- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 43(2); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To develop a new tool for aspiration risk prediction based on pharyngeal width at rest in older adults with symptoms of aspiration.
Methods
Lateral cervical spine roentgenograms were obtained from 33 older adult patients who complained of dysphagia and from 33 healthy, age-matched controls. Pharyngeal width at rest was measured at two points. We named the average of these two pharyngeal widths ‘JOSCYL Width’, calculated ‘JOSCYL Scale’, and compared these parameters between dysphagia and control groups. Correlations of individual JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale, with Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) and Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale (DOSS) scores were analyzed for the dysphagia group. To determine optimal cutoff points for predicting aspiration, a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed on JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale.
Results
Both JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale of the dysphagia group were larger than those of the control group (p<0.001). The correlation between JOSCYL Width and severity of dysphagia was significant for the dysphagia group (PAS p=0.007; DOSS p=0.012). The correlation between JOSCYL Scale and the severity of dysphagia was also significant for the dysphagia group (PAS p=0.009; DOSS p=0.011). Optimal cutoffs for JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale for predicting aspiration were 20.0 mm and 5.9, respectively.
Dysphagia is a common consequence of aging. Its prevalence has been reported to be approximately 15% [1]. Silent aspiration occurs more frequently in elderly people than that in younger people. It is a leading cause of death in older adults [2]. Although stroke, degenerative brain disease, and neuromuscular disease are frequent causes of dysphagia in older people, those without neurological diseases may also develop dysphagia because of a delayed oropharyngeal transit time, dysfunction of hyolaryngeal excursion, and decreased peristaltic contraction velocity and amplitude [3-5].
The human pharynx comprises tube-like muscular walls composed of smooth muscle tissue. The smooth muscle of the pharynx maintains steady and partial contraction for breathing at rest. To swallow successfully, the smooth muscle of the pharynx is activated through glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves such that it constricts sufficiently to drive a bolus downward into the esophagus [6,7]. However, in elderly people, age-related changes cause the pharynx to lack the strength to constrict sufficiently. Aging-related changes in soft tissue include atrophy, edema, decreased elasticity, and demyelination [8]. Additionally, in the pharynx, atrophy of muscles can result in increase of pharyngeal lumen while reduction of connective tissue elasticity can result in weakness of constriction, both of which have been described as possible causes of pharyngeal dysphagia in older adults [9,10].
Aspiration in elderly people can cause pneumonia and poor oral intake, leading to increased mortality [11]. Therefore, precise and easy assessment of dysphagia is essential for elderly people with dysphagia. Bedside water swallowing test is commonly administered for stroke patients before oral feeding. However, many bedside dysphagia screening tests are weak in terms of sensitivity and reliability [12,13]. A videofluoroscopic swallow study (VFSS) is the most reliable method for confirming the presence and degree of a swallowing disorder. It has been proposed as the standard test for evaluating swallowing disorders [14]. However, it is difficult to administer VFSS to elderly people who exhibit difficulty in cooperating or maintaining a sitting position during the examination. Moreover, VFSS carries a risk of aspiration during the examination and exposes both the patient and physician to radiation. As the bedside swallowing test has limited sensitivity and reliability, and the VFSS has limited indications, new dysphagia testing tools are needed to compensate for these weaknesses of these existing tools. The new testing tool should be sufficiently sensitive to predict aspiration. It also should be able to easily assess the severity of dysphagia.
The hypothesis in this study was that older adults with dysphagia symptoms would exhibit decreased muscle strength and muscle tone. This would affect their pharyngeal muscle, causing the pharyngeal tube to remain wider than a normal pharynx at rest, which could facilitate the onset of aspiration. The purpose of this study was to measure two-dimensional width of the pharyngeal tube and determine whether the measurement could be useful as an index to determine the risk of aspiration in older adults. Development of an easy and simple indicator to predict aspiration would be valuable for preventing pneumonia in older adults, enabling them to be treated early.
