- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 46(1); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To determine the effects of the Paraplegia Fitness Integrated Training (PARAFiT) program, which is an integrated graded physical exercise and health education program for individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI).
Methods
This nonrandomized single-blind study included 44 participants, who were assigned to either an intervention (PARAFiT) group or an active control (conventional physiotherapy) group. The intervention group underwent the PARAFiT program (8 weeks), which consisted of circuit-based interval training, progressive upper limb resistance training, and health education sessions. During the unsupervised period, the intervention group continuously underwent health education program once a month for 2 months (8 weeks). Repeated-measures analysis of variance was used for the analysis.
Results
The intervention group presented with a higher level of physical activity than did the control group; however, the difference was not significant (p=0.36). Additionally, the intervention group presented with better exercise self-efficacy and cardiorespiratory fitness and stronger bilateral shoulder muscle and handgrip than did the control group (all p<0.05). Exercise adherence was higher in the intervention group than in the control group during both the supervised (80% vs. 75%) and unsupervised (40% vs. 20%) periods.
Conclusion
The PARAFiT program enhanced the level of physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, physical fitness, and exercise adherence among the patients with SCI. Future studies should incorporate guidelines for home-based exercises and regular monitoring to promote long-term adherence to exercise and physical activity among individuals with SCI.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) may result in loss of motor function and sensation and dysregulation of the autonomic body systems. These impairments lead to substantial changes from active to inactive lifestyles that may cause secondary complications, including cardiovascular diseases [1], metabolic disorders [2], and obesity [3]. Physical impairments may also cause physical dysfunction that affects numerous aspects of quality of life [4], thereby leading to early morbidity and mortality. The level of physical activity among individuals with SCI is usually higher in supervised periods than in unsupervised periods. However, after discharge from in-patient rehabilitation, the level of daily physical activity becomes low. Therefore, health promotion programs are needed to promote an active lifestyle and prevent secondary complications.
Physical activities may enhance physical fitness, functional capacity [5], and participation and prevent physical deconditioning [6]. However, the level of physical activity is low among patients, particularly after discharge from rehabilitation, fitness, or exercise programs. The limited physical activity can be attributed to intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic factors include exercise self-efficacy [7], motivation [8], and lack of knowledge [9]. Meanwhile, extrinsic factors include program costs, equipment, and inaccessible facilities [10]. Hence, strategies to overcome exercise barriers should be incorporated into SCI rehabilitation programs to promote a healthy lifestyle.
A strategy to enhance exercise self-efficacy through educational programs may help individuals with SCI overcome exercise barriers to becomeactive. Previous studies have shown a positive relationship between the level of physical activity and educational interventions [11]. Therefore, an educational program should be incorporated into SCI rehabilitation or exercise programs to increase the level of physical activity and promote continuous engagementin an active lifestyle. Although educational interventions may have benefits on the level of physical activity, the effects of education combined with exercise interventions on physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, and physical fitness are inconclusive.
A previous study has shown the benefits of exercise on physical capacities, such as strength, body composition, aerobic fitness, and functional performance [12]. A recent review found positive effects of exercise on physical fitness and cardiometabolic health among individuals with SCI [13]. To prevent cardiovascular diseases, individuals with SCI should have a sufficient dose of aerobic exercise (at least 30 minutes), as recommended in exercise guidelines [14]. Despite the numerous benefits of aerobic exercise, individuals may not adhere to aerobic exercise for 30 minutes owing to muscle fatigue or boredom. Hence, aerobic circuit-based interval training may be utilized as a regime, given that variations in circuit training may prevent boredom [15]. Additionally, frequent rest and high effort during interval training may minimize fatigue and yield powerful insulin sensitivity [16].
