- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 35(5); 2011 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of botulinum toxin type A (BTXA) on drooling and the morphologic change of the salivary gland in patients with cerebral palsy.
Method
Eight cerebral palsy patients suffering from severe drooling participated in this study. BTXA was injected into both submandibular and parotid glands under intravenous sedation and with ultrasound guidance (1 unit/gland/kg: maximum 100 units) in an outpatient or inpatient procedure. The severity of drooling was measured before injection and 3 weeks after injection using the Teacher Drooling Scale, the Drooling Score-severity, frequency and the Visual Analog Scale. To investigate the morphologic change of the salivary glands, the size of salivary glands were measured before injection and 3 weeks after injection using computed tomography of the neck. The measurement values were analyzed by Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Drooling is the unintentional loss of saliva from the mouth due to immature or damaged oral motor skills. It occurs more frequently and severely in patients with neurological deficits such as cerebral palsy, motor neuron disease or Parkinson's disease.1,2 Persistent drooling may cause adverse events such as problems in social development and dignity of patients, as well as hygiene problems including unpleasant odor, contaminated clothing and furniture, and skin damage by repeated stimulation.3,4 Additionally, in patients with brain injury who have swallowing disorders, posterior drooling may cause coughing, nausea, vomiting, aspiration into the airway, and if severe, aspiration pneumonia.5
Many studies have investigated the clinical improvement in drooling after the injection of botulinum toxin type A (BTXA). In one study, BTXA was injected into rat salivary glands and the resulting change in structure and function was monitored.6 Another study reported salivary gland shrinkage following the injection of BTXA into rat salivary glands.7 However, there has been no research studying human subjects. This study used neck computed tomography (CT) to compare the size of the salivary glands before and after BTXA injection, aiming to examine morphological changes in the salivary glands along with clinical improvement in drooling after BTXA injection.
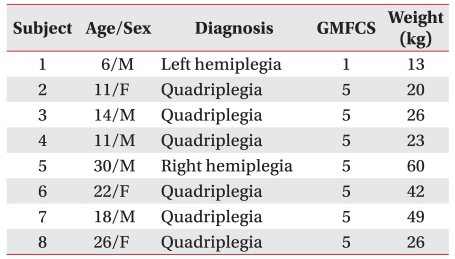
From November 2009 to August 2010, eight cerebral palsy patients (6-30 years-of-age; mean 17.25±8.26 years; five men, three women) presented to our hospital for treatment of drooling. Six patients had spastic tetraplegia and two patients had spastic hemiplegia. According to the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS), one was rated as level 1 and the remaining seven as level 5. They maintained oral feeding (Table 1).
To evaluate the effect of BTXA injection on drooling, measurements were done before injection and after 3 weeks using the Teacher Drooling Scale (TDS; Table 2),1 Drooling Score System (DSS)-severity, frequency (Table 3),8 and a 0-10 Visual Analogue Scale (VAS; mild - 0 point; severe - 10 points). To observe morphological changes in the salivary glands, neck CT was done originating from Frankfort horizontal plane as a basis, which is known to represent the size of salivary glands most accurately, to measure the maximum cross-sectional area (MCSA) in the parotid gland and the submandibular gland before injection and after 3 weeks (Fig. 1). At this time, individual glands were measured three times to calculate the mean for indicating the size of the salivary glands.
BTXA Botox® (Allergan, CA, USA) was injected into the both submandibular and parotid glands in each patient by ultrasound guidance (1 unit/gland/kg: maximum 100 units). The procedure was cooperative in three patients, who underwent aseptic procedures without anesthesia. The remaining patients received an aseptic injection under intravenous sedation using midazolam and fentanyl citrate. Electrical nerve stimulation was used for injection into the parotid glands to confirm that it was not a facial nerve. SPSS 12.0 version for Windows (SPSS, Chicago, USA) was used for statistical analysis; VAS, TDS, DSS, and Wilcoxon signed rank test were used to compare the size of salivary glands before and after injection. The results are presented as median and range (min and max), with a p-value of 0.05 indicating significance. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Dae-gu Fatima Hospital.
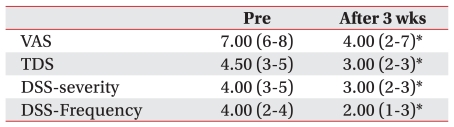
Statistically significant improvements in drooling were shown in all four parameters; from VAS 7.00 (6-8) to 4.00 (2-7), TDS 4.50 (3-5) to 3.00 (2-3), DSS-severity 4.00 (3-5) to 3.00 (2-3), and frequency 4.00 (2-4) to 2.00 (1-3) (p<0.05) (Table 4).
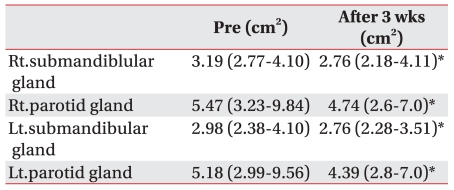
The mean MCSA was statistically significantly reduced after 3 weeks from 3.19 (2.77-4.10) cm2 to 2.76 (2.18-4.11) cm2 in the right submandibular glands; 2.98 (2.38-4.10) cm2 to 2.76 (2.28-3.51) cm2 in the left submandibular glands; 5.47 (3.23-9.84) cm2 to 4.74 (2.6-7.0) cm2 in the right parotid glands; and 5.18 (2.99-9.56) cm2 to 4.39 (2.8-7.0) cm2 in the left parotid glands (p<0.05) (Table 5).
