- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 41(2); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether the polymorphisms of CASP3 gene (rs4647602, intron A/C and rs1049216, UTR C/T) and CASP9 gene (rs1052576, Gln/Arg G/A and rs1052571, Ser/Val T/C) were associated with the development, and clinical severity of ischemic stroke and functional consequences after stroke.
Methods
Genomic DNA from 121 ischemic stroke patients and 201 healthy control subjects were extracted, and polymerase chain reaction products were sequenced. To investigate the association of polymorphisms and the development, and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (K-NIHSS), logistic regression models were analyzed.
Results
Polymorphism of the untranslational region of CASP3 (rs1049216, UTR C/T) has been associated with the development of ischemic stroke—in codominant1 model (odds ratio [OR], 0.51; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.29–0.88; p=0.017), in dominant model (OR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.34–0.97; p=0.034), and in the overdominant model (OR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29–0.87; p=0.011). A missense SNP of CASP9 gene (rs1052571, Ser/Val T/C) was associated with the development of ischemic stroke (OR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.05–3.55; p=0.034 in recessive model).
Ischemic stroke is a cerebrovascular accident caused by occlusion of cerebral arteries that results in a sudden neurologic deficit, such as loss of motor functions, altered sensations, and impairments of cognition or language. Despite recent advancements in the prevention and treatment of stroke, the latter event remains the leading cause of disability and the fifth-leading cause of death [1]. Especially in those older than 65 years, stroke is a leading cause of death and disability [2]. Although stroke has been believed to be a multifactorial disorder with minimal classical patterns of inheritance, accumulating evidence has shown the importance of genetic factors [1,3,4,5].
Caspases, a family of cysteinyl-aspartate-specific proteases, are executioners of apoptotic cell death and their activation is considered a commitment to cell death. They are essential in cells for programmed cell death [6,7,8]. Apoptosis has an important role in the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction ischemia, autoimmune diseases, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, transplantation rejection, traumatic brain injury, and tumor responses to chemotherapy and radiation [9,10,11].
In this study, we investigated whether polymorphisms of the caspase 3 (CASP3; rs4647602 and rs1049216) and caspase 9 (CASP9; rs1052576 and rs1052571) genes were associated with the development, clinical severity or impediments in daily activities associated with ischemic stroke.
All participants with stroke were recruited from who visited in Stroke Center of Kyung Hee University Medical Center. One hundred and twenty-one patients with ischemic stroke (mean age, 65.21±8.92 years) with ischemic stroke were enrolled. Patients were diagnosed based on magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, or angiography. Exclusion criteria included other causes of cerebrovascular events, including a hemorrhagic stroke, trauma, vascular malformation, brain tumors, and congenital brain disorders.
