- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 46(5); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To clarify the profile of cognitive dysfunction and the effects of intensive exercise in spinocerebellar degeneration (SCD).
Methods
We enrolled 60 healthy controls and 16 patients with purely cerebellar type SCD without gait disturbance or organic changes other than cerebellar changes. To assess cognitive function, we evaluated the participants using the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB), and Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese (MoCA-J) at admission and after intensive exercise.
Results
Compared to the controls, SCD patients showed significant cognitive decline. As a result of intensive exercise, significant improvements in motor and cognitive functions were observed: the MMSE score improved from 27.7±1.9 to 29.0±1.3 points (p<0.001); the FAB score improved from 14.8±2.2 to 15.8±2.0 points (p=0.002); and the MoCA-J score improved from 24.6±2.2 to 26.7±1.9 points (p<0.001). For sub-scores, significant improvements were noted in serial 7, lexical fluency, motor series, and delayed recall.
Patients with lesions involving the posterior lobe and vermis of the cerebellum have been found to have executive dysfunction, spatial cognitive impairments, affective disorder, and linguistic processing disorder. Schmahmann and Sherman [1] referred to the condition characterized by these cognitive dysfunctions as “cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome.” In subsequent studies, physiological, anatomical, and functional neuroimaging indicated cerebellar posterior lobe activation during a variety of cognitive tasks [2–4]. In particular, lobule VII (including Crus I and Crus II) participates in cognitive function, and there are circuits between the cerebellum and cerebrum that are involved in cognitive function [2,4].
Previous studies have found cognitive dysfunction in patients with spinocerebellar degeneration (SCD), including spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) types 1, 2, 3, and 6, multiple system atrophy, and cortical cerebellar atrophy (CCA) [5–11]. Patients with SCA6, representing pure cerebellar degeneration, present with a significant decline in lexical fluency, visual memory, and mild executive dysfunction involving tasks such as cognitive flexibility, response inhibition, and sequencing [8,9,11]. In addition, frontal dysfunction and cognitive decline have been observed in CCA [10]. Intensive exercise is a major milestone in the current treatment for motor dysfunction in SCD [12,13]. However, the effects of intensive exercise on cognitive dysfunction in SCD remain unclear.
We hypothesized that intensive exercise incorporating aerobic exercise may improve not only motor dysfunction but also cognitive dysfunction in patients with SCD. In the present study, we sought (1) to determine the profile of cognitive dysfunction in patients with SCD of the purely cerebellar type and (2) to clarify the effect of 4 weeks of intensive exercise on the cognitive function of patients with SCD of the purely cerebellar type.
Herein, SCD patients were recruited between April 2018 and January 2020. To simplify the interpretation of the relationship between the cerebellum and cognitive function, we enrolled patients diagnosed with SCD of the purely cerebellar type (CCA, SCA6, and SCA31), who were identified by an expert neurologist based on the results of DNA analysis. Particularly, CCA was diagnosed in patients with no family history of cerebellar ataxia and no evidence of secondary ataxia. Patients with CCA were observed for ≥5 years from the onset of disease, which allowed for multiple system atrophy to be excluded. In addition, patients had to be capable of independent activities of daily living (ADL) and walking, to be eligible for the study. Exclusion criteria included any abnormalities other than those within the cerebellum on magnetic resonance imaging and voxel-based specific regional analysis system for Alzheimer’s disease (VSRAD), muscle weakness, marked range of motion limitation, sensory deficits including superficial/deep sensation, vestibular dysfunction, motor dysfunction due to other diseases, and mental illness.
As a control group, we recruited volunteers with no history of neurological or psychiatric disorders that affect cognitive function and selected those of the equal age and education.
This was a comparative study with a control group for assessing cognitive function, but a single-arm pilot study with only an intervention group and no comparison group for assessing post-exercise intervention. Each participant in the control group underwent cognitive function tests. Participants in the patient group underwent cognitive and motor function and ADL assessments on admission. The same assessments were then performed again after intensive exercise therapy to evaluate the effect of exercise.
Cognitive function tests were administered to all subjects, including the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), the Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB), and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese (MoCA-J). The MMSE is a clinical scale for assessing general cognitive dysfunction with scores ranging from 30 (normal) to 0 (most severe). MMSE was performed to ensure that there was no serious overall cognitive dysfunction. The FAB assesses frontal cognitive dysfunction with scores ranging from 18 (normal) to 0 (most severe). The patient was evaluated for frontal dysfunction, which shows a decrease in SCD. The MoCA is a clinical scale for assessing mild cognitive dysfunction where scores range from 30 (normal) to 0 (most severe). It was chosen for its superior sensitivity to detect patients with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and reflects frontal functions such as attention, working memory, and abstract thinking [14]. The same occupational therapist, blinded to the study design, performed these evaluations.
Motor function and ADL assessment was performed only in the patient group. Motor function was evaluated by the Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia (SARA) and the Berg Balance Scale (BBS). The SARA is a standardized clinical scale for assessing ataxia, with scores ranging from 0 (normal) to 40 (most severe). The BBS is a clinical scale for assessing functional balance performance, with scores from 56 (normal) to 0 (most severe). ADLs were evaluated using the Functional Independence Measure (FIM). In the FIM, scores range from 126 (normal) to 18 (most severe). The same physiotherapist, blinded to the study design, performed these evaluations.
Intensive exercise consisted of 4 weeks of physiotherapy (60 minutes, twice daily) and aerobic exercise (30 minutes/day), performed 6 days/week. Physiotherapy comprised goal-based training, including the following categories: (1) static balance (e.g., kneeling and standing on one leg); (2) dynamic balance (e.g., side-step and climbing up and down stairs); (3) whole-body movements to train trunk-limb coordination; and (4) walking (e.g., walking indoors and outdoors). Each patient received an individual exercise schedule for these categories. The physical therapy sessions were supervised by a physical therapist and constituted goal-based training that included cognitive engagement such as learning, motivation, and attention maintenance through verbal and visual feedback during exercise. Although the exercise content was standardized, the difficulty of the exercises was adjusted according to each patient’s severity of ataxia and balance ability. The difficulty level was adjusted when the patients significantly lost their balance or found the exercise too difficult. Additionally, the intensity of aerobic exercise was assessed using the Borg scale. This scale is often used to quantify an individual’s perception during exercise [15]. The intensity was prescribed as 10−13 on the Borg scale. Aerobic exercise was performed using a treadmill.
