- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 37(5); 2013 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the hemispheric contributions to prosody recognitions and interference effects of semantic processing on prosody for stroke patients by using the Korean language.
Methods
Ten right hemisphere damaged patients (RHD), nine left hemisphere damaged patients (LHD), and eleven healthy controls (HC) participated. In pure prosody recognition task, four semantically neutral sentences were selected and presented in both sad and happy prosodies. In interference task, participants listened to emotionally intoned sentences in which the semantic contents were congruent or incongruent with prosody. Participants were asked to rate the valence of prosody while ignoring the semantic contents, and thus, reaction time and accuracy were estimated.
Results
In pure prosody recognition task, RHD showed low accuracy as compared to HC (p=0.013), and the tendency of group response showed that RHD performed worse than HC and LHD with regards to accuracy and reaction time. In interference task, analysis of accuracy revealed a significant main effect of groups (p=0.04), and the tendency implied that RHD is less accurate as compared to LHD and HC. The RHD took longer reaction times than HC in congruent and incongruent items (p<0.001).
Conclusion
Right hemispheric laterality to prosody processing of Korean language in stroke patients was observed. Interference effects of semantic contents to prosody processing were not observed, which suggested unique characteristics of prosody for Korean language. These results could be referred as preliminary data for future researches on Korean languages.
Heilman et al. [1] showed that the right hemisphere damaged patients (RHD) without aphasia had more decreased comprehension on emotional speech as compared to the left hemisphere damaged patients (LHD), thus, he described it as "auditory affective agnosia".
To perform a successful conversation, the transfer of emotion is important. Most of speaker's emotional delivery is done through tone of speech i.e., prosody (melodic and rhythmic components of speech), and prosody is known to be mainly related with acoustic parameters, such as pitch, stress, and duration (including pauses and prolongations) [2]. The meaning could change when you say the same sentence depending on the tone of speech, thus prosody makes up non-verbal aspects of language that are necessary for recognizing and conveying emotions during communication. Ross [3] said that right hemisphere (RH) is primarily responsible for processing of affective languages and defined "aprosodia" corresponding to aphasia for all kind of affective prosodic deficits after damage on right Broca's homologue.
It has been revealed that RH is mainly related with prosody recognitions. Right lateralized response to prosody was evidenced from dichotic listening [4], event-related brain potentials [5], and imaging modalities [6-8].
Despite the established knowledge on role of the RH in prosody recognition, there are continuous increments in reports that both hemispheres have been advocated to be required in prosody recognition [9-11]. RH is mainly related with analyzing emotional details from prosody, while left hemisphere (LH) takes a role of linguistic and integrative processing accompanied by prosody.
There is a lack of study on prosody with Korean language despite the many researches with prosody in English and aphasia in Korean. Research on prosody with the use of Korean is necessary when considering unique characters of the Korean language.
The aim of this study is to investigate hemispheric contributions to prosody recognitions and interference effects of semantic processing on prosody for stroke patients by using the Korean language.
Total of 19 stroke patients (RHD, n=10; LHD, n=9) and 11 healthy controls (HC) participated in this study. RHD and LHD were recruited from our clinic, whereas HC was recruited from the community with informed consents. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board. The general characteristics of the participants including gender, age, educational level, Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE), and Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression scale (CES-D) are all listed in Table 1. All characteristics were not significantly different across the three groups.
The diagnosis of stroke was based on neurologic examinations and findings of brain computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging studies. An inclusion criterion was the right handed hemiplegic patients being secondary to first onset unilateral stroke whose first language is Korean. Exclusion included: subjects who had difficulties with vision or hearing, evidence of multifocal or bilateral damages, cerebellum or brainstem lesions, uncontrolled medical problems, any psychiatric or neurologic abnormalities before the stroke, K-MMSE<25 points, and habitual drug abuses that interfered with the activities of the brain. Persons who cannot perform simple reaction tasks were also excluded. HC were also evaluated by the examiners to rule possible histories of major neurologic or psychiatric diseases. The nature of language impairment for each participant was evaluated by experienced language pathologists with the Korean version of Western Aphasia Battery assessment.