Tahmassebi and Curzon10 studied people in special-education schools and reported that 58% of children with cerebral palsy displayed drooling and 33% of them displayed severe drooling. Ekedahl11 demonstrated that about 10% of children with cerebral palsy have severe drooling. In Korea, Park et al.12 performed a survey on drooling in children with cerebral palsy, reporting that about 23% of them presented with drooling and 84% with severe drooling for which their parents desired corrective treatment. Among the many treatment methods developed for drooling, anti-cholinergic agents such as benzotropine, glycopyyrolate, and bezhexol hydrochloride are effective. However, these agents can produce various adverse events such as orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, urinary retention, constipation, and diarrhea.13 Drooling can also be surgically treated by the changing direction of the secretory duct of parotid glands and removing the salivary glands. However, this might bring about complications such as dysphagia, airway stenosis, and xerostomia.14,15 Since the 1997 report that drooling is improved by BTXA injection into the salivary glands in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,16 injection of BTXA into the salivary glands in patients with brain injury including cerebral palsy has been attempted. The collective results have led to the view that BTXA injection is an effective treatment for improving drooling without significant adverse events compared to existing methods such as the use of anti-cholinergic agents or surgery.17-19
Salivary secretion is regulated by the autonomic nervous system; the sympathetic system primarily controls composition of saliva while the parasympathetic system regulates the secretion amount. As acetylcholine is secreted at the terminals of parasympathetic nerve fibers, saliva is produced.20 When BTXA reaches the target tissue, it is internalized via endocytosis into the nerve cells at the axon terminal, where it binds to the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) protein complex, which contributes to release of acetylcholine, resulting in proteolytic cleavage of the SNARE protein complex. It is assumed, but as yet unproven, that BTXA reduces drooling by suppressing the secretion of acetylcholine in the neuroglandular junction, the terminal of parasympathetic nerve fibers.21,22
Coskun et al.7 injected BTXA into the submandibular glands of 15 rats, 4 to 6-month-old rats and observed morpho logical changes using ultrasound. Shrinkage of salivary glands were observed at 2 and 4 weeks after injection. However, there was no particular change other than lymphocyte infiltration in histologic examination. On the other hand, Teymoortash et al.6 injected BTXA and saline into rat submandibular glands and examined morphological change through histologic examination, and observed shrinkage of glandular cells, decreased size of acinar cells, and reduced granules in acinar cells. It is assumed that the action of SNARE protein complex is controlled by BTXA, causing denervation due to suppressed release of acetylcholine in the neuroglandular junction, resulting in decreased secretion of granules from acinar cells. To date, studies have attempted to clarify the action mechanism of BTXA, which reduces drooling, in the salivary glands of animals. However, little is known concerning human subjects. This study used CT to identify clinical improvement in drooling and morphological changes in the salivary glands after BTXA injection. According to Heo et al.,9 neck CT originating from Frankfort horizontal plane as a basis most accurately represent the size of salivary glands. Thus, CT was used to measure and compare the mean size of salivary glands before injection and after 3 weeks based on the method above, confirming the clinical improvement in drooling and significant reduction of salivary gland size after 3 weeks of injection. Our results with cerebral palsy patients echo those of Coskun et al.7, who suggested that BTXA injection in patients with cerebral palsy leads to shrinkage of salivary glands and it might contribute to clinical improvement in drooping. The present result may corroborate the suggestion of Jongerius et al.1 that the BTXA effect lasts longer by repeated injection in patients with cerebral palsy because of salivary glands shrunk due to denervation.
However, in this study, there were few subjects and no histologic examination was performed so that it could not observe any histologic change in salivary gland cells after injection. It might be helpful to demonstrate the action mechanism of BTXA in the salivary glands by long-term follow-up for BTXA injection and changes in the size of salivary glands with more patients, or additional research on correlation between the degree of shrinkage of salivary glands and the degree of improvement in drooling.
BTXA was injected into the salivary glands in patients with cerebral palsy having severe drooling, demonstrating clinical improvement in drooling. CT performed before injection and after 3 weeks was done to show the action mechanism of BTXA in the salivary glands, resulting in significant reduction in its size. Therefore, it is thought that shrinkage of salivary glands might contribute to improvement of drooling.
References
1. Jongerius PH, van Hulst K, vanden Hoogen FJ, Rotteveel JJ. The treatment of posterior drooling by botulinum toxin in a child with cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2005;41:351-353. PMID: 16131993.