A total of 33 elderly people (age 78.9±7.1 years; 17 women and 16 men) with dysphagia were included in the dysphagia group (Table 1). The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) 65 years of age or older; (2) complaints of dysphagia symptoms such as swallowing difficulty; and (3) the ability to sit for a sufficient period of time to complete the VFSS (3–5 minutes). The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) a history of brain disease; (2) a history of head, neck, or cervical spine surgery; (3) tracheostomy; (4) sacral sore limiting the ability to maintain a sitting position; (5) dysphagia in the oral or esophageal phase confirmed on VFSS (to exclude non-pharyngeal dysphagia patients); and (6) post-swallowing aspiration because of residue on the vallecular sinus or piriformis sinus on VFSS. The control group had a total of 33 volunteers (age 77.6±8.9 years; 21 women and 12 men) without aspiration symptoms while eating who had not been diagnosed with pneumonia in the prior year. All control group participants met the same inclusion and exclusion criteria as participants in the dysphagia group except that this control group did not undergo the VFSS. Age, sex, height, weight, neck circumference, body mass index (BMI), and grasp power of the dominant hand were investigated for all participants. The dominant hand was determined using the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory [15]. All aspects of this study, including enrollment, clinical assessment, VFSS protocol, and statistical analysis, were approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital (No. 2017-I040), and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. This clinical trial was registered on the Clinical Research Information Service (CRIS), a primary registry of the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (CRIS Registration No. KCT0002352).
Lateral neck roentgenograms were acquired for both dysphagia and control groups (Fig. 1). To prevent different measurements of pharyngeal width by neck flexionextension angle, one physician ensured that the participant’s head was held steady so that the participant was looking straight ahead for the lateral neck roentgenogram. The participant’s neck was rotated and bilateral mandible lines were aligned to the fluoroscope. Each participant held their breath for a few seconds without swallowing saliva to prevent pharyngeal motion. Perpendicular lines A and B from the posterior pharyngeal wall were located at positions corresponding to the middle level of the second (C2) and third (C3) cervical vertebral bodies (Fig. 2). The perpendicular line A was positioned around the lower margin of the mandible while the perpendicular line B was positioned around the epiglottis. We measured lengths (in mm) of lines A and B on the screen directly connected with the fluoroscopy device using a default measurement program. We named the average of two pharyngeal widths ([A+B]/2) JOSCYL Width. JOSCYL is a combination of the first letters of the authors’ surnames. We then measured neck circumference and calculated JOSCYL Scale, because neck size might affect the pharyngeal width.
Next, a VFSS was performed only for the dysphagia group. To stabilize their anatomical position, participants initially sat laterally and were observed for 4–5 seconds. Three types of diets with different viscosities (25 mm, 55 mm, and 10 mm by line-spread test for semisolid, water, and solid, respectively) were tested [16]. Radiopaque material (barium sulfate, 960 mg/g; Taejoon Pharm Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea) was administered with incremental increases in bolus volume and texture, as tolerated [12,17]. For the semisolid test, barium was mixed with yogurt to yield 40% w/v, and two tests using 2 mL and 5 mL were conducted. For the water test, barium was diluted with water to yield 20% w/v, and three tests using 2 mL, 5 mL, and 15 mL were conducted [18,19]. Notably, in the third step of the water test, participants were allowed to drink water from a cup by themselves. For the solid test, a liquid thickener (Blue Bio-S, Gwangju, Korea) was mixed with water at a 1:1 ratio and formed into a ball with a diameter of approximately 13 mm, which was used to perform the test once [20]. The solid test was not performed if a participant was unable to eat a solid diet because of dental problems. Three physicians who did not know the patients’ JOSCYL Width determined the Penetration Aspiration Scale (PAS) and Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale (DOSS) scores by watching videos recorded during VFSS [21,22].
Independent t-test and chi-square test were used to investigate differences in demographic characteristics between the two groups. The JOSCYL Width, and the JOSCYL Scale of the two groups were compared using independent t-test. For the dysphagia group, correlations of JOSCYL Width with severity of dysphagia (PAS and DOSS), BMI, and grasp power were examined using Spearman correlation analysis. Correlations of JOSCYL Scale with severity of dysphagia (PAS and DOSS), BMI, and grasp power were also examined using Spearman correlation analysis.