Stimuli consisted of a total of 40 Korean sentences that were recorded by a trained female Korean speaker in two kinds of prosody: happy and sad. The sentences were established throughout unpublished previous studies according to the consultation of the psychiatrist, where hundreds of healthy Korean volunteers rated emotional valences for 100 sentences on 7-point Likert scale. After sentences with high standard deviations were excluded based on these ratings, sentences with low standard deviations representing semantically positive, negative, and neutral valence were selected.
Participants were asked to judge prosody as either positive or negative while ignoring the meaning of semantic contents. The auditory stimuli were presented directly through headphones in a quiet room. Experimental block order was counterbalanced across subjects. Before the experiment began, the participants received two practice trials. Feedbacks were provided for the correctness and speed of the responses during the practice.
To identify pure prosody recognition, four semantically neutral sentences were selected and they are presented in sad and happy prosodies from the recording program.
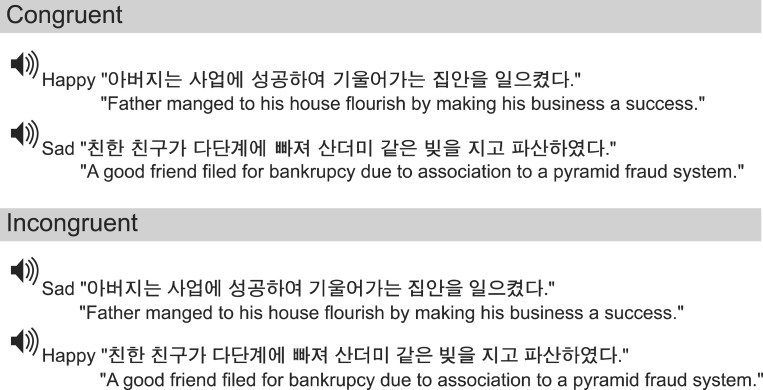
To carry out interference tasks using semantic contents, eight sentences of semantic positive and negative valence were selected respectively. All 16 sentences were presented with happy and sad prosodies, thus, it yielded two kinds of items: incongruent item for which the semantic valence and prosody were in conflict (e.g., semantically negative sentence pronounced with happy prosody or semantically positive sentence pronounced with a sad prosody) and congruent item for which the semantic valence and the prosody were either both positive or negative (Fig. 1).
Participants answered by pressing one of two keyboard buttons as quickly and accurately as possible. Reaction time from the ending of each sentence and percentage of correct responses were estimated. We expected interference effects to be reflected in longer reaction times and lower accuracies for incongruous items as compared to congruous item.
We performed statistical analyses to compare data among groups by using the Kruskal-Wallis test. To assess group differences, a series of post hoc Mann-Whitney U tests were conducted. The p-values less than 0.05 in the Kruskal-Wallis test and less than 0.017 in the Mann-Whitney U test were considered statistically significant. The SPSS ver. 12.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) program was used for the statistical analyses.
The analysis of accuracy for pure prosody recognition revealed a significant main effect of groups (p=0.013). Post hoc analysis revealed that RHD (68.8±25.2%, 95% confidence interval [CI] 50.7 to 86.7) was significantly less accurate as compared to HC (96.5±11.3%, 95% CI 88.9 to 104.1) (p=0.013) (Fig. 2A).
The analysis of the reaction time for pure prosody did not reveal any significant main effect between groups (Fig. 2B). However, it implies that RHD (1.1±0.4 ms; 95% CI 0.8 to 1.3) performed worse than HC (0.8±0.2 ms, 95% CI 0.7 to 0.9) and LHD (0.9 ± 0.4 ms, 95% CI 0.6 to 1.2).
The analysis of accuracy for interference task revealed a significant main effect of groups (p=0.04) (Fig. 3A). Tendency of the group response in congruent items implies that RHD (83.8±15.4%, 95% CI 75.8 to 94.7) is less accurate as compared to LHD (89.6±15.3%, 95% CI 77.8 to 101.4) and HC (91.5±7.0%, 95% CI 86.8 to 96.2). In terms of incongruent items, similar tendency was founded (RHD: 75.6±24.7%, 95% CI 57.9 to 93.3; LHD: 95.1±12.4%, 95% CI 85.6 to 104.7; HC: 94.3±6.5%, 95% CI 89.9 to 98.7) (Fig. 3B).
The analysis of the reaction time for congruent and incongruent items revealed a significant main effect between groups (congruent item, p=0.006; incongruent item, p=0.003). Post hoc analysis revealed that RHD (congruent items: 1.2±0.3 ms, 95% CI 1.0 to 1.4; incongruent items: 1.3±0.7 ms, 95% CI 0.8 to 1.8) took longer reaction times than HC (congruent items: 0.7±0.1 ms, 95% CI 0.6 to 0.8; incongruent items: 0.7±0.1 ms, 95% CI 0.6 to 0.8) for congruent and incongruent items (p<0.001) (Fig. 4).
The present results showed that right hemisphere takes a prominent role in the process of prosody when using Korean language. In order to investigate hemispheric contributions to pure prosody recognitions, semantically neutral sentences were utilized in experiment 1.