Comparisons of cognitive function between the patient and control groups were made using the Mann-Whitney U test. The effects of intensive exercise on motor dysfunction, impairment of ADLs, and cognitive dysfunction were analyzed by paired t-tests and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, as applicable. In addition, to compute the power of the statistical test, we used a post hoc power analysis. Statistical evaluations were performed using JMP version 14 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) and G*Power 3.1. The p-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
This study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kumamoto Southern Regional Hospital (No. H30-01) in January 2018, and written informed consent was obtained from each patient. This study was registered with the University hospital Medical Information Network (UMIN) Clinical Trials Registry (No. UMIN000040079) in April 2018.
This study included 16 patients with purely cerebellar type SCD—CCA (n=7), SCA6 (n=8), and SCA31 (n=1). The mean age was 64.9±8.1 years; the mean duration of disease, 4.6±3.6 years; the male/female ratio, 11:5; and years of education, 13.5±2.3 years. Eight patients had full-time employment. The usual exercise undertaken by six patients consisted of only light walking or stretching. All patients were taking taltirelin hydrate. Moreover, no patient had previously undergone rehabilitation for ataxia. In addition, 60 age-and-sex and years-of-education matched subjects were included as healthy controls in this study (mean age, 65.1±8.5 years; male/female ratio, 28:32; and years of education, 13.2±2.5 years). Table 1 shows the characteristics of the patients with SCD of purely cerebellar type and healthy controls.
Compared to healthy controls (MMSE 29.0±1.6, FAB 16.2±2.1, MoCA-J 27.3±2.6), patients with SCD of purely cerebellar type showed significant declines in the results of all cognitive function tests including MMSE (27.7±1.9, p=0.001), FAB (14.8±2.2, p=0.006), and MoCA-J (24.6±2.2, p<0.001) (Fig. 1). By item, there was a significant decrease in serial 7 (p<0.001) on the MMSE; lexical fluency (p<0.001) and motor series (p=0.006) on the FAB; and serial 7 (p=0.007), language repeat (p<0.001), language fluency (p<0.001), abstraction (p<0.001), and on MoCA-J (Fig. 2).
On assessment using the SARA, patients showed limb/trunk ataxia and ataxic dysarthria before exercise. SARA scores significantly improved from 10.7 to 8.1 points after exercise (p<0.001, effect size of −1.53, power 1-β=0.99) (Fig. 3A). In particular, the improvement in truncal ataxia (gait and stance) was more prominent. On assessment using the BBS, patients showed impaired balance ability, including “tandem standing,” “standing on one leg,” “turning 360°,” and “placing alternate foot on stool” before exercise. BBS scores significantly increased from 43.6 to 48.8 points after exercise (p<0.001, effect size of 1.61, power 1-β=0.99) (Fig. 3B). Regarding ADLs, patients showed reduction in the scores for items of locomotion before exercise. FIM scores significantly increased from 119.7 to 122.3 points after exercise (p<0.001, effect size of 1.13, power 1-β=0.98) (Fig. 3C). The improvements were more prominent for gait and climbing up/downstairs than for other FIM motor items.
MMSE scores significantly improved from 27.7 to 29.0 points after exercise (p<0.001, effect size of 1.31, power 1-β=0.99) (Fig. 4A). In particular, the improvement in the serial 7 score (0.9 points) was significant (p=0.007, effect size of 0.8, power 1-β=0.82) (Fig. 4B). FAB scores increased significantly from 14.8 to 15.8 points after exercise (p=0.002, effect size of 0.91, power 1-β=0.91) (Fig. 5A). Particular improvements were observed in the lexical fluency scores (0.5 points) (p=0.04, effect size of 0.8, power 1-β=0.82) and motor series scores (0.4 points) (p=0.04, effect size of 0.8, power 1-β=0.82) (Fig. 5B). MoCA-J scores significantly increased from 24.6 to 26.7 points after exercise (p<0.001, effect size of 1.17, power 1-β=0.99) (Fig. 6A). Particularly, improvement was seen in the delayed recall scores (0.9 points) (p=0.003, effect size of 0.9, power 1-β=0.91) (Fig. 6B).
In this study, cognitive function was compared between patients with purely cerebellar type SCD and healthy controls. Subsequently, 16 patients with SCD performed physiotherapy consisting of goal-based training (balance and walking training) and aerobic exercise for 4 weeks. Our results demonstrate that compared to the controls, SCD patients showed a significant decline in cognitive function. Furthermore, 4 weeks of intensive exercise significantly improved their motor dysfunction, impairment of ADLs, and cognitive dysfunction.
The present study showed that MMSE, FAB, and MoCA-J scores showed significant declines in patients with SCD compared to healthy controls, indicating a possible decline in cognitive function. It has been reported that patients with SCD have lower MMSE, FAB, and MoCA-J scores compared to healthy controls, consistent with previous reports [8,10]. By item, verbal fluency, serial 7, motor series, language repeat, and abstraction, showed declines. The verbal fluency task requires participants to recall as many words beginning with a given letter as possible in a 1-minute trial. Functional imaging studies have shown activation of cerebellar and cortical areas during the verbal fluency task [16]. In addition, a decrease in verbal fluency in SCD has been reported, supporting our finding [7,8,17]. Serial 7 is known to be a test of attention and working memory [18]. There have been reports of decreased attentional function and working memory in SCD [7,18,19], and it is possible that these factors influenced the decrease in the serial 7 test. The motor series is known as a test of executive function [20]. It is widely known that executive function is impaired in SCD [5,6,8,9]. Furthermore, our result is supported by reports that Luria’s fist-edge-palm test, a motor series task, is impaired in patients with stroke, limited only to the cerebellum [21]. Language repeat is a task of language function and verbal memory, in which participants listen to, retain, and recite a sentence. Here, the percentage of correct responses was high for short sentences, but omissions and substitutions were conspicuous for long sentences and interfered with the performance of the task. It has been reported that patients with cerebellar damage experience impairment in language memory and language dysfunctions other than dysarthria [5,22–24]. Furthermore, patients with neurodegenerative cerebellar ataxia tend to perform better on cued tasks that do not require vocalization. Increased cognitive load required for vocalization has been reported to reduce cognitive task performance [25]. Thus, it is possible that the effects of the cognitive load of language impairment, verbal memory impairment, and dysarthria led to the decrease in the language repeat item. Conceptualization involves conceptualizing the link between two objects. Our result is consistent with previous reports that cerebellar damage reduces verbal conceptualization and abstract reasoning [6,26].
The role of the cerebellum in cognitive tasks has been discussed as part of a wider network of regions that include the prefrontal cortex and other areas, and anatomical studies have reported connections between the cerebellum and the prefrontal cortex [5]. Schmahmann and Sherman [1] demonstrated that damage to the cerebellum alone can affect cognitive function. In a group of patients with SCA6, Kawai et al. [27] found evidence of reduced cerebral blood flow in the prefrontal cortex that correlated with reduced performance on cognitive tasks. These findings may reflect cognitive decline due to dysfunction of the circuit with the prefrontal cortex caused by cerebellar damage. The participants in this study had purely cerebellar type SCD, limited only to the cerebellum, as cases with organic changes outside the cerebellum were excluded. This means that the cognitive dysfunction observed in this study is attributable to damage to the cerebellum and may be specific to SCD.
