- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 37(2); 2013 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the short-term clinical effects of the intra-articular injection of botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis.
Methods
A prospective, controlled trial compared the effects of intra-articular BoNT-A (Dysport; 200 IU, n=15) with the steroid triamcinolone acetate (TA; 20 mg, n=13) in patients suffering from adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. All patients were evaluated using a Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) of the pain intensity and a measurement of the range of motion (ROM) at baseline (before treatment) and at 2, 4, and 8 weeks post-treatment.
Results
The NRS at 2 weeks (BoNT-A vs. TA; 5.0 vs. 5.2), 4 weeks (4.1 vs. 4.9) and 8 weeks (3.8 vs. 4.6) of both treatment groups were significantly lower than that measured at baseline (7.4 vs. 7.6). The ROM of patients' shoulders increased significantly from baseline in both treatment groups. There was no significant difference in the NRS of pain intensity or the ROM between the two groups. Reduction in the pain intensity score was maintained for 8 weeks post-injection in both groups. There were no significant adverse events in either treatment group.
Conclusion
The results suggest that there are no significant short-term differences between the intra-articular injections of BoNT-A and TA. Although BoNT-A has a high cost, it may be used as a safe alternative of TA to avoid the steroid-induced side effects or as a second-line agent, for patients who have failed to respond to the current treatments.
Adhesive capsulitis is one of the most common causes of shoulder pain and is characterized by a spontaneous onset of shoulder pain accompanied by a progressive limitation of both active and passive glenohumeral movements [1]. The selective limitation of movements in adhesive capsulitis may initially result from involuntary spasms in the muscles that protect the inflamed joint from further overstretching. Long-standing capsular inflammation then leads to the fibrosis and thickening of the fibrous capsule [2]. Treatments for adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder aim to reduce pain and maintain or improve functions, including the range of motion (ROM) and the activities of daily living.
Intra-articular steroid injections are commonly used to treat adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, irrespective of the underlying etiology, and have been proven to be an effective and cost-effective option for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder [3]. The rationale for the use of the intra-articular steroid injections is based on the pathological findings of both the inflammation and fibrosis in the synovial membrane in the individuals with adhesive capsulitis [4,5]. The injection is also used in the glenohumeral capsular, particularly localized to the coracohumeral ligament in the rotator interval [6]. However, although the intra-articular steroid injections are relatively well-tolerated in the short-term, its long-term use can weaken the shoulder tendons and cause histological changes such as inflammation, focal necrosis and fragmentation of the collagen bundles [7]. As such, there is a pressing need for new treatment options which may reduce the shoulder pain and improve functions related to adhesive capsulitis.
Botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) is currently used for pain control. It is widely used to treat musculoskeletal pain and other forms of muscle-related disease, including dystonia, myofascial pain syndrome, tension-type headache and neuropathic pain.
A number of potential antinociceptive mechanisms of BoNT-A has been proposed on the basis of the animal studies to date. Some of the mechanisms include its direct effects on the pain fibers via a blockade of the neurotransmitter release and the effects on autonomic function and decreased central sensitization [8-14].
Recently, BoNT-A has been evaluated for the treatment of the chronic joint pain. Previous studies have shown that intra-articular treatment with BoNT-A may be useful in improving pain and the ROM in patients with chronic osteoarthritic pain in the knee, chronic joint pain disorders, and chronic arthritis joint pain [15-18]. Nociceptive afferent nerve terminals with substance P and calcitonin gene-related protein (CGRP) are associated with synovial blood vessels and the network of free-endings in the subsynovial layer [19-23]. Persistent joint pain may lead to articular nociceptor sensitization as well as an increase in the release of neurotransmitters in the joint area. The intra-articular injection of the botulinum toxin into the painful shoulder joints may inhibit the inflammatory mediator and the neuropeptide release of the articular nociceptors and reduce joint pain [16]. Furthermore, botulinum toxin was found to decrease joint fibrosis through an inhibition of the fibroblast growth in one animal study [24].
These results suggest that intra-articular injections of BoNT-A into the shoulder joint may benefit patients with adhesive capsulitis. We conducted a pilot controlled trial to compare the short-term efficacy of a single intra-articular BoNT-A injection and intra-articular triamcinolone acetate (TA) injection in patients with adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder.
