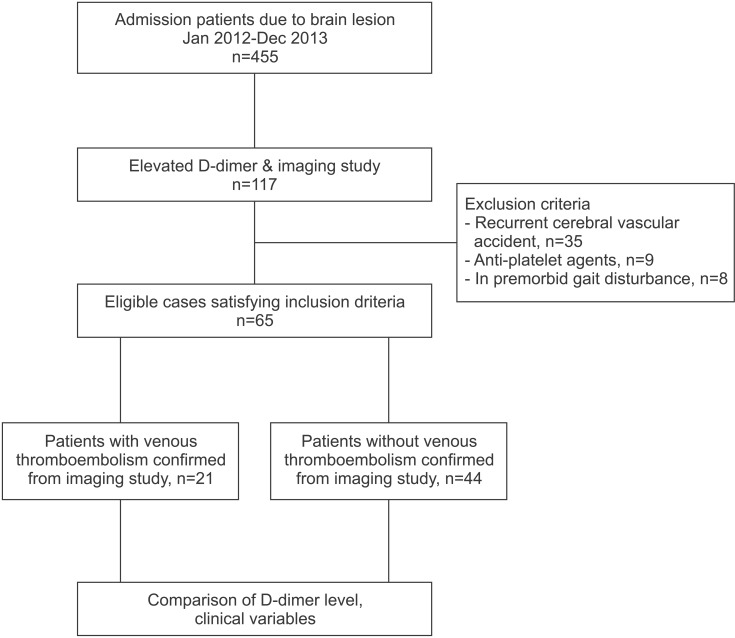
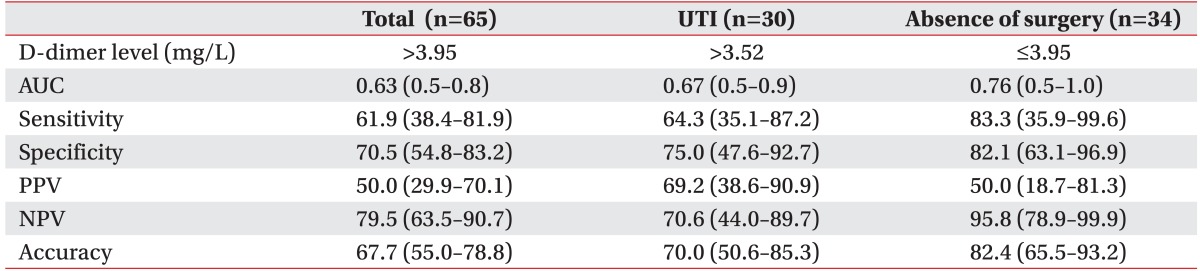
1. Brandstater ME, Roth EJ, Siebens HC. Venous thromboembolism in stroke: literature review and implications for clinical practice. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1992;73(5-S): S379-S391. PMID:
1301012.

2. Geerts WH, Code KI, Jay RM, Chen E, Szalai JP. A prospective study of venous thromboembolism after major trauma. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1601-1606. PMID:
7969340.


3. Hong MY, Lee C, Yoo SY, Shin DH, Cheong SS, Kwon JH, et al. Cut-off value and factors associated with a false positive D-dimer result for venous thromboembolism in Koreans. Korean J Med 2013;84:372-378.

4. Schrecengost JE, LeGallo RD, Boyd JC, Moons KG, Gonias SL, Rose CE Jr, et al. Comparison of diagnostic accuracies in outpatients and hospitalized patients of D-dimer testing for the evaluation of suspected pulmonary embolism. Clin Chem 2003;49:1483-1490. PMID:
12928229.


5. Sadovsky R. ELISA D-dimer testing: high sensitivity but low specificity. Am Fam Physician 2002;66:2310.
6. Darwood RJ, Smith FC. Deep vein thrombosis. Surgery (Oxford) 2013;31:206-210.

7. Jiang Y, Li J, Liu Y, Li YC, Zhang WG. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery and the diagnostic value of D-dimer. Ann Vasc Surg 2015;29:675-681. PMID:
25728333.


8. Matsumoto M, Sakaguchi M, Okazaki S, Furukado S, Tagaya M, Etani H, et al. Relationship between plasma (D)-dimer level and cerebral infarction volume in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Cerebrovasc Dis 2013;35:64-72. PMID:
23428999.


9. Park YW, Koh EJ, Choi HY. Correlation between serum D-dimer level and volume in acute Ischemic stroke. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 2011;50:89-94. PMID:
22053225.