Unlike previous studies using other languages such as English and French, the whole process of prosody was consistently impaired in RHD only. The RHD showed significant low accuracy as compared to HC with no differences of reaction time between groups. However, the tendency showed that RHD had the lowest value in accuracy and reaction time as compared to LHD and HC, meaning that RHD had more difficulty in the process of pure prosody recognitions. It is consistent with "right hemisphere hypothesis for prosody", in which right hemisphere takes a dominant role for recognizing nonverbal expressions.
As interference task, experiment 2 was designed to investigate the impact of semantic contents on prosodic processing. We originally hypothesized that interference would be more evident in LHD, since previous studies which showed LH is known to be activated when prosody and valence of semantic content are in conflict. Bilateral prefrontal cortex mainly in LH was activated during emotional perceptions by semantic contents on positron emission tomography scan [8]. Contrasting to our expectation, the RHD depicted poor performances in interference task. It can be interpreted as RH plays a major role regardless of semantic contents. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging, Mitchell et al. [12] also showed that right lateral temporal lobe was activated during prosody processing whether the presence of semantic content was available or not.
This right lateralized feature of prosody processing for this study deduce that participants exert high levels of selective attention during the experiments unlike in daily lives. In our experiment, participants were asked to focus their attention on the prosody by ignoring the valence of semantic content. Selective attention is an essential part of cognitive processing, and it is linked to the suppression of cortical activities to other stimuli. Attentional modulation for different characteristics of identical stimuli controls early sensory processing which leads to different hemisphere's activation [13]. Right anterior auditory cortex is more activated in prosody detection when comparing to semantic content detections for the identical stimuli [6]. This role of RH on selective attention may account for impaired prosody detection of RHD.
Additionally, cultural differences should be considered in prosody processing. Japanese showed difficulties for ignoring prosody than semantic content which is opposite to the American. Oriental culture has been known to be the "highly contextual culture", which meant that nonverbal information including prosody is more important when compared to Western culture [14,15]. As the participants were all Koreans, the tendency of concentrating on prosody rather than semantic content diminishes interference effects, resulting in the impaired prosody processing for RHD in this study.
Also, more evident features of depression in RHD compared to LHD and HC, despite the lack of significance, as inferred from the results of CES-D, might contribute to the impaired perceptions of prosody in RHD. Several studies demonstrated impaired recognitions for a broad range of emotions expressed by prosody and attenuated perceptions of positive emotions in subjects with depression [16,17].
The present study has following limitations. Gender ratio between groups was different although not significant in this study. However, gender effects on prosody processing tasks were not consistent [18-20]. Most importantly, even minor differences in prosody processing between genders disappeared when the subject's attention was directed towards valence of prosody [21]. The subject number was insufficient to generalize our results and to find out the relationship with characteristics of participants such as brain lesions. Also, the provided auditory stimuli only consisted of speech-like stimuli, instead of filtered utterances of basic intonation patterns, which could cause interferences on pure prosody recognition. As the auditory stimuli were presented with prosody from the beginning of experiment, the participants could ignore the semantic contents which cause interference effects. In addition, auditory stimuli were established throughout the previous study, which excluded sentences of high standard deviations. It meant the sentences were relatively easy, but not enough to fully provoke semantic processing in participants, especially for LHD.
This study is important in spite of these limitations, because the present study is the first trial showing right hemispheric laterality to prosody processing of Korean language. Interference effects of semantic contents to prosody processing were not observed, which suggested unique characteristics for prosody of Korean language. These results could be referred as preliminary data for future research on Korean languages.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (MCST) and Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA) in the Culture Technology R&D Program 2012.
References
1. Heilman KM, Scholes R, Watson RT. Auditory affective agnosia: disturbed comprehension of affective speech. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1975;38:69-72. PMID: 1117301.



