points can be produced when the recording electrode is placed over sites other than the end-plate zone and are characterized by marked delayed onset latencies due to flattening of the initial segment and phase transition in motor-nerve conduction studies [5]. Reducing false motor points is important for improving the accuracy of motor-nerve conduction studies, because false motor points can lead to misdiagnosis of various peripheral neuropathies defined by the prolongation of distal motor latencies [6]. A few studies have located the motor point of the abductor hallucis muscle, although there has been no consensus about E1 location. This study was conducted to identify the location of the anatomical motor points of the abductor hallucis muscles in terms of the anatomical landmarks.
Eight feet from four fresh Korean adult cadavers were dissected (3 men and 1 woman, ranging in age from 52 to 79 years). There were no deformed or injured feet, and all limbs were positioned with neutral ankle alignment. The skin and subcutaneous tissues were dissected to expose the medial plantar nerve and abductor hallucis muscle from the tarsal tunnel to the first metatarsal base along the medial aspect of the foot. We carefully removed the subcutaneous tissues and held onto the nerves with just enough tension to avoid injury. Then the branches of the medial plantar nerve were identified and traced to their penetration point into the abductor hallucis muscle. The most distal point, where the motor branch entered the muscle belly, was designated as the anatomical motor point in this study [7].
For each foot, three bony landmarks were defined as the reference points: the metatarsal base of the hallux (H), the medial tubercle of the calcaneus (C), and the navicular tuberosity (N). The reference line was defined as the line connecting the metatarsal base of the hallux and the medial tubercle of the calcaneus (H–C line). The x coordinate was defined as the horizontal distance from the motor point to the perpendicular line from the navicular tuberosity. The y coordinate was defined as the perpendicular distance from the motor point to the navicular tuberosity (Fig. 1). The x and y coordinates of the motor points were measured, and the ratio of the coordinates to the length of the H–C line was calculated. The number of motor points (the number of branches to the muscle) was also counted.
The intramuscular penetrations of the medial plantar nerves were divided into multiple branches before they entered the abductor hallucis muscles in 62.5% (5 of 8) of the feet (Fig. 2). Two motor branches were observed in 37.5% (3 of 8) of the feet and three motor branches in 25.0% (2 of 8) of the feet. The thickest branch of each medial plantar nerve was designated as the main motor point and the others as the minor motor points. One cadaver showed multiple motor points on both feet, while three cadavers showed multiple motor points on only one foot.
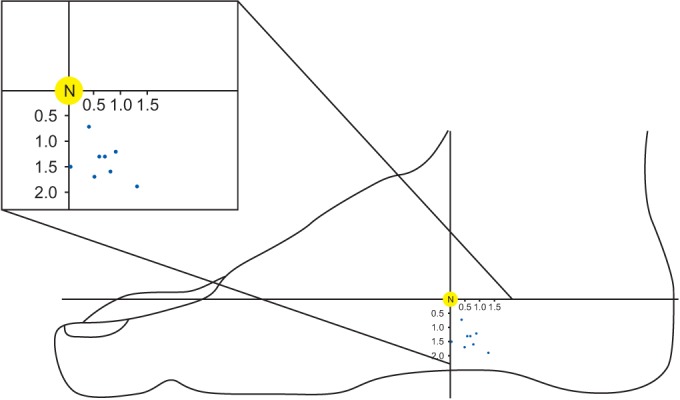
The mean length of the H–C line was 15.5±1.00 cm (mean±standard deviation). The main motor point was located at 10.63±0.74 cm, with a ratio of 68.79%±5.69%, from the H point of the H–C line. The second motor point was located at 11.4±0.43 cm, with a ratio of 73.45%±3.25%, from the H point of the H–C line. The mean x coordinate from the main motor point was 0.65±0.49 cm (4.14%±2.25%). The mean y coordinate from the main motor point was 1.43±0.35 cm. All the motor points of the abductor hallucis were consistently found inferior and posterior to the navicular tuberosity (Fig. 3).
This study was designed to identify the anatomical motor points in the abductor hallucis muscle. We found multiple motor points in the abductor hallucis muscle and identified their location by distance and ratio relative to anatomical landmarks. Since the sizes of cadavers' feet might differ with sex and age, absolute distances might not reflect the average well. Therefore, using the ratio to the length of the H–C reference line would improve the accuracy of placing the E1 over the motor point regardless of foot size.
For the tibial nerve, the onset latency of CMAP and the presence of initial negativity are more meaningful than the amplitude of CMAP when determining the innervation zone [8]. The initial positive deflection mainly occurs as the wave of depolarization no longer originates under the motor point, but propagates toward it [1]. As the electrode is placed further away from the end-plate region, the initial positive deflection becomes more obvious and the duration increases [9]. When the initial positive deflection is observed or does not disappear by repositioning the active recording electrode, other factors, such as volume conduction from undesired excitable tissues, anomalous innervation, premotor potential, or a misplaced reference electrode, should be considered [1,10,11,12]. The proximity of several foot-intrinsic muscles and the difference in length of the motor nerves to the intrinsic muscles created the excessive false motor points in a previous tibial motor conduction study [13]. To minimize these errors, it is important to place the E1 on an accurate motor point.