To determine optimal cutoff points for predicting aspiration, a receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed for JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale. The statistical package used for data processing was SPSS version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Statistical significance was defined at p-value <0.05 and confidence interval (CI) >95%.
Mean age, height, weight, neck circumference, and BMI of the two groups were similar to each other (Table 1). Regarding sex of participants, males accounted for a greater portion in the dysphagia group (48.5%) than that in the control group (36.4%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.319). However, there was a significant difference in grasp power between the two groups (p<0.001). Correlation between JOSCYL Width and BMI or between JOSCYL Width and grasp power was not significant. Correlation between JOSCYL Scale and BMI or between JOSCYL Scale and grasp power was not significant either.
JOSCYL Width of the dysphagia group (19.3±5.0 mm) was larger than that of the control group (15.0±3.4 mm) by independent t-test (p<0.001) (Table 2). Both pharyngeal widths A and B of the dysphagia group were larger than those of the control group by independent t-test (p<0.001). JOSCYL Scale of the dysphagia group (5.7±1.4) was larger than that of the control group (4.4±1.0) by independent t-test (p<0.001). The JOSCYL Width of the dysphagia group showed significant correlations with both PAS score (r=0.461, p=0.007) and DOSS score (r=-0.430, p=0.012). The JOSCYL Scale of the dysphagia group also showed significant correlations with both PAS score (r=0.434, p=0.009) and DOSS score (r=-0.438, p=0.011).
The optimal cutoff of the JOSCYL Width for predicting aspiration was 20.0 mm (area under the curve [AUC]=0.76; 95% CI, 0.596–0.934; sensitivity=62.5%; specificity=64.0%) in the dysphagia group (Fig. 3A). The optimal cutoff of the JOSCYL Scale for predicting aspiration was 5.9 (AUC=0.76; 95% CI, 0.584–0.926; sensitivity=62.5%; specificity=64.0%) in the dysphagia group (Fig. 3B).
This study investigated JOSCYL Width (pharyngeal width at rest on lateral neck roentgenogram) and JOSCYL Scale (JOSCYL Width divided by neck circumference) in healthy and dysphagic elderly people. Results of this study support the hypothesis that swallowing musculature is prone to sarcopenic changes associated with individual aging [23]. Previous studies have shown that elderly people with sarcopenia demonstrate decreased tongue pressure and dysphagia [23-25]. Elderly people with atrophy of the geniohyoid muscle diagnosed by computed tomography and ultrasonography are known to have swallowing difficulty resulting from decreased strength of the swallowing muscle [24,25].
Considering aging-related changes in oropharyngeal muscles and the prevalence of aspiration in elderly people, a simple and precise tool to measure the condition of pharyngeal muscles is needed to screen for aspiration risk. VFSS is the method that is most commonly used to perform detailed investigations of dysphagia; however, it cannot be performed in certain cases, as it requires special equipment and techniques, as well as the cooperation of the people being tested. Previous studies have used simple lateral neck roentgenograms to evaluate dysphagia [26,27]. Kendall and Leonard [26] have observed that dysphagic patients have larger pharyngeal area at maximal contraction, suggestive of poor pharyngeal contraction and pharyngeal weakness which can result in increased aspiration. Stokely et al. [27] have found that the pharyngeal area at maximal contraction is correlated with post-swallowing residue in valleculae and pyriform sinuses. This indicates poor pharyngeal contraction, resulting in increased pharyngeal residue. In fact, it has been shown that residue in valleculae and pyriform sinuses due to pharyngeal muscle weakness can increase the risk of aspiration [28]. Therefore, wider pharyngeal width at rest might be a risk factor of aspiration, reflecting the weakness or atrophy of pharyngeal muscle that is correlated with aging.
The present study began with two hypotheses. The first hypothesis was that JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale could reflect muscle tone and strength of pharyngeal constrictor muscles at rest. The second hypothesis was that JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale could be new indicators of aspiration risk in elderly people. Regarding the first hypothesis, we noted a definite limitation in that JOSCYL Width was not a direct measurement of the strength of pharyngeal constrictor muscles as it was determined with a manometer. However, it is known that grasp power is correlated with muscle mass and age. In the present study, the grasp power was lower in the dysphagia group. Thus, we suspected that these patients might have a smaller muscle mass than controls which might impact the pharyngeal muscle and keep the pharynx wider [29]. Maeda and Akagi [30] have reported similar findings, showing that sarcopenia is an independent risk factor of dysphagia in hospitalized older people through measuring hand grip strength and skeletal muscle mass to demonstrate sarcopenia. Therefore, in the case of an elderly patient with dysphagia and low grasp power in the dominant hand, the JOSCYL Width might be applicable in screening for aspiration. The JOSCYL Scale was designed to consider individual anatomical variations in the pharynx and neck, because neck size could affect pharyngeal width. However, sensitivities and specificities of JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale were very similar. Therefore, after evaluating a sufficient number of patients, it might be possible to determine whether JOSCYL Width or JOSCYL Scale is more accurate for predicting aspiration.