To prevent muscle deconditioning and dysfunction, individuals with SCI should perform progressive resistance exercises, as recommended in exercise guidelines [14]. The majority of guidelines on strengthening exercise prescriptions show uniform recommendations [14,17]. Nevertheless, only a few studies have investigated the effects of circuit-based aerobic interval training combined with progressive strengthening exercise on physical fitness, including cardiorespiratory performance and muscle strength. Therefore, the primary objective of our study was to examine the effects of a physical fitness training program consisting of circuit-based interval training and progressive strengthening exercise integrated with an educational program on the level of physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, physical fitness, and exercise adherence. We hypothesized that the Paraplegia Fitness Integrated Training (PARAFiT) program would have significant effects on physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, cardiorespiratory fitness, shoulder and handgrip strength, and exercise adherence among individuals with SCI.
This nonrandomized controlled trial study was conducted in a private rehabilitation center; the participants were divided into an intervention (PARAFiT) group and an active control (conventional physiotherapy) group. The inclusion criteria were sub-acute and chronic SCI (>4 months post-injury), 18–55 years of age, wheelchair dependency with high (T1–T6) or low (>T7) paraplegia, non-involvement in regular exercise training (at least 30 minutes, any intensity, three times a week), and ability to understand or read instructions in Malay or English language. The exclusion criteria were contraindications for physical training and testing (pregnancy, pressure sores, or severe cardiovascular problems), psychiatric problems that could interfere with study participation, and progressive neurological diseases that may worsen over time. The study was conducted from 2016 to 2020.
The primary outcome was the level of physical activity, while the secondary outcomes were exercise self-efficacy, cardiorespiratory fitness, shoulder isokinetic strength, handgrip strength, and exercise adherence.
The level of physical activity was measured using the “Physical Activity Scale for Individuals with Physical Disabilities (PASIPD),” which is a 13-item self-reported questionnaire, including items on leisure, household activities, and occupational tasks, during the previous 7 days. The score is based on the metabolic equivalent of task (MET), frequency, and duration summed over each independent category. Frequency is categorized as never, seldom (1–2 days/week), sometimes (3–4 days/week), or often (5–7 days/week). The average duration per day is categorized as <1 hour, 1–2 hours, 2–4 hours, or >4 hours for items #1–12 and <1 hour, 1–4 hours, or 5–8 hours for item #13. The PASIPD score is the sum of the scores from items #2 to #13, and each item score is obtained by multiplying the average duration per day with the MET value associated with the intensity of the activity. Possible scores range from 0 to 199.5 MET (highest) hr/day [18]. The PASIPD is a valid [18] and reliable tool for individuals with SCI (Cronbach’s alpha=0.37–0.65; Spearman correlation=0.77) [19].
Exercise self-efficacy was evaluated by utilizing the Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale (ESES); it measures the belief or confidence of individuals in performing various types of physical activity and exercises at home or a gym in the past 12 months. The ESES was developed specifically for populations with SCI based on expert comments and interviews with individuals with SCI. This self-report questionnaire expects a response using a 4-point Likert scale and takes approximately 5 minutes to administer. The total score is derived by summing the scores, with possible scores ranging from 10 to 40. The ESES is internally consistent (Cronbach’s alpha=0.92) and reliable (Spearman correlation=0.316) and has been used in individuals with SCI [20].
Cardiorespiratory fitness was evaluated using the 6-minute push test (6-MPT); this test is a friendly approach for measuring the levels of cardiovascular fitness of individuals with SCI. The 6-MPT was performed using a personal wheelchair at a 30-m loop course, marked 15 m apart by two cones (30-m loop) with 2.8 m on either end to allow space for turning. Two 180° turns were needed to complete one 30-m loop. The participants were required to propel the wheelchair as far as possible and advised that they could stop or slow down at any point during the test. They were allowed to perform 2 minutes of the self-selected slow-velocity practice test. For the practice test, the participants were instructed to propel at a comfortable velocity as if they were pushing around a grocery store, turning in the direction of their choice. The distance traveled in 6 min was computed by multiplying the number of completed laps by 15 m and adding the distance traveled in the last lap. The distance traveled at the turns was not measured. The 6-MPT is reliable and valid for measuring cardiorespiratory fitness (intraclass correlation coefficient [ICC] >0.90) [21].
Shoulder isokinetic strength was assessed using a Biodex III isokinetic dynamometer (Biodex Medical System Inc., Shirley, NY, USA). Shoulder isokinetic strength (peak torque) for the external and internal rotators of the right and left shoulders, abductors and adductors, flexors, and extensors was measured using Biodex Isokinetic System 3 [22], which is reliable (ICC=1.00) and valid (ICC=0.99) [23] for measuring peak torque.