During this study, we identified the exact anatomical locations of the motor points in the abductor hallucis muscles by using landmarks, such as the navicular tuberosity. Interestingly, all the anatomical motor points of the abductor hallucis were consistently found to be inferior and posterior to the navicular tuberosity. As mentioned earlier, many textbooks have suggested various locations for E1 on the abductor halluces. Dumitru et al. [1] and Liveson and Ma [2] proposed placing it anterior and inferior to the navicular tuberosity, while Lee et al. [3] and Pease et al. [4] recommended placing it posterior and inferior to the navicular tuberosity. There were other suggestions about the correct location for the E1 on an abductor hallucis muscle. Del Toro and Park [5] evaluated this matter by using electrophysiological mapping and cadaveric dissection. They recommended placing it at the shortest distance from the medial plantar nerve to the navicular tuberosity, but did not calculate the ratio. In addition, they did not consider the possibility that there may be multiple branches of motor points of the muscles. Our result corresponds well with that of a previous cadaveric study [5], that the motor point in the abductor hallucis muscle is posterior and inferior to the navicular tuberosity.
The abductor hallucis muscle can have more than one motor point from the medial plantar nerve. None of the previous studies of the abductor hallucis reported this result. However, Del Sol et al. [14] reported that the lateral plantar nerves for the abductor digiti minimi muscle could divide from one into two or three branches, comparable to the results of this study.
The innervation ratio is the ratio of muscle fibers innervated by one axon, and the skeletal muscles in various parts of the body have different numbers of muscle fibers per motor unit, depending on the size of the muscle groups. Small muscles requiring fine motor control have a low innervation ratio, whereas large muscles that perform gross movements have a high innervation ratio [1]. The abductor hallucis muscles need continuous motor control to maintain and control the medial arch of the foot during standing and gait [15,16]. The multiple motor-nerve branches found to innervate the intrinsic foot muscle in our study might be another example of a low innervation ratio for muscles requiring fine motor control. With multiple motor points, the muscle action potentials evoked from each motor point could produce the initial positive deflection or initial segment flattening of CMAP by phase cancellation [17].
Our study has several limitations. First, only a few feet were dissected, mostly from elderly people. However, since the topographical distribution of motor end-plate zones for adults is similar to the results obtained from children, our results would probably help to locate motor points for younger individuals if our ratio is applied [18]. Second, the anatomical motor point that was defined as the most distal point where the motor branch entered the muscle belly in this study may not reflect the end-plate zone. However, the term ‘motor point’ is occasionally to mean the location of the terminal portion of the motornerve fibers, or the end-plate zone [7,19,20]. Further large-scale and clinical studies are warranted to validate the average coordinates of the motor points.
In conclusion, this study located anatomical motor points in cadavers and found multiple motor points in the abductor hallucis muscle. The results of this study suggest that the ideal location for the motor point is posterior and inferior to the navicular tuberosity. Further large-scale studies for the anatomical localization of motor points may provide useful knowledge for clinical practice that deals with tibial motor-nerve conduction and may help avoid initial positive deflection or erroneous prolongation of CMAP onset latencies, which could cause misdiagnosis of the various neuropathies associated with the tibial nerve component.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts MJ. Electrodiagnostic medicine. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus; 2002.
2. Liveson JA, Ma DM. Laboratory reference for clinical neurophysiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 1992. p.204-205.
3. Lee HJ, DeLisa JA, Lee HJ. Manual of nerve conduction study and surface anatomy for needle electromyography. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. p.80-83.
4. Pease WS, Lew HL, Johnson EW. Johnson's practical electromyography. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. p.242.
5. Del Toro DR, Park TA. Abductor hallucis false motor points: electrophysiologic mapping and cadaveric dissection. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:1138-1143. PMID: 8761270.