Regarding the second hypothesis, the cutoff values of the JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale for detecting aspiration were approximately 20.0 mm and 5.9, respectively. For the assessment of dysphagia risk in elderly people, the JOSCYL Width (sensitivity 62.5%, specificity 64.0%) and JOSCYL Scale (sensitivity 62.5%, specificity 64.0%) showed similar sensitivity and specificity to the bedside swallowing assessment (sensitivity 68%, specificity 67%) [12]. However, since bedside swallowing assessment carries a risk of aspiration during the examination, the JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale hold merit in terms of safety with reasonable sensitivity and specificity.
The present study successfully developed a simple and precise tool to predict aspiration. The advantage of the JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale is that they can be applied easily. Compared to studies that evaluated maximal pharyngeal contraction by simple lateral neck roentgenography, the JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale have considerable merit in terms of simplicity [25,26]. Determining JOSCYL Width and JOSCYL Scale requires a few seconds of sitting to acquire two pharyngeal antero-posterior widths at rest. Molfenter et al. [9] have measured the size of the pharyngeal lumen using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and found that pharyngeal muscles appear to atrophy with age, resulting in an increased size of the pharyngeal lumen. We noted that JOSCYL Width could be used to measure pharyngeal width as efficiently as MRI.
The present study is also meaningful in terms of reducing radiation exposure. If the average time for performing VFSS is 171 seconds, the resulting average radiation exposure is 1.4 Gy·cm2 [31]. However, the JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale can reduce the hazard of radiation exposure to both patients and physicians.
This study has some limitations. First, we included only Asian people as participants. Different dietary culture might impact the physiology of the pharyngeal muscle. In the context of food culture of Asian people, rice and vegetables are more common in most Asian cuisines than meats. Therefore, a study with participants from other dietary cultures is needed. Second, we did not completely exclude participants with silent aspiration from the control group because we did not perform VFSS for this group. To exclude participants with dysphagia, we surveyed symptoms of aspiration and history of pneumonia in the prior year before enrollment in the study; therefore, participants with silent aspiration might have been included.
In conclusion, the JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale can be new indicators for predicting aspiration in older adults; moreover, they are precise and easy to use.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Yun Jae Lee, Sun Woo Park, Wan Ho Noh, and Chan Sun Jung of the Department of Radiology, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, for their help in acquiring VFSS measurements.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Ohn SH. Methodology: Cha E, Song J, Jung IH, Jung KI, Yoo WK. Formal analysis: Lee HY. Funding acquisition: none. Writing – original draft: Lee HY. Writing – review and editing: Ohn SH. Approval of final manuscript: all authors.
Fig. 1.
Lateral cervical spine roentgenogram and VFSS. A lateral cervical spine roentgenogram was obtained at the beginning of the VFSS performed using three types of diets with different viscosities. VFSS, video fluoroscopic swallow study.
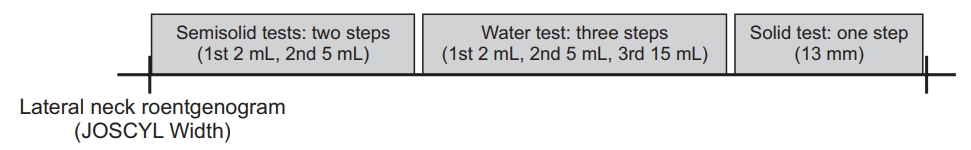
Fig. 2.
The JOSCYL Width. The JOSCYL Width was calculated as an average of two pharyngeal widths, A and B. Lines A and B are for illustrative purposes only and differ from the screen shown on the fluoroscopy device.
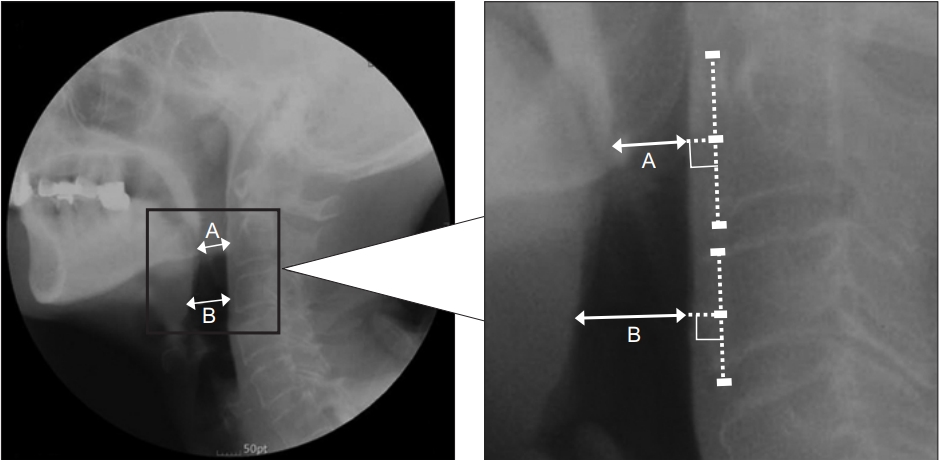
Fig. 3.
Receiver-operating characteristic curves of the JOSCYL Width (A) and the JOSCYL Scale (B) for detecting aspiration (dotted line). The optimal cutoff values of the JOSCYL Width and the JOSCYL Scale for predicting aspiration were 20.0 mm (area under the curve=0.76; 95% CI, 0.596–0.934; sensitivity=62.5%; specificity=64.0%) and 5.9 (area under the curve=0.76; 95% CI, 0.584–0.926; sensitivity=62.5%; specificity=64.0%), respectively, in the dysphagia group.