10. Prell J, Rachinger J, Smaczny R, Taute BM, Rampp S, Illert J, et al. D-dimer plasma level: a reliable marker for venous thromboembolism after elective craniotomy. J Neurosurg 2013;119:1340-1346. PMID:
23915033.


11. Park JH, Kwon YC. Standardization of Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K) for use in the elderly. Part II: diagnostic validity. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 1989;28:508-513.
12. Lee HJ, Choi HY, Yun KW, Kim YC, Lim WJ, Kim JH, et al. Association between obesity indices and MMSE-K in elderly. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 2013;52:447-453.

13. Jung HY, Park BK, Shin HS, Kang YK, Pyun SB, Paik NJ, et al. Development of the Korean version of Modified Barthel Index (K-MBI): multi-center study for subjects with stroke. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2007;31:283-297.
14. Kim EJ, Kim SS, Kim WH, Lee WJ, Nam KY, Park CW, et al. The selection of exercise stress test in hemiplegic patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2008;32:26-31.
15. Ramanan B, Gupta PK, Sundaram A, Lynch TG, Mac-Taggart JN, Baxter BT, et al. In-hospital and postdischarge venous thromboembolism after vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg 2013;57:1589-1596. PMID:
23395207.


16. Jeong HS, Miller TJ, Davis K, Matthew A, Lysikowski J, Lazcano E, et al. Application of the Caprini risk assessment model in evaluation of non-venous thromboembolism complications in plastic and reconstructive surgery patients. Aesthet Surg J 2014;34:87-95. PMID:
24327763.



18. Chua K, Kong KH, Chan SP. Prevalence and risk factors of asymptomatic lower extremity deep venous thrombosis in Asian neurorehabilitation admissions in Singapore. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2008;89:2316-2323. PMID:
19061744.


19. Sachdev U, Teodorescu VJ, Shao M, Russo T, Jacobs TS, Silverberg D, et al. Incidence and distribution of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in rehabilitation patients: implications for screening. Vasc Endovascular Surg 2006;40:205-211. PMID:
16703208.


20. Yablon SA, Rock WA Jr, Nick TG, Sherer M, McGrath CM, Goodson KH. Deep vein thrombosis: prevalence and risk factors in rehabilitation admissions with brain injury. Neurology 2004;63:485-491. PMID:
15304579.


21. Cifu DX, Kaelin DL, Wall BE. Deep venous thrombosis: incidence on admission to a brain injury rehabilitation program. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1996;77:1182-1185. PMID:
8931533.


22. Smeeth L, Cook C, Thomas S, Hall AJ, Hubbard R, Vallance P. Risk of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism after acute infection in a community setting. Lancet 2006;367:1075-1079. PMID:
16581406.


24. Fujita Y, Nakatsuka H, Namba Y, Mitani S, Yoshitake N, Sugimoto E, et al. The incidence of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis and their predictive risk factors after lower extremity arthroplasty: a retrospective analysis based on diagnosis using multidetector CT. J Anesth 2015;29:235-241. PMID:
25097087.


25. Kimmell KT, Jahromi BS. Clinical factors associated with venous thromboembolism risk in patients undergoing craniotomy. J Neurosurg 2015;122:1004-1011. PMID:
25495743.


26. Kim JY, Khavanin N, Rambachan A, McCarthy RJ, Mlodinow AS, De Oliveria GS Jr, et al. Surgical duration and risk of venous thromboembolism. JAMA Surg 2015;150:110-117. PMID:
25472485.


27. Legnani C, Palareti G, Cosmi B, Cini M, Tosetto A, Tripodi A, et al. Different cut-off values of quantitative D-dimer methods to predict the risk of venous thromboembolism recurrence: a post-hoc analysis of the PROLONG study. Haematologica 2008;93:900-907. PMID:
18443269.


28. Pulivarthi S, Gurram MK. Effectiveness of d-dimer as a screening test for venous thromboembolism: an update. N Am J Med Sci 2014;6:491-499. PMID:
25489560.



29. Hu X, Fang Y, Ye F, Lin S, Li H, You C, et al. Effects of plasma D-dimer levels on early mortality and longterm functional outcome after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. J Clin Neurosci 2014;21:1364-1367. PMID:
24631325.


30. Stein J, Brandstater ME. Stroke rehabilitation. In: Frontera WR, DeLisa JA, editors. DeLisa's physical medicine & rehabilitation: principles and practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. p.551-574.