2. Monrad-Krohn GH. Dysprosody or altered melody of language. Brain 1947;70:405-415. PMID: 18903253.



3. Ross ED. The aprosodias: functional-anatomic organization of the affective components of language in the right hemisphere. Arch Neurol 1981;38:561-569. PMID: 7271534.


4. Ley RG, Bryden MP. A dissociation of right and left hemispheric effects for recognizing emotional tone and verbal content. Brain Cogn 1982;1:3-9. PMID: 6927552.


5. Paulmann S, Kotz SA. An ERP investigation on the temporal dynamics of emotional prosody and emotional semantics in pseudo- and lexical-sentence context. Brain Lang 2008;105:59-69. PMID: 18177699.


6. Buchanan TW, Lutz K, Mirzazade S, Specht K, Shah NJ, Zilles K, et al. Recognition of emotional prosody and verbal components of spoken language: an fMRI study. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 2000;9:227-238. PMID: 10808134.


7. Gandour J, Wong D, Dzemidzic M, Lowe M, Tong Y, Li X. A cross-linguistic fMRI study of perception of intonation and emotion in Chinese. Hum Brain Mapp 2003;18:149-157. PMID: 12599272.



8. George MS, Parekh PI, Rosinsky N, Ketter TA, Kimbrell TA, Heilman KM, et al. Understanding emotional prosody activates right hemisphere regions. Arch Neurol 1996;53:665-670. PMID: 8929174.


9. Kotz SA, Meyer M, Alter K, Besson M, von Cramon DY, Friederici AD. On the lateralization of emotional prosody: an event-related functional MR investigation. Brain Lang 2003;86:366-376. PMID: 12972367.


10. Pell MD. Cerebral mechanisms for understanding emotional prosody in speech. Brain Lang 2006;96:221-234. PMID: 15913754.


11. Friederici AD, Alter K. Lateralization of auditory language functions: a dynamic dual pathway model. Brain Lang 2004;89:267-276. PMID: 15068909.


12. Mitchell RL, Elliott R, Barry M, Cruttenden A, Woodruff PW. The neural response to emotional prosody, as revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychologia 2003;41:1410-1421. PMID: 12757912.


13. Woldorff MG, Gallen CC, Hampson SA, Hillyard SA, Pantev C, Sobel D, et al. Modulation of early sensory processing in human auditory cortex during auditory selective attention. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1993;90:8722-8726. PMID: 8378354.



14. Kitayama S, Ishii K. Word and voice: spontaneous attention to emotional utterances in two languages. Cogn Emot 2002;16:29-59.

15. Ishii K, Reyes JA, Kitayama S. Spontaneous attention to word content versus emotional tone: differences among three cultures. Psychol Sci 2003;14:39-46. PMID: 12564752.


16. Peron J, El Tamer S, Grandjean D, Leray E, Travers D, Drapier D, et al. Major depressive disorder skews the recognition of emotional prosody. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2011;35:987-996. PMID: 21296120.


17. Schlipf S, Batra A, Walter G, Zeep C, Wildgruber D, Fallgatter A, et al. Judgment of emotional information expressed by prosody and semantics in patients with unipolar depression. Front Psychol 2013;4:461PMID: 23888149.



18. Schirmer A, Kotz SA. ERP evidence for a sex-specific stroop effect in emotional speech. J Cogn Neurosci 2003;15:1135-1148. PMID: 14709232.


19. Paulmann S, Pell MD, Kotz SA. How aging affects the recognition of emotional speech. Brain Lang 2008;104:262-269. PMID: 17428529.


20. Ross ED, Monnot M. Affective prosody: what do comprehension errors tell us about hemispheric lateralization of emotions, sex and aging effects, and the role of cognitive appraisal. Neuropsychologia 2011;49:866-877. PMID: 21182850.


21. Schirmer A, Kotz SA, Friederici AD. On the role of attention for the processing of emotions in speech: sex differences revisited. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 2005;24:442-452. PMID: 16099357.