Handgrip measurements were obtained three times (both hands) using a JAMAR hand dynamometer [24], and the average values were used as the final values [24,25]. The rest period between trials ranged from 15 to 60 seconds to avoid fatigue. Isometric duration generally ranged from 3 to 5 seconds [24] with level 3 difficulty. The wheelchair should be stabilized without wobbling or unexpected movements. The posture must be straight, with the tested hands placed on a table, the shoulder of the tested side abducted to 30°, the elbow flexed to 90°, and the forearm in a half-supinated position. The JAMAR hand dynamometer is reliable (Spearman correlation=0.82) and valid (r=0.75) [25].
The participant retention rate was assessed by tracking the number of participants lost to follow-up during the supervised and unsupervised periods. Exercise adherence was assessed using an exercise logbook or a diary. Adherence was calculated on the basis of the percentage of a maximum of 80 sessions (five times per week for 16 weeks). When the participants in the intervention and control groups missed any sessions during the program, they were given 4 weeks to complete the makeup sessions. The adherence rates, including those during the makeup sessions, were presented as percentages. The outcome evaluation flowchart is shown in Fig. 1.
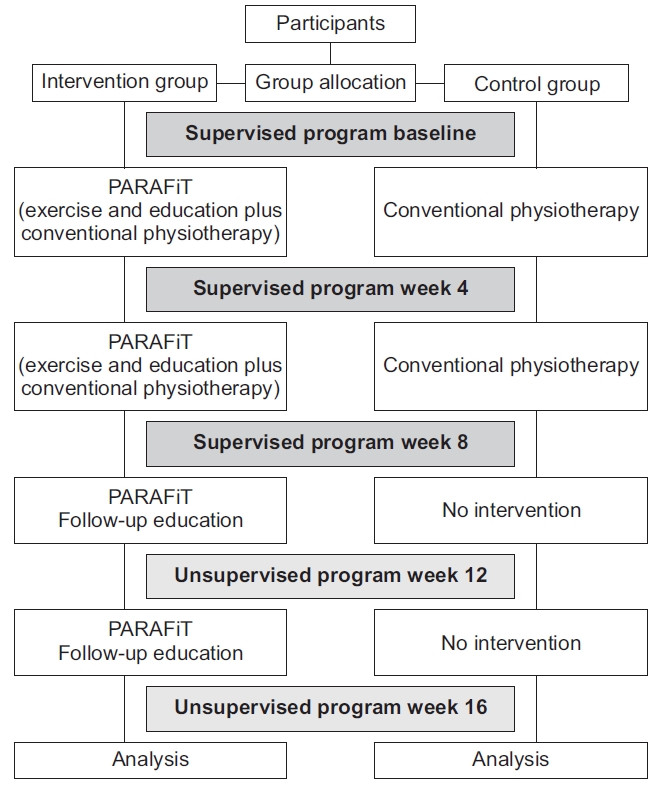
The participants were assigned to either the intervention group or the active control group. The intervention group underwent the PARAFiT program, which consisted of integrated circuit-based interval training, progressive strengthening exercise, and a health educational program as well as conventional physiotherapy. Meanwhile, the control group received conventional physiotherapy (non-structured and non-progressive exercise only). The intervention flowchart is shown in Fig. 2.
The circuit-based interval training (aerobic exercise) was modified from a previous study [15] to meet the recommendation from a recent position statement [14], which suggested that participants should perform at least 20 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise (Borg scale 12–15) for 3 days alternately in a week. The circuit training started at moderate intensity (Borg scale 12–14) and progressed at a higher intensity (Borg scale 14–18) according to the progression criteria. The participants progressed to the next level when they could complete the exercise minutes and complete the exertion goal at the current performance level without overbearing fatigue (i.e., reported fatigue that interferes with their regular therapy and daily activities) or pain. The circuit consisted of wheelchair propelling exercise (30-m loop), punching bag boxing, and arm ergometry hand-cycling (MOTOmed viva2 light; RECK-Technik GmbH & Co. KG, Betzenweiler, Germany). Two rounds of three different exercises were performed at each level (six cumulative exercises). The participants were required to perform 2 minutes of hand-cycling without resistance to warm-up and cooling down.
The progressive resistance strength training followed the recommendation from a recent position statement [14], which suggested that individuals with SCI should perform at least four to five types of strengthening exercises targeting the major muscles, such as the shoulder stabilizers and internal and external rotators for three sets at 8–12 repetitions, with 1–2 minutes rest between sets for at least 2 days a week. The training was in a circuit, utilizing a closed-chain multi-gym for vertical chest press and butterfly press, vertical row, wide latissimus pull-down, and internal and external rotations. The dumbbell exercises focused on triceps push, biceps curl, shoulder flexion, and abduction. The intensity was between moderate and high, starting from 50% of one repetition maximum [26,27]. A full repetition is defined as a 6-second movement pattern, with approximately 3-second concentric and 3-seccentric contraction phases [28]. The intensity progressed weekly when the participants could complete the sets without any signs of tremor or compensatory movements.
The educational topics were as follows : (1) type of physical activity and exercise the participants can perform, (2) benefits of physical activity and exercise, (3) strategy to overcome exercise barriers, (4) action planning and goal setting formulation, and (5) risk and safety of physical activity and exercise. The educational material was developed following the Appraisal of Guidelines Research and Evaluation [29]. The educational sessions were conducted by the main researcher and supervised by a resident clinical psychologist during the supervised program. During the unsupervised program, 1-hour telephone motivational counseling was conducted with the participant proposing the topics of conversation related to health conditions, physical activity, or exercise. The coach was also advised on home and environment optimization for overcoming barriers in performing physical activities. A video call via WhatsApp was held when necessary, including for exercise demonstration or home and environment optimization.
