- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 47(3); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
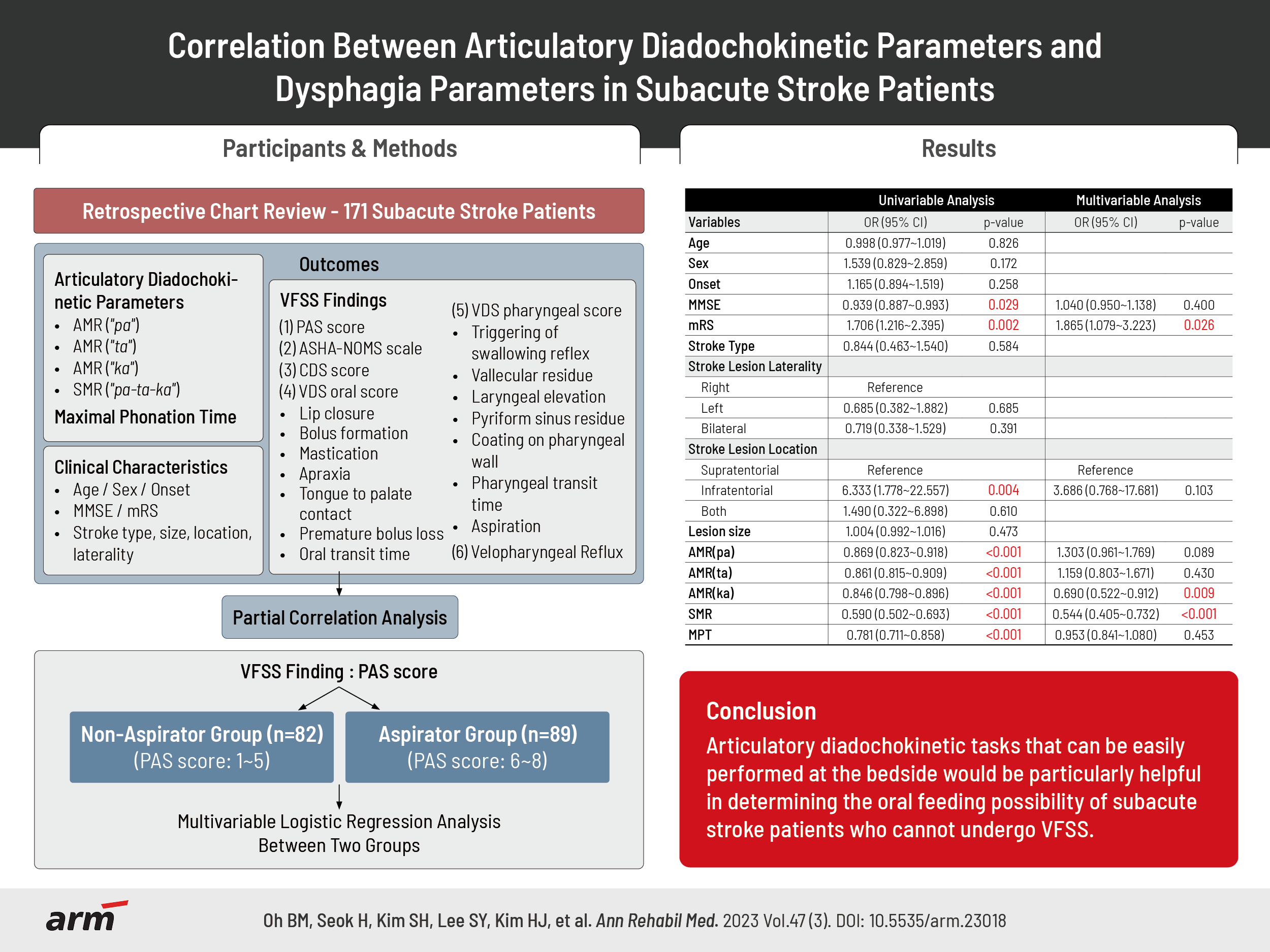
Methods
Results
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Seok H, Kim SH, Lee SY, Kim HJ, Oh BM. Methodology: Kim SH, Kim HJ, Oh BM, Park SJ, Kim BJ. Formal analysis: Kim HJ, Oh BM. Project administration: Seok H, Kim SH, Lee SY, Kim HJ, Oh BM. Visualization: Kim HJ, Oh BM, Park SJ, Kim BJ. Writing – original draft: Kim HJ, Oh BM. Writing – review and editing: Seok H, Kim SH, Lee SY, Kim HJ, Oh BM, Park SJ, Kim BJ. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.

Table 1.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range).
AMR, alternation motor rate; SMR, sequential motor rate; MPT, maximum phonation time; VFSS, video fluoroscopic swallowing study; MMSE, mini-mental state examination; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; ASHA-NOMS, American Speech-Language-Hearing Association National Outcomes Measurement System; CDS, clinical dysphagia scale; VDS, videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale.
Table 2.
Table 3.
The correlation coefficient was adjusted by other possible effectors such as age, sex, MMSE, mRS, the size of the stroke lesion, the location of stroke lesion, the type of stroke, and the laterality of stroke lesion.
AMR, alternation motor rate; SMR, sequential motor rate; MPT, maximum phonation time; VDS, videofluoroscopic dysphagia scale; PAS, penetration-aspiration scale; ASHA-NOMS, American Speech-Language-Hearing Association National Outcomes Measurement System; CDS, clinical dysphagia scale.