This was a prospective, controlled trial study to investigate the efficacy and safety of BoNT-A (http://www.consultingroom.com/treatments/dysport) for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, which was unresponsive to conventional treatments. The study conformed to the principles of good clinical practice and the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local ethics committees. All patients were required to give a written informed consent before completing any study-related procedures.
Patients were aged 18-70 years with a "painful freezing phase" [4,25] resistant to conventional treatments of the following: physical therapy, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, exercise, and trigger point injection in predominantly one shoulder lasting 10-36 weeks. The patients also had severe shoulder pain with an intensity of five or higher on a Numeric Rating Scale (NRS; scored from 0-10). Patients were required to have stage II or greater shoulder adhesive capsulitis, defined as symptoms meeting one or more of the following criteria [26]: 1) pain at rest; 2) pain below the elbow; 3) disturbed sleep on the painful side at night; and 4) hard end-feel on lateral rotation. All patients were required to have a significant limitation of passive movements in the glenohumeral joint (more than 30 degrees for at least two of the following three movements: forward flexion, abduction or external rotation) compared with the unaffected side [27]. Patients with previous adhesive capsulitis in the opposite shoulder were accepted, even if the difference between the sides were somewhat less than 30 degrees.
We excluded patients with a significant trauma within 6 months, significant pathology such as bone fracture and nerve damage, pregnancy, lactation, a known allergy or sensitivity to study treatments or severe psychiatric conditions. Patients who were not able to comply with the ROM assessments due to excessive pain or with significant difficulties in relaxing sufficiently to allow the investigator to make adequate recordings were also excluded.
Eligible patients were randomized (1:1) to receive BoNT-A or TA by an intra-articular injection after providing informed consent and undergoing baseline evaluation. The patients who were blinded to the treatments were randomly assigned to a scheme, using a table of random numbers.
The injections were carried out under the fluoroscopic guidance, with the patient in the supine position. The patient's arm was placed as far as possible to the side, with the elbow flexed at 90 degrees and the palm facing up to hold the shoulder in external rotation. The central X-ray was vertically oriented over the joint. Prior to the injection, the skin was cleaned with an iodine solution and the area anesthetized with a local injection of 1% lidocaine. A 21-gauge 2.5-3 inch needle was vertically inserted under the fluoroscopic guidance into the anterior aspect of the joint. Prior to the study treatment, 2-3 mL of the contrast material Omnipaque (Sanofi-Winthrop, Markham, ON, Canada) was injected into the glenohumeral space to confirm the correct intra-articular needle position. This was then followed by an injection of either BoNT-A (200 units in 2 mL of 0.9% saline solution) or 20 mg TA (1 mL) and 1 mL of 0.9% saline solution.
All patients were evaluated using the NRS of pain severity and by the measurement of the ROM at baseline, 30 minutes after injection and at 2, 4, and 8 weeks post-treatment. Pain severity was assessed on a 0-10 NRS, where 0=no pain to 10=worst possible pain. The ROM assessments included an assessment of active flexion and abduction and passive flexion, abduction, external rotation and internal rotation, which were measured using a manual goniometer. Flexion and abduction were examined with the elbow joint extended in a sitting position, and the upper limb movement range was measured in the sagittal and coronal surfaces, respectively. External and internal rotation were defined as the movement range with the shoulder joint abducted and the elbow joint flexed to 90 degrees in a supine position.
The study was planned to have 30 patients completing the study. This would have given the study a statistical power of 0.8, to detect a difference in the pain relief of two points on the NRS at a significance level of 0.05.