The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee, Universiti Teknologi MARA (REC/138/18). Prior to the study, written informed consent was obtained from all the participants.
The effect size was determined from a previous study on the level of physical activity [30]. A total of 34 subjects were required to detect the differences in the changes, with an effect size of 0.26, a power of 0.95, and an alpha of 0.05. This study aimed to include 44 subjects to allow for a 30% dropout. The primary outcome was the PASIPD score, while the secondary outcomes were the ESES score, 6-MPT result, shoulder isokinetic strength (N·m), handgrip strength (kg), and exercise adherence. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to investigate the normality of the related variables. Repeated-measures two-way analysis of variance was used to determine the effects within and between the groups. All measurements were presented with their effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals at baseline and at the 4th week, 8th week, 12th week, and 16th week. SPSS (version 21.0; IBM SPSS, Armonk, NY, USA) was used for all data analyses.
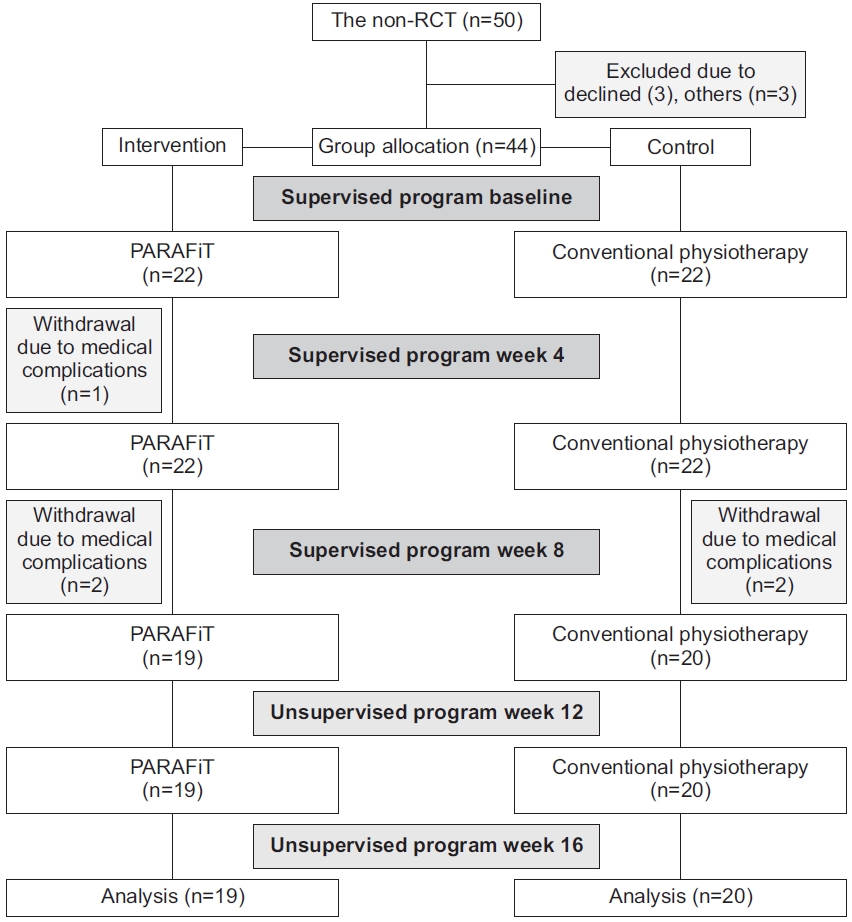
A total of 44 participants were enrolled in the study. However, three participants in the intervention group withdrew owing to medical complications (n=1) and unknown reasons (n=2). Dropouts in the control group were attributed to medical complications (n=2). An intention-to-treat analysis was performed to deal with the missing data owing to dropout using the last observation carried forward technique. This technique includes data for the last known state of the subject in the analysis by assuming that it is a valid information on the subject’s true outcome [31]. The mean participant age did not significantly differ (p=0.451) between the intervention (32.8±9.3 years) and control (36.2±7.9 years) groups. No significant differences were noted in weight (p=0.707) between the intervention (67±17.1 kg) and control (66.4±15.7 kg) groups. Table 1 shows the demographic characteristics of the participants. Fig. 3 shows the participant recruitment flowchart.
No significant difference (p<0.05) was observed in the level of physical activity over time between the groups (F(1, 42) =0.872, p=0.356). The mean level in the intervention group significantly increased from baseline to the 8th week (p=0.004). However, the mean level did not significantly decrease at the 12th week (p=1.000) and 16th week (p=0.384). Meanwhile, the mean level in the control group did not significantly increase from baseline to the 8th week (p=0.177). The mean level did not significantly decrease at the 12th week (p=0.704) and 16th week (p=0.449). Table 2 shows the levels of physical activity.
Significant differences (p<0.05) were noted in exercise self-efficacy over time between the groups (F(1, 42)=13.010, p=0.001). The mean level in the intervention group significantly increased from baseline to the 8th week (p=0.001). However, the mean level did not significantly decrease at the 12th week (p=1.000) and 16th week (p=0.384). Meanwhile, the mean level in the control group significantly increased from baseline to the 8th week (p=0.001). However, the mean level significantly decreased at the 12th week (p=1.000) but not at the 16th week (p=0.102). Table 2 shows the levels of exercise self-efficacy.
A significant difference was observed in the group time interaction effects on cardiorespiratory fitness at baseline and at the 4th week and 8th week (F(2, 41)=6.773, p=0.013). The mean difference in the intervention group significantly increased at the 4th week (p=0.001) and 8th week (p=0.001). The mean difference in the control group significantly increased at the 8th week (p=0.004). Table 3 shows the results of the cardiorespiratory fitness tests.
There were significant differences observed in the isokinetic muscle strength of the right and left shoulder external and internal rotators, abductors and adductors, flexors, and extensors between the intervention group and control group at baseline and at the 4th week and 8th week (p<0.001). Table 4 shows the values of shoulder isokinetic strength.
A significant difference was noted in the group time interaction effects on the right handgrip strength at baseline and at the 4th week and 8th week (F(1, 42)=19.99, p=0.001). A significant difference was also observed in the group time interaction effects on the left handgrip strength at baseline and at the 4th week and 8th week (F(1, 42)=4.591, p=0.038). The handgrip on the right and left sides in the intervention group was significantly stronger than that in the control group.