Neurological deficits on admission were measured by using the Korean version of the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (K-NIHSS) within 72 hours after the onset of a stroke. The neurological outcome was measured by using a Korean version of the Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI) within 3–6 months after a stroke. To determine the relationship between caspase gene polymorphisms and clinical phenotypes, ischemic stroke patients were divided into subgroups according to their respective NIHSS (<6 and ≥6), and MBI scores (<60 and ≥60) [12,13]
Control subjects above 45 years old had any evidence of prior ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, ischemic heart diseases, and malignancy.
This study was approved by the ethics review committee of the Medical Research Institute, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine. Informed consent of each patient or guardian was obtained.
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of CASP3 (rs4647602 and rs1049216) and CASP9 (rs1052576 and rs1052571) were searched using a SNP database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP; dbSNP BUILD 131) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and we selected the following SNPs, i.e., rs4647602, rs1049216, rs1052576, and rs1052571. Blood samples were collected from each subject and then stored in a −20℃ refrigerator. Genomic DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood using a QIAamp DNA Mini kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA). Genotypes were determined by direct sequencing (Macrogen, Seoul, Korea). Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were performed with the following primers: for rs4647602 (sense, 5'-GGTG CTGACTG TGAGATACTCG-3'; antisense, 5'-CACTT ACTGAGAATGGG GGAAG-3'); for rs1049216 (sense, 5'-CTGGTGCAGTCATTATGAGAGG-3'; antisense, 5'-TCAGG ACAAACATCACAA AACC-3'); for rs1052576 (sense, 5'-ACGGTCCAGTCTGC ATCTAGACC-3'; antisense, 5'-GTTCCCTGGGCAGGCATTGGGTA-3'), and for rs1052571 (sense, 5'-GGTGGGGAGCGAAGACTGACCC-3'; antisense, 5'-ACA CCCGA CTAAGAGGTGTTTG-3'). PCR products were sequenced using an ABI PRISM 3730XL analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). Sequence data were analyzed using SeqMan II software (DNASTAR Inc., Madison, WI, USA). To analyze genetic data, we used HelixTree (Golden Helix Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA), SNPStats (http://bioinfo.iconcologia.net/SNPstats), and SNPAnalyzer (ISTECH Inc., Goyang, Korea).
The associations between genotypes of SNPs and ischemic stroke were estimated by computing the odds ratios (ORs) and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CIs) with logistic regression analyses, controlling for age and gender as covariables. Logistic regression analysis with adjustment for age and gender was performed using the following criteria: codominant1 (major allele homozygotes versus heterozygotes), codominant2 (major allele homozygotes versus minor allele homozygotes), dominant (major allele homozygotes versus heterozygotes + minor allele homozygotes), recessive (major allele homozygotes + heterozygotes versus minor allele homozygotes), overdominant (major allele homozygotes + minor allele homozygotes vs. heterozygotes) and log-additive (major allele homozygotes vs. heterozygotes vs. minor allele homozygotes). An analysis was performed to identify correlations between the polymorphisms and the scores of K-MBI and K-NIHSS by same logistic regression analyses.