Table 1.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants
| Dysphagia group (n=33) | Control group (n=33) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 16 | 12 |
| Female | 17 | 21 |
| Age (yr) | 78.9±7.1 | 77.6±8.9 |
| Height (cm) | 159.8±7.3 | 159.3±7.1 |
| Weight (kg) | 55.7±9.6 | 56.8±7.7 |
| Neck circumference (cm) | 33.6±2.3 | 33.7±1.8 |
| BMI | 21.7±3.2 | 22.3±2.6 |
| Grasp power (kg) | 12.3±7.0* | 19.7±8.2 |
| Dysphagia scale | ||
| PAS | 3.5±2.6 | NA |
| DOSS | 4.1±1.6 | NA |
REFERENCES
1. Madhavan A, LaGorio LA, Crary MA, Dahl WJ, Carnaby GD. Prevalence of and risk factors for dysphagia in the community dwelling elderly: a systematic review. J Nutr Health Aging 2016;20:806-15.



2. Kikuchi R, Watabe N, Konno T, Mishina N, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. High incidence of silent aspiration in elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;150:251-3.


3. Buchholz DW. Neurogenic dysphagia: what is the cause when the cause is not obvious? Dysphagia 1994;9:245-55.



4. Robbins J, Hamilton JW, Lof GL, Kempster GB. Oropharyngeal swallowing in normal adults of different ages. Gastroenterology 1992;103:823-9.


5. Tracy JF, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Jacob P, Kobara M, Krugler C. Preliminary observations on the effects of age on oropharyngeal deglutition. Dysphagia 1989;4:90-4.