This study aimed to examine the effects of exercise integrated with education on the level of physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, physical fitness, and exercise adherence compared with those of conventional physiotherapy. The addition of an educational intervention with an exercise program consisting of circuit-based interval training and progressive strengthening exercise was successful in maintaining or slowing down the decline in the level of physical activity during unsupervised periods from any exercise program or after discharge from a rehabilitation program. The maximum possible score for the level of physical activity based on the MET was 199.5 MET-hr/day [32,33]. However, the majority of the individuals with SCI only scored 22.74 MET-hr/day [18]. The intervention group scored 35.52 MET-hr/day, which is above the usual MET value obtained among most individuals with SCI. This study showed that applying a health educational program that consists of various topics likely helps individuals obtain knowledge, awareness, confidence, and efficacy to overcome the barriers in performing physical activity.
The intervention group showed significant ESES score changes compared with the control group. The normal ESES score has been reported to be 28.3 [20]. However, the average ESES score in this study (32.46) was slightly above the normal value. Although the ESES score abruptly decreased after discharge from the rehabilitation program, it remained significant in the intervention group compared with that in the control group. Exercise self-efficacy was found to have a direct relationship with behavior. If individuals believe they have exercise self-efficacy, they will reveal the capability, tolerance, and accomplishment of behaviors. If exercise self-efficacy increases, it may increase exercise behaviors to perform physical activity. Additionally, the vicarious experience of seeing others remain active, including engagement in exercise or physical activity, may enhance individuals’ belief that they have the capability to perform the behavior [31]. The consistent feedback on individual performance given by therapists during education and training sessions may also enhance the ESE score. Hence, the PARAFiT approach may help individuals become aware of how to deal with the exercise barriers they experience.
The health outcomes examined were cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle strength. The PARAFiT program may significantly enhance functional cardiorespiratory fitness, indicating high exercise tolerance and endurance for wheelchair mobility to participate in daily life activities, such as sports, recreation, social activities, and work. The threshold 6-MPT value among individuals with SCI has been reported to be 604 m [34]. In another study, the threshold value was 280 m in an Indian population [35]. However, our study noted only a threshold value of 242 m. Although the average performance was below the normal value, the PARAFiT program enhanced the functional speed of the wheelchair; the average speed was 374.29 m compared with only 360 m in a previous study [36]. The threshold value may vary, as previously reported. This result may be attributed to the wheelchair weight, tire type, propelling technique, and shoulder strength. Mobility was found to be one of the life priorities of patients with paraplegia.
We also noted a significant difference in the shoulder isokinetic strength of the right and left external rotators, internal rotators, abductors, adductors, flexors, and extensors between the groups. The normal value for shoulder strength was 40.58 N·m [37]. However, we observed a slightly high strength value of 45.62 N·m. The value was significant in the intervention group compared with that in the control group. Strong individuals may exert a high force on the push rim to increase the push time, decrease cadence, and increase the push angle during propulsion and arm extension during hand release [37]. Although upper limb strength training does not necessarily indicate enhancement in wheelchair propelling [37], strength training was confirmed to improve cardiorespiratory fitness. This result may be associated with the high involvement of individuals with SCI in social life, sports, recreation, and employment. Moreover, strength training is important to preserve shoulder function from subacromial impingement caused by repetitive use of the shoulder to propel the wheelchair. This result may be important in achieving long-term benefits for individuals with SCI to prevent shoulder pain or subacromial impingement. After discharge from rehabilitation, the participants may continue the strengthening exercise without supervision by utilizing any weight that is not substantially heavy or light, as mentioned in the PARAFiT toolkit. We also observed significant improvements in the handgrip strength in the intervention group compared with those in the control group, in relation to the components of the Functional Independence Measure, which is important for activities of daily living and physical activity [24].
Exercise adherence may have been positively influenced by the nature of the exercise program. Exercise programs with frequent supervision and appointment with therapists, instructors, or coaches tend to higher adherence have rates than do unsupervised exercise programs. This indicates that individuals with SCI require an extensive exercise program with frequent supervision or meetings to keep active and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