A general linear model repeated measurements ANOVA (SPSS ver. 11.5; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with the Huynh-Feldt method was used for the comparison of NRS and ROM (active shoulder abduction and flexion, passive shoulder abduction, external rotation, and internal rotation) between the two groups at each visit. The chi-squared test was used to analyze the association between the categorical variables. The level of statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
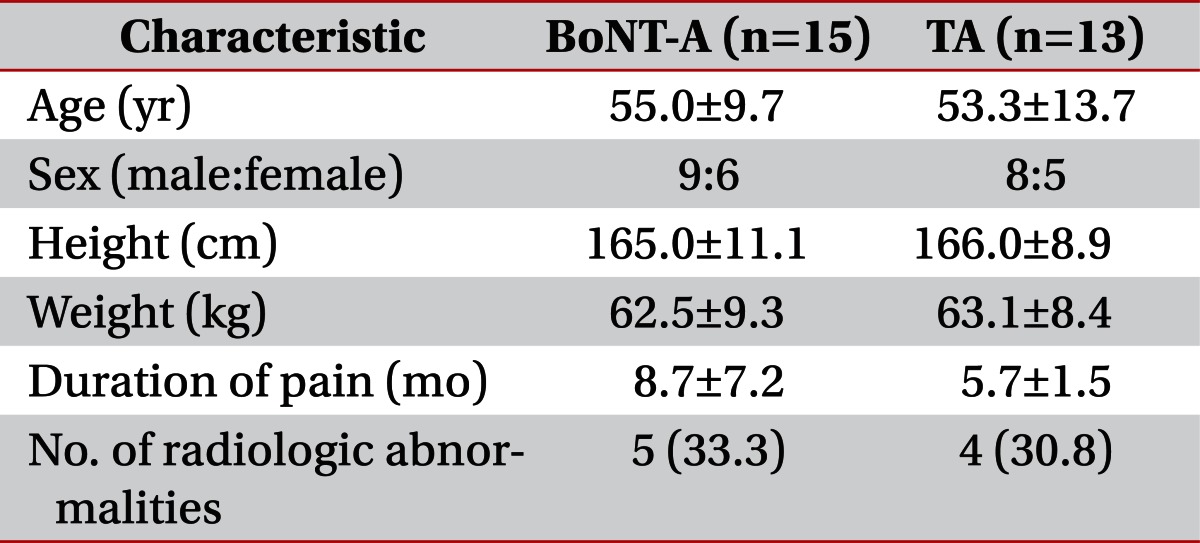
In total, 15 patients received the BoNT-A treatment, and 13 patients received the treatment with TA. Two patients in the TA group were excluded, as they did not give consent. The demographic characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1. There were no significant differences in the diagnosis between the two groups. Five patients in the BoNT-A group and four patients in the TA group experienced mild radiologic abnormalities, including tendinosis and degenerative arthritis on the plain X-ray or ultrasonographic images. All radiologic findings were confirmed by a specialized radiologist.
The mean NRS scores for each treatment group over the course of the follow-up are shown in Fig. 1. The baseline NRS scores were 7.4 in the BoNT-A group and 7.6 in the TA group. At week 8, both treatment groups showed a significant decrease in the NRS scores compared to baseline (mean week 8 score: BoNT-A group, 3.8; TA group, 4.6; both p<0.05). There was no significant difference in the NRS scores between the two groups at baseline or after 8 weeks. The reduced pain intensity score was maintained continuously throughout the 8 weeks post-injection period in both groups.
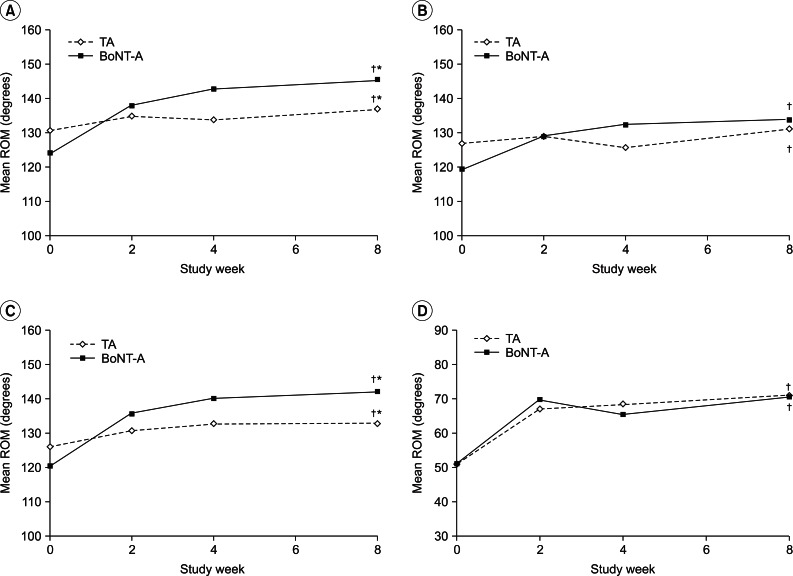
Improvements in the ROM for each treatment group over the course of the follow-up are shown in Fig. 2. At week 8, both treatment groups showed significant improvements in the active shoulder abduction and flexion as well as the passive shoulder abduction and external rotation compared to baseline (all p<0.05).