The significance level for all statistical tests was set at p<0.05. Linkage disequilibrium (LD) blocks and haplotypes were evaluated using HaploView ver. 4.2 (Daly Lab Inc., Cambridge, MA, USA).
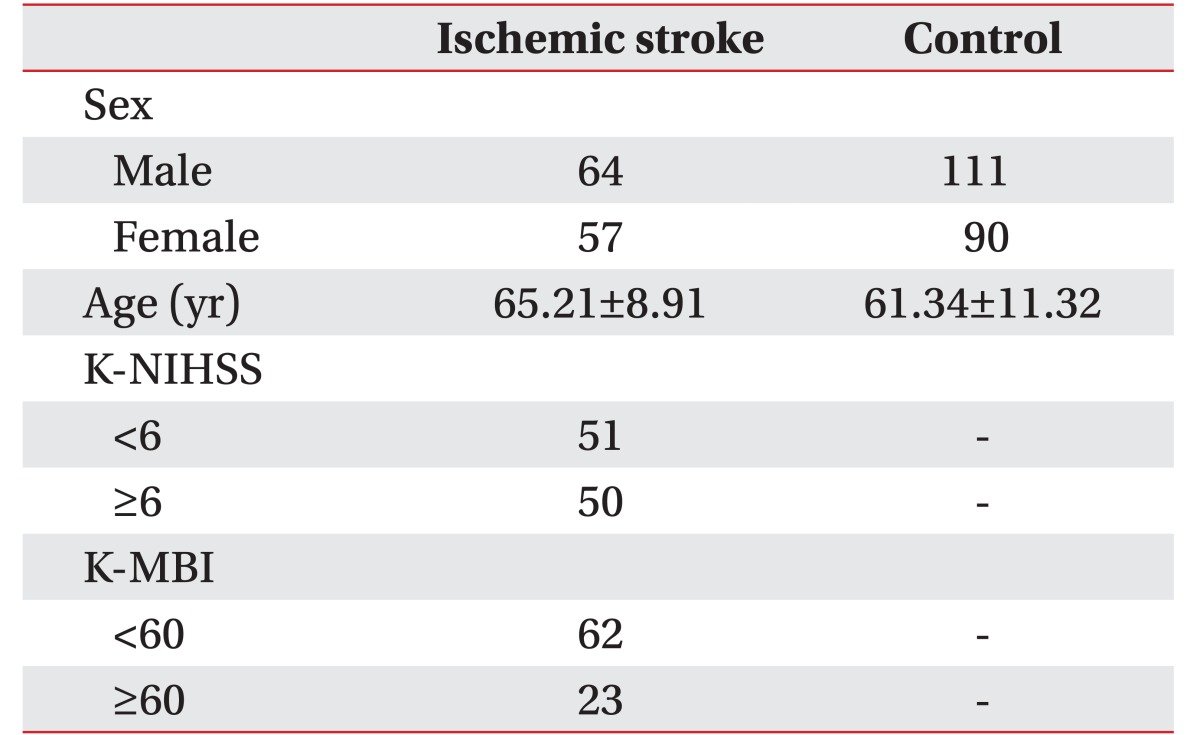
Three hundred and twenty-two subjects were included, 121 subjects were the patients with ischemic stroke (IS group), and 201 were healthy persons (control group). The mean age of patients with ischemic stroke was 65.21±8.92 years, and the mean age of control group was 61.34±11.32 years. The numbers of ischemic stroke patients with NIHSS score <6 and ≥6 were 51 and 50, respectively. The numbers of ischemic stroke patients with MBI score ≤60 and >60 were 62 and 23, respectively (Table 1).
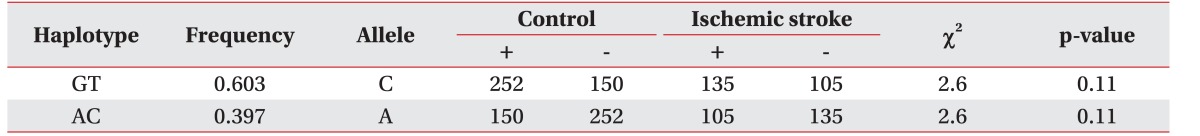
The CASP3 gene (rs4647602, Intron) was not associated with the development of ischemic stroke (p>0.05). There are no statistically significant results in logistic regression. A polymorphism of the untranslational region of CASP3 (rs1049216) has been associated with the development of ischemic stroke—in codominant1 model (OR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.29–0.88; p=0.017), in dominant model (OR, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.34–0.97; p=0.034), and in the overdominant model (OR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29–0.87; p=0.011) (Table 2). Whereas the missense SNP of CASP9 gene (rs1052576, Gln/Arg) was not associated with the development of ischemic stroke (p>0.05), another missense SNP of CASP9 gene (rs1052571, Ser/Val) was associated with the development of ischemic stroke (OR, 1.93; 95% CI, 1.05–3.55; p=0.034) in recessive model (Table 3). Genotype and allele frequency of the SNPS of CASP3 gene (rs4647602 and rs1049216) and CASP9 gene (rs1052576 and rs1052571) was not associated with K-NIHSS and K-MBI scores (p>0.05).
HaploView ver. 4.2 was used to evaluate the LD block and haplotypes of the SNPs of CASP3 (rs4647602 and rs1049216) and CASP9 (rs1052576 and rs1052571). A moderate LD block was found between rs4647602 and rs1049216 (D'=0.858; 95% CI, 0.71–0.94; r2=0.156) (Fig. 1). A complete LD block was detected between rs1052576 and rs1052571 (D'=1 and r2=1) (Fig. 2).
Values of |D'| are divided into three categories: strong LD (|D'| near 1, which implies little or no evidence of historical recombination); weak LD (|D'| significantly <1, which implies historical recombination); and intermediate/unknown LD. Two or more sites can be grouped together into a block if the outermost pair of sites is in strong LD, and, if, for all pairwise comparisons in the LD block, the number of pairs in strong LD is at least 19-fold greater than the number of pairs in weak LD [14].