A limitation of this study is the evaluation of physical fitness, which was almost impossible after the participants were discharged from the in-patient rehabilitation (supervised) program (12th week and 16th week). This is unlike the evaluation using the ESES and PASIPD, which can be self-administered during the supervised and unsupervised periods (baseline, 4th week, 8th week, 12th week, and 16th week). Additionally, the participants were unable to return to the center for physical fitness assessment after they returned home.
In conclusion, the PARAFiT program enhanced the level of physical activity, exercise self-efficacy, physical fitness, and exercise adherence among the individuals with SCI. However, the level of physical activity and exercise self-efficacy may decline during the unsupervised period after discharge from the rehabilitation program. Therefore, future studies should incorporate guidelines for home-based exercises and regular monitoring to promote long-term adherence to exercise and physical activity among individuals with SCI.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Hisham H. Methodology: Hisham H, Manaf H. Formal analysis: Hisham H, Manaf H. Funding acquisition: None. Project administration: Hisham H, Justine M, Hasnan N, Manaf H. Visualization: Hisham H. Writing – review and editing: Hisham H, Justine M, Manaf H. Approval of the final manuscript: All authors.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Universiti Teknologi MARA for funding the research project through Geran Penyelidikan Khas (No. 600-RMC/GPK 5/3 [134/202]).
Table 1.
Demographic data of the intervention and control groups
Table 2.
Level of physical activity (PASIPD) and exercise self-efficacy (ESES)
| Variable | Group |
Week |
p-value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 8th | 12th | 16th | Within-group effect | Between-group effect | |||
| PASIPD | Intervention | 23.45±15.18 | 41.20±22.64 | 38.83±11.65 | 28.49±18.76 | 0.001* | 0.356 | |
| p-value | - | 0.004 | 1.000 | 0.348 | ||||
| Control | 22.28±14.42 | 36.75±22.93 | 32.60±21.73 | 26.43±16.13 | ||||
| p-value | - | 0.177 | 0.704 | 0.449 | ||||
| ESES | Intervention | 27.23±4.33 | 35.00±3.63 | 35.41±3.08 | 33.00±3.72 | 0.001* | 0.001* | |
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.384 | ||||
| Control | 27.14±4.51 | 31.82±3.71 | 29.91±4.07 | 28.55±4.47 | ||||
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.102 | ||||
Table 3.
Cardiorespiratory fitness (6-minute push test)
| Variable | Group |
Week |
p-value |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 4th | 8th | Within-group effect | Between-group effect | |||
| Cardiorespiratory fitness | Intervention | 246.50±64.74 | 327.09±74.46 | 374.29±59.10 | 0.001* | 0.024* | |
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||||
| Control | 242.07±71.92 | 270.72±61.94 | 295.09±54.71 | ||||
| p-value | - | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||||
Table 4.
Shoulder isokinetic muscle strength
| Muscle |
Intervention group |
Control group |
p-value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 4th week | 8th week | Baseline | 4th week | 8th week | Within-group effect | Between-group effect | |
| Right external rotation | 27.90±4.01 | 42.96±10.56 | 55.35±9.67 | 27.80±7.28 | 29.30±10.78 | 30.78±11.49 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.479 | 0.000 | - | 0.941 | 0.549 | ||
| Right internal rotation | 30.09±9.72 | 41.64±10.30 | 53.00±9.28 | 28.45±7.26 | 29.96±10.80 | 31.96±10.39 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 0.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.845 | ||
| Left external rotation | 22.40±4.10 | 41.90±8.58 | 54.38±7.89 | 25.07±4.64 | 27.30±9.01 | 31.96±10.39 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Left internal rotation | 29.37±5.54 | 36.13±9.00 | 32.91±9.47 | 28.88±8.55 | 29.12±9.06 | 31.51±11.56 | 0.001* | 0.04* |
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 0.175 | - | 0.349 | 1.000 | ||
| Right abduction | 35.92±11.40 | 53.46±13.46 | 68.13±17.91 | 35.52±11.59 | 37.73±17.04 | 44.59±12.99 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.479 | 0.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.26 | ||
| Right adduction | 33.49±15.57 | 48.66±13.10 | 57.67±12.88 | 30.70±5.44 | 30.23±8.74 | 33.28±15.57 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.496 | ||
| Left abduction | 32.05±11.40 | 45.00±13.11 | 52.00±17.91 | 32.72±11.59 | 33.52±13.18 | 36.19±12.99 | 0.001* | 0.049* |
| p-value | - | 0.001 | 1.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.873 | ||
| Left adduction | 32.13±20.44 | 50.00±22.22 | 51.29±17.94 | 32.05±11.40 | 45.00±13.11 | 52.00±17.91 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.004 | 1.000 | - | 1.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Right extensor | 30.07±7.19 | 36.92±7.79 | 49.23±9.45 | 30.41±6.53 | 32.06±7.26 | 32.97±8.83 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
| Right flexor | 31.78±10.19 | 57.81±9.62 | 67.55±11.28 | 29.37±7.92 | 47.55±7.28 | 53.42±7.86 | 0.001* | 0.001* |
| p-value | - | 0.000 | 0.050 | - | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
REFERENCES
1. Nooijen CF, de Groot S, Postma K, Bergen MP, Stam HJ, Bussmann JB, et al. A more active lifestyle in persons with a recent spinal cord injury benefits physical fitness and health. Spinal Cord 2012;50:320-3.