The patients in this study showed limb/trunk ataxia resulting from impaired motor control involving only cerebellar degeneration. Therefore, balance and gait disorders were attributed to ataxia. Previous studies have shown that continuous coordination exercise for 4 weeks can improve motor performance and reduce ataxia symptoms in patients with SCD [12]. In addition, a previous randomized controlled trial found that 4 weeks of intensive rehabilitation significantly improved ataxia, ADLs, and gait in 42 patients with purely cerebellar type SCD [13]. The present study also showed that 4 weeks of intensive exercise could significantly improve scores on all evaluations (SARA, BBS, and ADL) in patients with purely cerebellar type SCD. These results are consistent with those of previous studies.
Interestingly, the results show a significant improvement in all cognitive evaluations of MMSE, FAB, and MoCA-J after intensive exercise. In particular, cognitive function was significantly improved in items involving series 7, verbal fluency, motor series, and delayed recall. To the best of our knowledge, there have been no reports on the effects of intensive exercise on cognitive dysfunction in human SCD, and this is the first report.
In this study, physiotherapy consisting of goal-based training (balance and walking training) and aerobic exercise were performed for 4 weeks. The effects of exercise on cognitive function are widely known. Many neurodegenerative diseases with cognitive dysfunction other than SCD have been investigated in a variety of ways. It has previously been reported that exercise improved cognitive dysfunction in patients with Parkinson disease (PD) and Alzheimer disease (AD) [28–31]. A randomized controlled trial (n=40) in PD reported that 4 weeks of physiotherapy (6 sessions/week, 1 hour), including goal-based training and aerobic exercise, showed improvements in attention and executive function in addition to MMSE and MoCA [31]. Furthermore, studies suggest that exercise in AD and PD may impart cognitive function improvement by promoting neurogenesis and synapse formation through increased release of neurotrophic factors and angiogenesis and by promoting neuroplasticity in the brain [28–30]. Thus, exercise may be effective to improve cognitive dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases.
However, although studies of human SCD have not reported any effects of exercise on cognitive dysfunction, it has been reported that physical activity significantly increased spatial learning ability in animal models of SCD [32]. This suggests that exercise has the potential to improve cognitive dysfunction in SCD. In studies of human, there are some very interesting reports. Burciu et al. [33] performed voxel-based morphometry (VBM) in 19 patients with cerebellar degeneration and observed a 2-week training-related increase in dorsal premotor cortex volume, insular cortex volume, anterior cingulate cortex volume and Crus I volume in the cerebellum. It is considered that these results reflect increase in the use of attention to the task and/or increased use of cognitive strategies in the motor learning. Considering thus reports, the effects of verbal and visual feedback and motor learning by the physical therapists in this study may have a positive effect on these brain regions. Increased capacity of the cingulate and bilateral insular cortices, which are involved in executive function systems of top-down control, such as attention allocation, may smooth the processing of cognitive tasks [34]. Crus I and Crus II regions of the cerebellum have also been reported to be associated with phonemic fluency, working memory, delayed recall, and motor tasks [35,36]. This suggests that increased volume of Crus I has the potential to improve cognitive function. Furthermore, aerobic exercise contributes to brain health through neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects [37,38]. This is no exception in the cerebellum, regarding which, for example, treadmill exercise has been reported to be effective against cognitive dysfunction after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats by inhibiting the loss of Purkinje cell in the posterior lobe of the cerebellum [39]. Thus, exercise has the potential to improve cerebellum-related cognitive dysfunction. Physiotherapy consisting of goal-based training (balance and walking training) and aerobic exercise in this study may be involved in structural changes and protection of the brain and may improve cognitive functions.
In summary, our results suggest that exercise interventions for SCD may improve cognitive function. Conversely, the improvements were localized and did not cover all cognitive functions that were impaired in the patients. Additional large-scale studies are needed to determine which cognitive functions exercise is effective for and what types of exercise are effective.
This study has several limitations. First, this was a single-arm study, and there was no comparison group. Therefore, it is unclear how specific exercises affected cognitive dysfunction. To elucidate the effect of specific exercises, it is necessary to conduct randomized controlled trials for each exercise program. The second limitation was the sample size. Our sample size was small because this was a single-center study targeting SCD of the purely cerebellar type. Therefore, in the future, we will consider expanding the study to different medical centers and including different types of SCD. However, our post-hoc power analyses of the statistical tests showed that most analyses had sufficient power. Third, we did not exclude elderly people and thus may have included patients with impaired cognitive function in this study. However, it was unlikely that only age affected cognitive dysfunction in patients because middle-aged people also showed cognitive dysfunction relevant to the frontal lobe. To clarify the effects of exercise, an age restriction may be required in future research. Fourth, we described the effects on neural plasticity and neural circuits in improving cognitive dysfunction but did not examine these in detail. Neurotrophic factors (important for neural plasticity) and exercise-related brain changes can be clinically measured using blood testing and neuroimaging tools (especially VBM), respectively. Such prospective studies are currently in progress. Fifth, it is unclear whether functional gains can be sustained over several months after intensive exercise because SCD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. The long-term effects of exercise require further investigation.
In this study, the purely cerebellar type SCD group showed a decline in cognitive function compared to the healthy control group. This suggests that in providing rehabilitation treatment, it is necessary to consider approaches to tackle cognitive dysfunction and motor dysfunction. Therefore, we conducted an intensive 4-week exercise program in patients with purely cerebellar type SCD. The results suggest that intensive exercise is effective not only for motor dysfunction, but also for cognitive dysfunction. This can be expected to have a positive impact on future treatment planning.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We express our deepest appreciation to colleagues in the Department of Rehabilitation.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Shimamoto T, Uchino K, Mori A, Nojima K, Iiyama J, Misumi Y, Ueda M, Makoto U. Methodology: Shimamoto T, Uchino K, Iiyama J. Formal analysis: Shimamoto T, Uchino K. Project administration: Shimamoto T. Writing-original draft: Shimamoto T, Uchino K, Mori A. Writing-review and editing: Iiyama J, Misumi Y, Ueda M, Makoto U. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1
Cognitive function scores for (A) MMSE, (B) FAB, and (C) MoCA-J comparing healthy controls and SCD. Note the significant reduction in MMSE, FAB, and MoCA-J scores of patients with SCD compared to healthy controls. SCD, spinocerebellar degeneration; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; FAB, Frontal Assessment Battery; MoCA-J, Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.