Apoptosis is a process by which a stressed or damaged cell commits ‘suicide.’ Caspases are key mediators of apoptosis that are activated in distinct molecular pathways. Caspase-3 is important in the apoptosis pathway, and plays decisive roles in the activation of microglia and inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity play a decisive role in the pathogenesis of a few neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease [6,15]. Active caspase-9, a member of the caspase family of proteases, is an initiator caspase protease apoptosis and plays an important role in mitochondrial programmed cell death. The intrinsic or mitochondrial pathway is initiated by the release of cytochrome c from mitochondria in response. Recent investigations have reported that following cerebral ischemia, caspase-3 to a variety of cellular stress [16]. Knockout mice had smaller infarct volumes than wild-type mice [17]. Moreover, mice over-expressing human caspase-3 presented increased apoptosis and larger lesion volumes after transient focal cerebral ischemia [18]. Kuida et al. [19] studied cells from caspase-9 deficient mice show resistance to apoptosis induced by a variety of cytotoxic drugs and radiation. Akpan et al. [20] identified caspases that are critical for neurodegeneration in cerebral ischemia. Their data show that caspases-9 is a regulator of neurodegeneration in cerebral ischemia and an early-stage mediator that also promotes caspase-6 activation of cell death in stroke.
In this study, a SNP of CASP3 (rs1049216, UTR) was associated with the development of ischemic stroke—codominant1 (OR, 0.51; p=0.017), dominant (OR, 0.57; p=0.034), overdominant model (OR, 0.50; p=0.011), and a SNP of CASP9 (rs1052571, Ser/Val) also correlates with ischemic stroke—recessive model (OR, 1.93; p=0.034).
In rs1049216, compared with other zygotes, it can be seen that heterozygotes (T/C genotype) showed a protective effect in the codominant model and overdominant model and compared with other zygotes, major allele homozygotes (CC genotype) were found to act as risk factors in the dominant model. Compared with other zygotes, in rs1052571, minor allele homozygotes (CC genotype) were found to act as risk factors in the recessive model. However, the SNPs of CASP3 (rs4647602) and CASP9 (rs1052576) were not associated with ischemic stroke. To our knowledge, this is the first report that synonymous SNPs of CASP3 (rs1049216) and CASP9 genes (rs1052571) may be associated with the development of ischemic stroke. We also studied the genotype frequencies of CASP3 and CASP9 polymorphisms in K-NIHSS and K-MBI. However, we did not find any significant associations between the clinical status of stroke and CASP polymorphisms.
This study had several limitations. First, there is the possibility of selection bias because this study targeted hospital-based samples and not the general population. Second, the adjustment for risk factors (cigarettes, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia) related to the development of ischemic stroke and ischemic stroke onset origin was not carried out. Third, the long-term effects of SNPs cannot be seen because functional outcome was not measured serially. Large-scale, long-term studies to considered pathogenesis such as risk factors, stroke origin, mutation and adjacent genetic sequences seem to be needed for additional studies.
In summery, the synonymous SNPs of CASP3 (rs1049216) and CASP9 genes (rs1052571) were associated with the development ischemic stroke.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Grysiewicz RA, Thomas K, Pandey DK. Epidemiology of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: incidence, prevalence, mortality, and risk factors. Neurol Clin 2008;26:871-895. PMID: 19026895.