6. Smithard DG, O’Neill PA, Parks C, Morris J. Complications and outcome after acute stroke. Does dysphagia matter? Stroke 1996;27:1200-4.


7. Martino R, Foley N, Bhogal S, Diamant N, Speechley M, Teasell R. Dysphagia after stroke: incidence, diagnosis, and pulmonary complications. Stroke 2005;36:2756-63.



9. Molfenter SM, Amin MR, Branski RC, Brumm JD, Hagiwara M, Roof SA, et al. Age-related changes in pharyngeal lumen size: a retrospective MRI analysis. Dysphagia 2015;30:321-7.



10. Sura L, Madhavan A, Carnaby G, Crary MA. Dysphagia in the elderly: management and nutritional considerations. Clin Interv Aging 2012;7:287-98.


12. Edmiaston J, Connor LT, Loehr L, Nassief A. Validation of a dysphagia screening tool in acute stroke patients. Am J Crit Care 2010;19:357-64.



13. Leigh JH, Lim JY, Han MK, Bae HJ, Kim WS, Paik NJ. A prospective comparison between bedside swallowing screening test and videofluoroscopic swallowing study in post-stroke dysphagia. Brain Neurorehabil 2016;9(2): e7.

14. Park S, Lee JY, Jung H, Koh SE, Lee IS, Yoo KH, et al. Use of videofluoroscopic swallowing study in patients with aspiration pneumonia. Ann Rehabil Med 2012;36:785-90.



15. Oldfield RC. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 1971;9:97-113.



16. Nicosia MA, Robbins J. The usefulness of the line spread test as a measure of liquid consistency. Dysphagia 2007;22:306-11.



17. Han TR, Paik NJ, Park JW. Quantifying swallowing function after stroke: a functional dysphagia scale based on videofluoroscopic studies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2001;82:677-82.


18. Eisenhuber E, Schima W, Schober E, Pokieser P, Stadler A, Scharitzer M, et al. Videofluoroscopic assessment of patients with dysphagia: pharyngeal retention is a predictive factor for aspiration. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;178:393-8.


19. Jaffer NM, Ng E, Au FW, Steele CM. Fluoroscopic evaluation of oropharyngeal dysphagia: anatomic, technical, and common etiologic factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;204:49-58.



21. Rosenbek JC, Robbins JA, Roecker EB, Coyle JL, Wood JL. A penetration-aspiration scale. Dysphagia 1996;11:93-8.



22. O’Neil KH, Purdy M, Falk J, Gallo L. The dysphagia outcome and severity scale. Dysphagia 1999;14:139-45.


23. Maeda K, Akagi J. Decreased tongue pressure is associated with sarcopenia and sarcopenic dysphagia in the elderly. Dysphagia 2015;30:80-7.


24. Feng X, Todd T, Lintzenich CR, Ding J, Carr JJ, Ge Y, et al. Aging-related geniohyoid muscle atrophy is related to aspiration status in healthy older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2013;68:853-60.




25. Baba T, Goto T, Fujimoto K, Honda T, Yagi K, Nagao K, et al. Age-related changes in geniohyoid muscle morphology predict reduced swallowing function. J Oral Health Biosci 2017;30:18-25.
26. Kendall KA, Leonard RJ. Pharyngeal constriction in elderly dysphagic patients compared with young and elderly nondysphagic controls. Dysphagia 2001;16:272-8.



27. Stokely SL, Peladeau-Pigeon M, Leigh C, Molfenter SM, Steele CM. The relationship between pharyngeal constriction and post-swallow residue. Dysphagia 2015;30:349-56.




28. Mirzakhani H, Williams JN, Mello J, Joseph S, Meyer MJ, Waak K, et al. Muscle weakness predicts pharyngeal dysfunction and symptomatic aspiration in long-term ventilated patients. Anesthesiology 2013;119:389-97.



29. Kallman DA, Plato CC, Tobin JD. The role of muscle loss in the age-related decline of grip strength: crosssectional and longitudinal perspectives. J Gerontol 1990;45:M82-8.



- TOOLS
-
METRICS

- Related articles in ARM
-
Prediction of Laryngeal Aspiration Using Voice Analysis.2003 December;27(6)