Fig. 2
Item-specific scores of cognitive function measures for (A) MMSE, (B) FAB, and (C) MoCA-J comparing healthy controls and patients with SCD. There was a significant decrease in (A) serial 7 (p<0.001) on the MMSE; (b) lexical fluency (p<0.001) and motor series (p=0.006) on the FAB; and (c) serial 7 (p=0.007), language repeat (p<0.001), language fluency (p<0.001), and abstraction (p<0.001) on the MoCA-J. SCD, spinocerebellar degeneration; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination; FAB, Frontal Assessment Battery; MoCA-J, Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
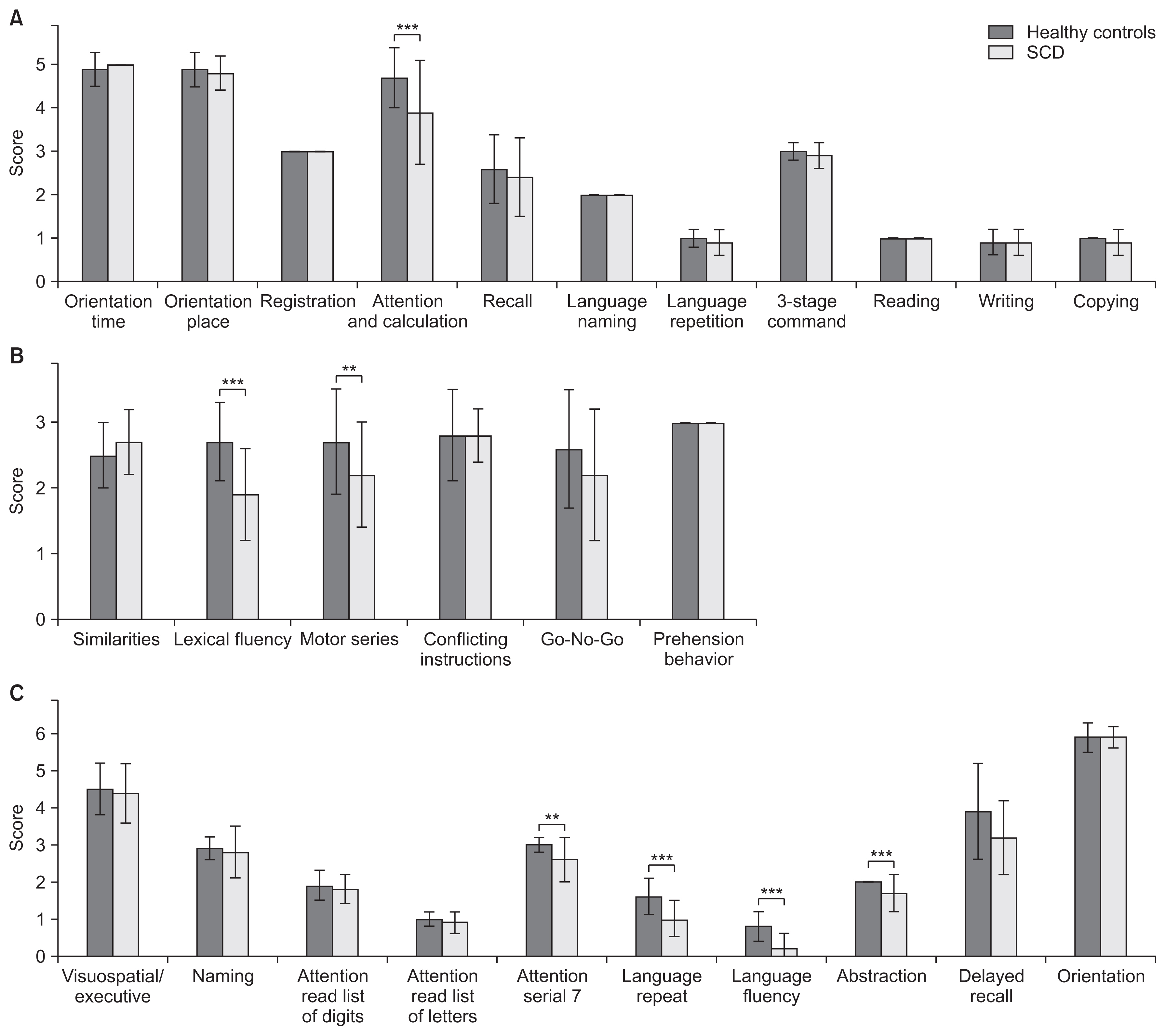
Fig. 3
Comparison of motor function and ADL before and after exercise. (A) SARA scores (significantly improved from 10.7±4.7 to 8.0±4.1 points after exercise). (B) BBS scores (significantly increased from 43.6±8.7 to 48.8±7.1 points after exercise). (C) FIM scores (significantly increased from 119.7±5.2 to 122.3±3.8 points after exercise). Each letter from A through P corresponds to a different patient. ADL, activities of daily living; BE, before exercise; AE, after exercise; SARA, Scale for the Assessment and Rating of Ataxia; BBS, Berg Balance Scale; FIM, Functional Independence Measure. *** p<0.001.