2. Andrawes WF, Bussy C, Belmin J. Prevention of cardiovascular events in elderly people. Drugs Aging 2005;22:859-876. PMID: 16245959.


3. Gil-Nunez A. The metabolic syndrome and cerebrovascular disease: suspicion and evidence. Cerebrovasc Dis 2007;24(Suppl 1): 64-75. PMID: 17971640.


4. Lanktree MB, Dichgans M, Hegele RA. Advances in genomic analysis of stroke: what have we learned and where are we headed? Stroke 2010;41:825-832. PMID: 20167918.


5. Shiber JR, Fontane E, Adewale A. Stroke registry: hemorrhagic vs ischemic strokes. Am J Emerg Med 2010;28:331-333. PMID: 20223391.


6. Burguillos MA, Deierborg T, Kavanagh E, Persson A, Hajji N, Garcia-Quintanilla A, et al. Caspase signalling controls microglia activation and neurotoxicity. Nature 2011;472:319-324. PMID: 21389984.



7. Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, et al. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 1995;376:37-43. PMID: 7596430.



8. Cohen GM. Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 1997;326(Pt 1): 1-16. PMID: 9337844.



9. Belhocine T, Steinmetz N, Hustinx R, Bartsch P, Jerusalem G, Seidel L, et al. Increased uptake of the apoptosis-imaging agent (99m)Tc recombinant human Annexin V in human tumors after one course of chemotherapy as a predictor of tumor response and patient prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:2766-2774. PMID: 12231515.

10. Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, Davis RE, Naumovski L, Ohtsuki K, et al. In vivo detection and imaging of phosphatidylserine expression during programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:6349-6354. PMID: 9600968.



11. Vriens PW, Blankenberg FG, Stoot JH, Ohtsuki K, Berry GJ, Tait JF, et al. The use of technetium Tc 99m annexin V for in vivo imaging of apoptosis during cardiac allograft rejection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1998;116:844-853. PMID: 9806391.


12. O'Donnell MJ, Xavier D, Liu L, Zhang H, Chin SL, Rao-Melacini P, et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): a case-control study. Lancet 2010;376:112-123. PMID: 20561675.


13. Weng WC, Huang WY, Chien YY, Wu CL, Su FC, Hsu HJ, et al. The impact of smoking on the severity of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 2011;308:94-97. PMID: 21665225.


14. Wall JD, Pritchard JK. Haplotype blocks and linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet 2003;4:587-597. PMID: 12897771.



15. Kuida K, Zheng TS, Na S, Kuan C, Yang D, Karasuyama H, et al. Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature 1996;384:368-372. PMID: 8934524.



16. Xu W, Jiang S, Xu Y, Chen B, Li Y, Zong F, et al. A meta-analysis of caspase 9 polymorphisms in promoter and exon sequence on cancer susceptibility. PLoS One 2012;7:e37443PMID: 22616010.



17. Le DA, Wu Y, Huang Z, Matsushita K, Plesnila N, Augustinack JC, et al. Caspase activation and neuroprotection in caspase-3-deficient mice after in vivo cerebral ischemia and in vitro oxygen glucose deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002;99:15188-15193. PMID: 12415117.



18. Kerr LE, McGregor AL, Amet LE, Asada T, Spratt C, Allsopp TE, et al. Mice overexpressing human caspase 3 appear phenotypically normal but exhibit increased apoptosis and larger lesion volumes in response to transient focal cerebral ischaemia. Cell Death Differ 2004;11:1102-1111. PMID: 15153940.



19. Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H, et al. Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 1998;94:325-337. PMID: 9708735.


20. Akpan N. The intrinsic caspase death pathway in stroke neurodegeneration [dissertation]. New York: Columbia University; 2013.
Fig. 1
The haplotype of CASP3 in the patients with ischemic stroke. LD block and haplotypes between rs1049216 and rs4647602 of the CASP3 gene. The LD block was moderately made between the two tested SNPs (D'=0.858, 95% confidence interval, 0.71–0.94; r2=0.156). LD, linkage disequilibrium; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.
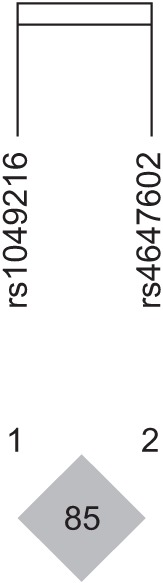
Fig. 2
The haplotype of CASP9 in the patients with ischemic stroke. LD block and haplotypes between rs1052576 and rs1052571 of the CASP9 gene. Complete LD block was found between the two tested SNPs (D'=1 and r2=1). LD, linkage disequilibrium; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.