6. Bromberg MB, Spiegelberg T. The influence of active electrode placement on CMAP amplitude. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1997;105:385-389. PMID: 9363004.


7. Downey JA, Myers SJ, Gonzalez EG, Lieberman JS. The physiological basis of rehabilitation medicine. 2nd ed. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann; 1994. p.576.
8. van Dijk JG, van Benten I, Kramer CG, Stegeman DF. CMAP amplitude cartography of muscles innervated by the median, ulnar, peroneal, and tibial nerves. Muscle Nerve 1999;22:378-389. PMID: 10086899.


9. Rodriguez-Carreno I, Malanda-Triqueros A, Gila-Useros L. Motor unit action potential duration: measurement and significance. In: Ajeena IM, editor. Advances in clinical neurophysiology. Rijeka: InTech; 2012. p.133-160.
10. Brashear A, Kincaid JC. The influence of the reference electrode on CMAP configuration: leg nerve observations and an alternative reference site. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:63-67. PMID: 8538671.


11. Park TA, Jurell KC, Del Toro DR. Generator sources for the early and late ulnar hypothenar premotor potentials: short segment electrophysiologic studies and cadaveric dissection. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1996;77:467-472. PMID: 8629923.


12. Bilbao A, Wilcox MS. The influence of the reference electrode on CMAP configuration: leg nerve observations and an alternative reference site. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:1055-1056. PMID: 8756176.


13. Monteiro A, Cricenti SV, Manzano GM, Nobrega JA. Anatomical observations and false motor points in intrinsic foot muscles. Muscle Nerve 2002;26:557PMID: 12362425.


14. del Sol M, Olave E, Gabrielli C, Mandiola E, Prates JC. Innervation of the abductor digiti minimi muscle of the human foot: anatomical basis of the entrapment of the abductor digiti minimi nerve. Surg Radiol Anat 2002;24:18-22. PMID: 12197005.


15. Wong YS. Influence of the abductor hallucis muscle on the medial arch of the foot: a kinematic and anatomical cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 2007;28:617-620. PMID: 17559771.


16. Fiolkowski P, Brunt D, Bishop M, Woo R, Horodyski M. Intrinsic pedal musculature support of the medial longitudinal arch: an electromyography study. J Foot Ankle Surg 2003;42:327-333. PMID: 14688773.


17. Dumitru D, DeLisa JA. AAEM Minimonograph #10: volume conduction. Muscle Nerve 1991;14:605-624. PMID: 1922167.


18. Aquilonius SM, Askmark H, Gillberg PG, Nandedkar S, Olsson Y, Stalberg E. Topographical localization of motor endplates in cryosections of whole human muscles. Muscle Nerve 1984;7:287-293. PMID: 6203034.


19. Rha DW, Yi KH, Park ES, Park C, Kim HJ. Intramuscular nerve distribution of the hamstring muscles: Application to treating spasticity. Clin Anat 2016;29:746-751. PMID: 27213466.


20. Yi KH, Rha DW, Lee SC, Cong L, Lee HJ, Lee YW, et al. Intramuscular nerve distribution pattern of ankle invertor muscles in human cadaver using sihler stain. Muscle Nerve 2016;53:742-747. PMID: 26467315.


Fig. 1
Motor branches of the medial plantar nerve to the abductor hallucis were dissected. (A) Multiple branches for the abductor hallucis muscle (arrow). (B) Enlarged image of multiple branches to the abductor hallucis muscle (arrow). (C) Schematic of the anatomical landmarks and nerves (H, metatarsal base of the hallux; C, medial tubercle of the calcaneus; N, navicular tuberosity; 1, posterior tibial nerve; 2, medial plantar nerve; 3, branch for the abductor hallucis).

Fig. 2
Anatomic dissection showed the medial plantar nerve branch entering the abductor hallucis muscle. The anatomical motor point was defined as the most distal point at which the motor branch entered the muscle (arrow).

Fig. 3
A plot of the location of the main motor points (blue dots) in the abductor halluces muscles. The x coordinate was defined as the horizontal distance from the motor point to the point where the perpendicular line from navicular tuberosity (N) crossed the reference line. The perpendicular distance from the motor point to the N point was defined as the y coordinate.