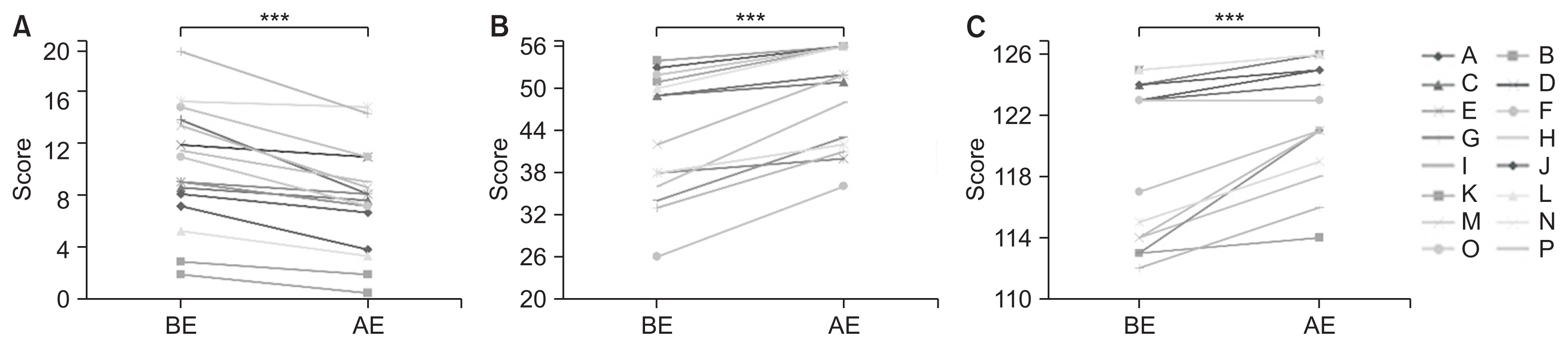
Fig. 4
Comparison of MMSE scores before and after exercise. ( A) Score comparison in each patient ( A through P). The scores significantly improved from 27.7±1.9 to 29.0±1.3 points after exercise. (B) Comparison of average scores for each item. Improvement in the “serial 7” score (attention and calculation) was the most prominent; it significantly improved from 3.9±1.1 to 4.8±0.4 points (p=0.007). BE, before exercise; AE, after exercise; MMSE, Mini-Mental State Examination. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
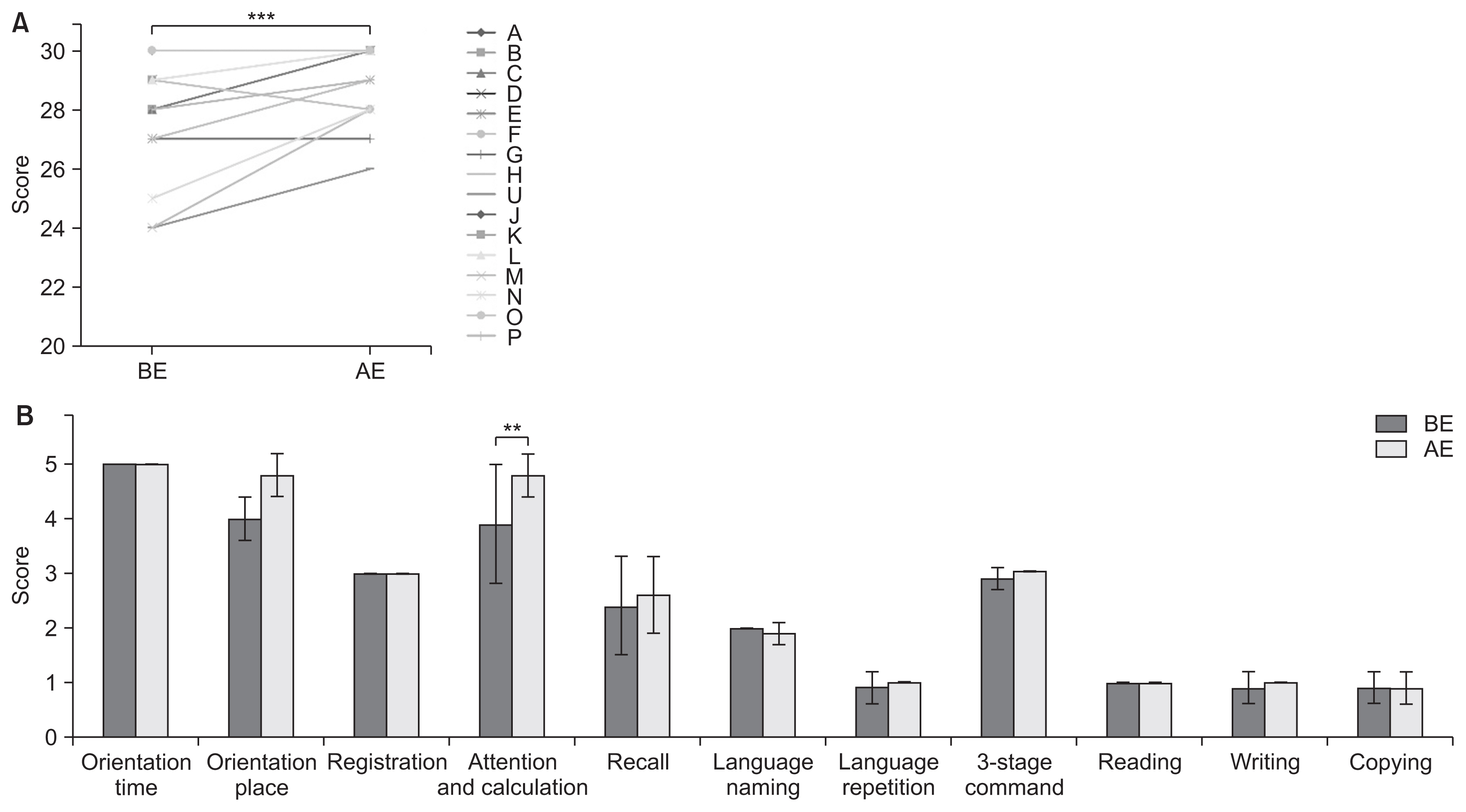
Fig. 5
Comparison of FAB scores before and after exercise. (A) Score comparison in each patient (A through P). The scores significantly improved from 14.8±2.2 to 15.8±2.0 points after exercise. (B) Comparison of average scores for each item. “Lexical fluency” and “motor series” scores significantly improved from 1.9±0.7 to 2.4±0.6 points (p=0.0353) and from 2.2±0.7 to 2.6±0.7 points (p=0.0353), respectively. BE, before exercise; AE, after exercise; FAB, Functional Independence Measure. *p<0.5, **p<0.01.