Fig. 2
(A) Accuracy with 95% confidence interval (CI) bars and (B) reaction time with 95% CI bars in pure prosody recognition task. RHD, right hemisphere damaged patients; LHD, left hemisphere damaged patients; HC, healthy controls. *p=0.013, significantly different according to Mann-Whitney U test.
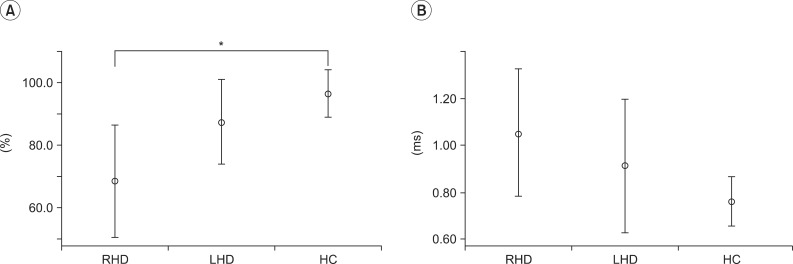
Fig. 3
Accuracy with 95% confidence interval bars of (A) congruent item and (B) incongruent item in interference task. RHD, right hemisphere damaged patients; LHD, left hemisphere damaged patients; HC, healthy controls.

Fig. 4
Reaction time with 95% confidence interval bars of congruent items (A) and incongruent items (B) in interference task. RHD, right hemisphere damaged patients; LHD, left hemisphere damaged patients; HC, healthy controls. *p<0.001, significantly different according to Mann-Whitney U test.
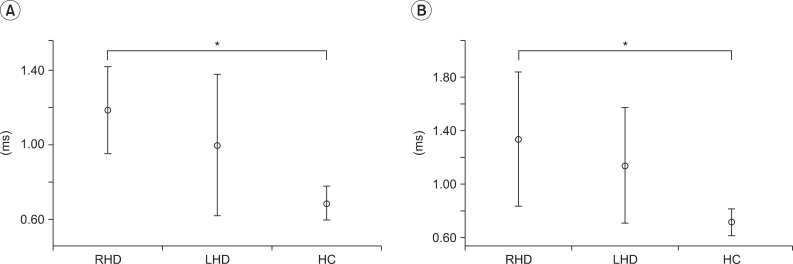
Table 1
Characteristics of participants
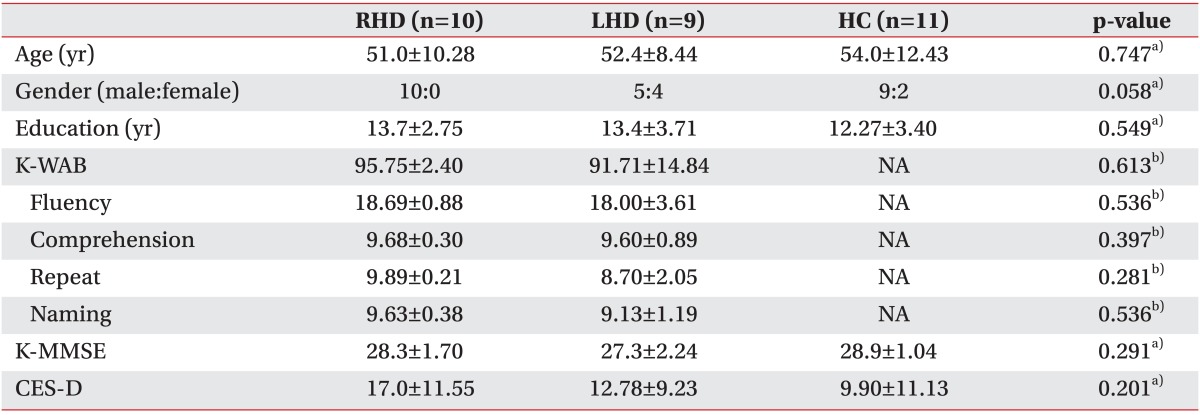
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation.
RHD, right hemisphere damaged patients; LHD, left hemisphere damaged patients; HC, healthy controls; K-WAB, Korean version of the Western Aphasia Battery; K-MMSE, Korean version of Mini-Mental State Examination; CES-D, Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression scale; NA, not applicable.
a)Analyzed between RHD and LHD, and HC. b)Analyzed between RHD and LHD.
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- Scopus
- 3,141 View
- 43 Download
- Related articles in ARM
-
Motor Evoked Potentials of Diaphragm in Stroke Patients.1998 August;22(4)
Soleus Myopathy Induced by Passive Stretch in a Stroke Patient: A case report.1999 June;23(3)