2. Ysasi NA, Kerwin S, Marini I, McDaniels B, Antol DL. A comprehensive literature review of secondary complications of spinal cord injury. J Life Care Plan 2016;14:25-58.
3. Shojaei MH, Alavinia SM, Craven BC. Management of obesity after spinal cord injury: a systematic review. J Spinal Cord Med 2017;40:783-94.



4. Stevens SL, Caputo JL, Fuller DK, Morgan DW. Physical activity and quality of life in adults with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 2008;31:373-8.



5. Hetz SP, Latimer AE, Ginis KA. Activities of daily living performed by individuals with SCI: relationships with physical fitness and leisure time physical activity. Spinal Cord 2009;47:550-4.


6. Maher JL, McMillan DW, Nash MS. Exercise and health-related risks of physical deconditioning after spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil 2017;23:175-87.



7. Nooijen CF, Post MW, Spooren AL, Valent LJ, Broek-steeg R, Sluis TA, et al. Exercise self-efficacy and the relation with physical behavior and physical capacity in wheelchair-dependent persons with subacute spinal cord injury. J Neuroeng Rehabil 2015;12:103.



8. Vissers M, van den Berg-Emons R, Sluis T, Bergen M, Stam H, Bussmann H. Barriers to and facilitators of everyday physical activity in persons with a spinal cord injury after discharge from the rehabilitation centre. J Rehabil Med 2008;40:461-7.


9. Scelza WM, Kalpakjian CZ, Zemper ED, Tate DG. Perceived barriers to exercise in people with spinal cord injury. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2005;84:576-83.


10. Mat Rosly M, Halaki M, Hasnan N, Mat Rosly H, Davis GM, Husain R. Leisure time physical activity participation in individuals with spinal cord injury in Malaysia: barriers to exercise. Spinal Cord 2018;56:806-18.


11. Nooijen CF, Stam HJ, Bergen MP, Bongers-Janssen HM, Valent L, van Langeveld S, et al. A behavioural intervention increases physical activity in people with subacute spinal cord injury: a randomised trial. J Physiother 2016;62:35-41.


12. Hicks AL, Martin Ginis KA, Pelletier CA, Ditor DS, Foulon B, Wolfe DL. The effects of exercise training on physical capacity, strength, body composition and functional performance among adults with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Spinal Cord 2011;49:1103-27.


13. van der Scheer JW, Martin Ginis KA, Ditor DS, GooseyTolfrey VL, Hicks AL, West CR, et al. Effects of exercise on fitness and health of adults with spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Neurology 2017;89:736-45.


14. Tweedy SM, Beckman EM, Geraghty TJ, Theisen D, Perret C, Harvey LA, et al. Exercise and sports science Australia (ESSA) position statement on exercise and spinal cord injury. J Sci Med Sport 2017;20:108-15.