Fig. 6
Comparison of MoCA-J scores before and after exercise. (A) Score comparison in each patient (A through P). The scores significantly improved from 24.6±2.2 to 26.7±1.9 points after exercise. (B) Comparison of average scores for each item. The “memory items” score (delayed recall) significantly improved from 3.2±1.0 to 4.1±0.8 points. BE, before exercise; AE, after exercise; MoCA-J, Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Japanese. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
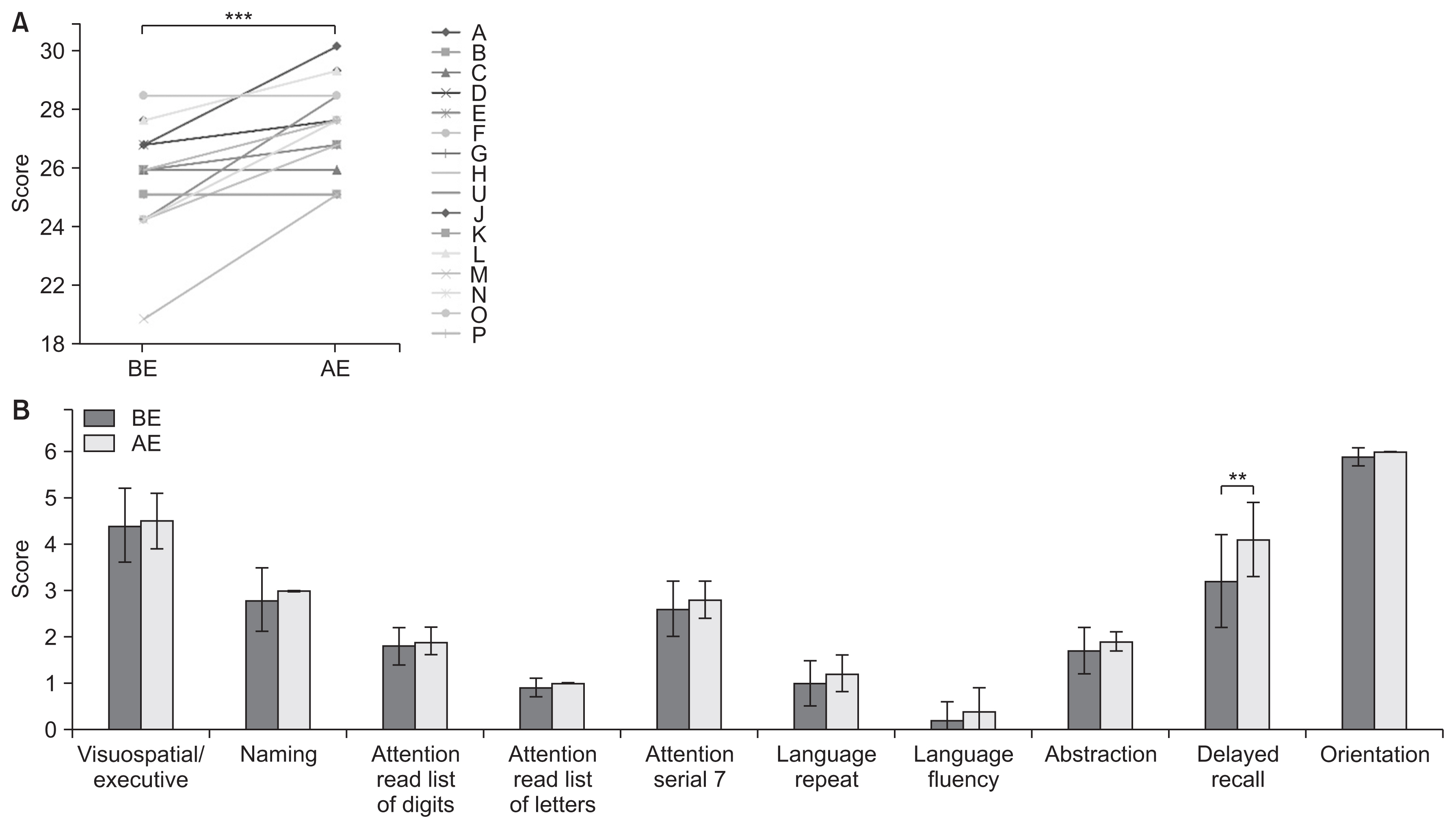
Table 1
Characteristics of patients with purely cerebellar type SCD and healthy controls
REFERENCES
1. Schmahmann JD, Sherman JC. The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 1998;121(Pt 4): 561-79.