2. Bhatia KP, Munchau A, Brown P. Botulinum toxin is a useful treatment in excessive drooling in saliva. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:697PMID: 10577041.

3. Harris SR, Purdy AH. Drooling and its management in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 1987;29:807-811. PMID: 3319742.


4. van der Burg JJ, Jongerius PH, van Limbeek J, van Hulst K, Rotteveel JJ. Social interaction and self-esteem of children with cerebral palsy after treatment for severe drooling. Eur J Pediatr 2006;165:37-41. PMID: 16172877.


5. Gisel EG, Applegate-Ferrante T, Benson J, Bosma JF. Oral-motor skills following sensorymotor therapy in two groups of moderately dysphagic children with cerebral palsy: aspiration vs nonaspiration. Dysphagia 1996;11:59-71. PMID: 8556880.


6. Teymoortash A, Sommer F, Mandic R, Schulz S, Bette M, Aumuller G, Werner JA. Intraglandular application of botulinum toxin leads to structural and functional changes in rat acinar cells. Br J Pharmacol 2007;152:161-167. PMID: 17618309.



7. Coskun BU, Savk H, Cicek ED, Basak T, Basak M, Dadas B. Histopathological and radiological investigations of the influence of botulinum toxin on the submandibular gland of the rat. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2007;264:783-787. PMID: 17285331.


8. Banerjee KJ, Glasson C, O'Flaherty SJ. Parotid and submandibular botulinum toxin A injections for sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2006;48:883-887. PMID: 17044954.


9. Heo MS, Lee SC, Lee SS, Choi HM, Choi SC, Park TW. Quantitative analysis of normal major salivary glands using computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2001;92:240-244. PMID: 11505274.


10. Tahmassebi JF, Curzon ME. Prevalence of drooling in children with cerebral palsy attending special schools. Dev Med Child Neurol 2003;45:613-617. PMID: 12948328.


12. Park HW, Sim YJ, Bang MS. A survey of drooling in children with cerebral palsy. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2007;31:535-540.
13. Jongerius PH, van Tiel P, van Limbeek J, Gabrels FJM, Rotteveel JJ. A systematic review for evidence of efficacy of anticholinergic drugs to treat drooling. Arch Dis Child 2003;88:911-914. PMID: 14500313.



14. Pena AH, Cahill AM, Gonzalez L, Baskin KM, Towbin RB. Botulinum toxin A injection of salivary glands in children with drooling and chronic aspiration. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2009;20:368-373. PMID: 19157908.


15. Bachrach SJ, Walter RS, Trzcinski K. Use of glycopyrrolate and other anticholinergic medication for sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1998;37:485-490. PMID: 9729704.


16. Bushara KO. Sialorrhea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis of a new treatment botulinum toxin A injections of the parotid glands. Med Hypotheses 1997;48:337-339. PMID: 9160288.


17. Savarese R, Diamond M, Elovic E, Millis SR. Intraparotid injection of botulinum toxin A as a treatment to control sialorrhoea in children with cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2004;83:304-311. PMID: 15024333.


18. Jongerius PH, Rotteveel JJ, van den Hoogen F, Joosten F, van Hulst K, Gabreels FJ. Botulinum toxin A: a new option for treatment of drooling in children with cerebral palsy. Presentation of a case series. Eur J Pediatr 2001;160:509-512. PMID: 11548191.


19. Suskind DL, Tilton A. Clinical study of botulinum-A toxin in the treatment of sialorrhea in children with cerebral palsy. Laryngoscope 2002;112:73-81. PMID: 11802042.


20. Jongerius PH, Joosten F, Hoogen FJ, Gabreels FJ, Rotteveel JJ. The treatment of drooling by ultrasoundguided intraglandular injections of botulinum toxin type A into the salivary glands. Laryngoscope 2003;113:107-111. PMID: 12514392.


21. Dressler D, Saberi FA, Barbosa ER. Botulinum toxin: mechanisms of action. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2005;63:180-185. PMID: 15830090.



22. Dressler D, Adib Saberi F. Botulinum toxin: mechanisms of action. Eur Neurol 2005;53:3-9. PMID: 15650306.

Fig. 1
Representative CT of salivary glands. Outline of salivary glands were drawn with yellow lines on this CT. CT was three millimeter contiguous axial scans and parallel to the Frankfort horizontal plane. (A), parotid gland; (B), submandibular gland.

-
METRICS

-
- 8 Crossref
- Scopus
- 4,498 View
- 43 Download
- Related articles in ARM
-
Cost of Rehabilitation Treatment of Patients With Cerebral Palsy in Korea2018 October;42(5)