15. Tawashy AE, Eng JJ, Krassioukov AV, Miller WC, Sproule S. Aerobic exercise during early rehabilitation for cervical spinal cord injury. Phys Ther 2010;90:427-37.


16. McMillan DW, Maher JL, Jacobs KA, Nash MS, Bilzon JL. Physiological responses to moderate intensity continuous and high-intensity interval exercise in persons with paraplegia. Spinal Cord 2021;59:26-33.


17. Martin Ginis KA, van der Scheer JW, Latimer-Cheung AE, Barrow A, Bourne C, Carruthers P, et al. Evidence-based scientific exercise guidelines for adults with spinal cord injury: an update and a new guideline. Spinal Cord 2018;56:308-21.


18. Washburn RA, Zhu W, McAuley E, Frogley M, Figoni SF. The physical activity scale for individuals with physical disabilities: development and evaluation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2002;83:193-200.


19. van der Ploeg HP, Streppel KR, van der Beek AJ, van der Woude LH, Vollenbroek-Hutten M, van Mechelen W. The Physical Activity Scale for Individuals with Physical Disabilities: test-retest reliability and comparison with an accelerometer. J Phys Act Health 2007;4:96-100.


20. Kroll T, Kehn M, Ho PS, Groah S. The SCI Exercise Self-Efficacy Scale (ESES): development and psychometric properties. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2007;4:34.



21. Cowan RE, Callahan MK, Nash MS. The 6-min push test is reliable and predicts low fitness in spinal cord injury. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012;44:1993-2000.


22. Collado-Mateo D, Dominguez-Munoz FJ, Batalha N, Parraca J, Tomas-Carus P, Adsuar JC. Test-retest reliability of isokinetic arm strength measurements in competitive swimmers. J Hum Kinet 2018;65:5-11.



23. Drouin JM, Valovich-mcLeod TC, Shultz SJ, Gansneder BM, Perrin DH. Reliability and validity of the Biodex system 3 pro isokinetic dynamometer velocity, torque and position measurements. Eur J Appl Physiol 2004;91:22-9.


24. Sisto SA, Dyson-Hudson T. Dynamometry testing in spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev 2007;44:123-36.


25. Mathiowetz V. Comparison of Rolyan and Jamar dynamometers for measuring grip strength. Occup Ther Int 2002;9:201-9.


26. Pelletier CA, Totosy de Zepetnek JO, MacDonald MJ, Hicks AL. A 16-week randomized controlled trial evaluating the physical activity guidelines for adults with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2015;53:363-7.


27. Totosy de Zepetnek JO, Pelletier CA, Hicks AL, Mac Donald MJ. Following the physical activity guidelines for adults with spinal cord injury for 16 weeks does not improve vascular health: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2015;96:1566-75.


28. Nash MS, van de Ven I, van Elk N, Johnson BM. Effects of circuit resistance training on fitness attributes and upper-extremity pain in middle-aged men with paraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2007;88:70-5.


29. Brouwers MC, Kho ME, Browman GP, Burgers JS, Cluzeau F, Feder G, et al. AGREE II: advancing guideline development, reporting and evaluation in health care. CMAJ 2010;182:E839-42.



30. Bakkum AJ, de Groot S, Stolwijk-Swuste JM, van Kuppevelt DJ; ALLRISC; van der Woude LH, et al. Effects of hybrid cycling versus handcycling on wheelchair-specific fitness and physical activity in people with long-term spinal cord injury: a 16-week randomized controlled trial. Spinal Cord 2015;53:395-401.


31. Ashford S, Edmunds J, French DP. What is the best way to change self-efficacy to promote lifestyle and recreational physical activity? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Health Psychol 2010;15(Pt 2): 265-88.


32. Mat Rosly M, Halaki M, Mat Rosly H, Davis GM, Hasnan N, Husain R. Malaysian adaptation of the physical activity scale for individuals with physical disabilities in individuals with spinal cord injury. Disabil Rehabil 2020;42:2067-75.


33. de Groot S, van der Woude LH, Niezen A, Smit CA, Post MW. Evaluation of the physical activity scale for individuals with physical disabilities in people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2010;48:542-7.


34. Baattaiah BA, Murray D, Cowan R, Groah SL, Liungberg IH, Rounds AK, et al. Association of six minute push test distance and measures of cardiorespiratory fitness in spinal cord injury. Med Sci Sport Exerc 2017;49(5S): 409.

35. Solanki R, Chaudhari P, Bhise A. Cardio respiratory fitness testing in spinal cord injury patients using 6 minute push test. Healthline J 2016;7:60-3.
- TOOLS