2. Buckner RL, Krienen FM, Castellanos A, Diaz JC, Yeo BT. The organization of the human cerebellum estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J Neurophysiol 2011;106:2322-45.



3. Stoodley CJ, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography in the human cerebellum: a meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. Neuroimage 2009;44:489-501.


4. EKH , Chen SH, Ho MH, Desmond JE. A meta-analysis of cerebellar contributions to higher cognition from PET and fMRI studies. Hum Brain Mapp 2014;35:593-615.



5. Burk K, Globas C, Bosch S, Graber S, Abele M, Brice A, et al. Cognitive deficits in spinocerebellar ataxia 2. Brain 1999;122(Pt 4): 769-77.


6. Burk K, Bosch S, Globas C, Zuhlke C, Daum I, Klockgether T, et al. Executive dysfunction in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Eur Neurol 2001;46:43-8.



7. Kawai Y, Takeda A, Abe Y, Washimi Y, Tanaka F, Sobue G. Cognitive impairments in Machado-Joseph disease. Arch Neurol 2004;61:1757-60.


8. Suenaga M, Kawai Y, Watanabe H, Atsuta N, Ito M, Tanaka F, et al. Cognitive impairment in spinocerebellar ataxia type 6. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008;79:496-9.


9. Cooper FE, Grube M, Elsegood KJ, Welch JL, Kelly TP, Chinnery PF, et al. The contribution of the cerebellum to cognition in spinocerebellar ataxia type 6. Behav Neurol 2010;23:3-15.




10. Kawahara Y, Ikeda Y, Deguchi K, Kurata T, Hishikawa N, Sato K, et al. Simultaneous assessment of cognitive and affective functions in multiple system atrophy and cortical cerebellar atrophy in relation to computerized touch-panel screening tests. J Neurol Sci 2015;351:24-30.


11. Tamura I, Takei A, Hamada S, Nonaka M, Kurosaki Y, Moriwaka F. Cognitive dysfunction in patients with spinocerebellar ataxia type 6. J Neurol 2017;264:260-7.



12. Ilg W, Synofzik M, Brotz D, Burkard S, Giese MA, Schols L. Intensive coordinative training improves motor performance in degenerative cerebellar disease. Neurology 2009;73:1823-30.


13. Miyai I, Ito M, Hattori N, Mihara M, Hatakenaka M, Yagura H, et al. Cerebellar ataxia rehabilitation trial in degenerative cerebellar diseases. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2012;26:515-22.



14. Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, et al. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:695-9.


16. Schlosser R, Hutchinson M, Joseffer S, Rusinek H, Saarimaki A, Stevenson J, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity in a verbal fluency task. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;64:492-8.



17. Rentiya ZS, Jung BC, Bae J, Liszewski CM, Fishman A, Du AX, et al. Selective patterns of cognitive impairment in spinocerebellar ataxia type 6 and idiopathic late-onset cerebellar ataxia. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2018;33:427-36.


18. Bristow T, Jih CS, Slabich A, Gunn J. Standardization and adult norms for the sequential subtracting tasks of serial 3’s and 7’s. Appl Neuropsychol Adult 2016;23:372-8.

19. Moriarty A, Cook A, Hunt H, Adams ME, Cipolotti L, Giunti P. A longitudinal investigation into cognition and disease progression in spinocerebellar ataxia types 1, 2, 3, 6, and 7. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2016;11:82.



20. Dubois B, Slachevsky A, Litvan I, Pillon B. The FAB: a frontal assessment battery at bedside. Neurology 2000;55:1621-6.


21. Taskiran-Sag A, Uzuncakmak Uyanik H, Uyanik SA, Oztekin N. Prospective investigation of cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome in a previously non-demented population of acute cerebellar stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2020;29:104923.


22. Burk K, Globas C, Bosch S, Klockgether T, Zuhlke C, Daum I, et al. Cognitive deficits in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1, 2, and 3. J Neurol 2003;250:207-11.



23. Justus T. The cerebellum and English grammatical morphology: evidence from production, comprehension, and grammaticality judgments. J Cogn Neurosci 2004;16:1115-30.




24. Ronning C, Sundet K, Due-Tonnessen B, Lundar T, Helseth E. Persistent cognitive dysfunction secondary to cerebellar injury in patients treated for posterior fossa tumors in childhood. Pediatr Neurosurg 2005;41:15-21.



25. Orsi L, D’Agata F, Caroppo P, Franco A, Caglio MM, Avidano F, et al. Neuropsychological picture of 33 spinocerebellar ataxia cases. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2011;33:315-25.


26. Hoche F, Guell X, Vangel MG, Sherman JC, Schmahmann JD. The cerebellar cognitive affective/Schmahmann syndrome scale. Brain 2018;141:248-70.



27. Kawai Y, Suenaga M, Watanabe H, Ito M, Kato K, Kato T, et al. Prefrontal hypoperfusion and cognitive dysfunction correlates in spinocerebellar ataxia type 6. J Neurol Sci 2008;271:68-74.


28. Valenzuela PL, Castillo-Garcia A, Morales JS, de la Villa P, Hampel H, Emanuele E, et al. Exercise benefits on Alzheimer’s disease: state-of-the-science. Ageing Res Rev 2020;62:101108.


29. Petzinger GM, Fisher BE, McEwen S, Beeler JA, Walsh JP, Jakowec MW. Exercise-enhanced neuroplasticity targeting motor and cognitive circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:716-26.



30. Petzinger GM, Holschneider DP, Fisher BE, McEwen S, Kintz N, Halliday M, et al. The effects of exercise on dopamine neurotransmission in Parkinson’s disease: targeting neuroplasticity to modulate basal ganglia circuitry. Brain Plast 2015;1:29-39.



31. Avenali M, Picascia M, Minafra B, Tassorelli C, Sinforiani E, Bernini S. Intensive physical therapy mitigates cognitive decline in people with Parkinson’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 2019;9:475.
32. Cendelin J, Korelusova I, Vozeh F. Preliminary study of the effect of repeated motor training on spatial learning ability in adult lurcher mutant mice. Prague Med Rep 2007;108:49-56.

33. Burciu RG, Fritsche N, Granert O, Schmitz L, Sponemann N, Konczak J, et al. Brain changes associated with postural training in patients with cerebellar degeneration: a voxel-based morphometry study. J Neurosci 2013;33:4594-604.



34. Petersen SE, Posner MI. The attention system of the human brain: 20 years after. Annu Rev Neurosci 2012;35:73-89.



35. Stoodley CJ, Valera EM, Schmahmann JD. Functional topography of the cerebellum for motor and cognitive tasks: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 2012;59:1560-70.



36. Kansal K, Yang Z, Fishman AM, Sair HI, Ying SH, Jedynak BM, et al. Structural cerebellar correlates of cognitive and motor dysfunctions in cerebellar degeneration. Brain 2017;140:707-20.



37. Cotman CW, Berchtold NC, Christie LA. Exercise builds brain health: key roles of growth factor cascades and inflammation. Trends Neurosci 2007;30:464-72.


- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- Scopus
- 3,477 View
- 76 Download
- Related articles in ARM
-
Effect of Donepezil on Cognitive Function in Patients with Brain Injury.2002 August;26(4)