There was no significant difference between the two groups in the range of active flexion, passive internal rotation, and passive external rotation. In contrast, the improvements in the range of active abduction (degrees improvement in ROM, 22┬░ vs. 6┬░) and passive abduction (22┬░ vs. 7┬░) in the BoNT-A group were significantly greater than those of the TA group (all p<0.05).
This study aimed to assess the effects of BoNT-A for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder and to establish if the treatment was associated with improvements in pain and ROM. To our knowledge, this is one of the first studies to investigate the efficacy of BoNT-A in the intra-articular treatment of adhesive capsulitis. Results showed that the intra-articular injections of both BoNT-A and TA resulted in a significant decrease in pain associated with adhesive capsulitis at week 8. Both treatments also effectively improved the ROM of the shoulder joint in all directions.
Botulinum toxin was initially thought to provide pain relief by decreasing the muscle tension and muscle spasm by blocking the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction [12]. However, recent studies have suggested that the pain reduction often occurs before the muscular improvement, suggesting that BoNT-A may have a more complex mechanism of action on the pain system [9,10,16]. Furthermore, the results of this study also suggest a non-muscular model of chronic pain relief, as the effects of BoNT-A were independent of the blocking action of BoNT-A at the neuromuscular junction in the cholinergic alpha motor neurons.
The proposed direct mechanisms of pain relief include inhibition of alpha- and gamma-motor neurons [10,11,13]; inhibition of the release of local nociceptive neuropeptides/agents via vesicle-dependent exocytosis [14]; and reduction in the release of a number of pain neurotransmitters, including substance P, CGRP, and bradykinin [9]. BoNT-A may also have indirect actions including the reduction in neurogenic inflammation, the alterations within the autonomic nervous system which result in changes to regional perfusion as well as central changes affecting behavior and stress, and the alterations in the sensory pattern within the central nervous system [8,12]. As the sensory neuropeptides substance P and CGRP play an important role in joint nociception and inflammation [28], these mechanisms may be responsible for the improvements in pain seen in this study.
Botulinum toxin can affect the cell cycle distribution of the fibroblasts. The efficacy of intra-articular botulinum toxin in preventing joint fibrosis and adhesion has been demonstrated in the histological evaluations of in vivo study [24,29]. The results may help to explain the increased ROM in the BoNT-A group.
The BoNT-A treatment group showed significant improvements in the active and passive shoulder abduction compared to the TA treatment group. A loss of motion in the scapulohumeral joint, in the early phases of adhesive capsulitis, can be the result of pain and muscle spasm [30]. It may be inferred that BoNT-A is more effective for pain relief than TA. In this study, 200 IU BoNT-A (Dysport, Ipsen Ltd.), administered into the localized shoulder joint cavity for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis, was well tolerated; and no serious adverse events were reported. No critical systemic complications were observed following the injection, although minor adverse events (AEs), including a flu-like illness, occurred in some patients. The tolerability profile reported here is consistent with the known tolerability profile of other studies [12,31].
Limitations of this pilot study include the relatively small sample size, the heterogeneous patient population, the short follow-up time and the effects of the repeat-treatments not having been evaluated. The present study has also enrolled patients with persistent joint pain despite treatment with physical therapy or NSAID. How these findings relate to different patient groups need to be established. It should also be noted that the dosage of TA used in this study was relatively low. Furthermore, this is not a double-blind trial; and biases in the patient's assessment of pain cannot be ruled out. Given the positive results reported, further double-blinded, placebo-controlled studies are warranted to further investigate the benefits of the single and repeated injections of BoNT-A for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis.
In conclusion, the results of this short-term pilot study suggest that the intra-articular injection of BoNT-A produces similar results to that of TA for the treatment of adhesive capsulitis in patients with chronic shoulder pain, who were refractory to other treatment regimens. Although BoNT-A has a high cost, it could be used as the safe alternative of TA to avoid steroid induced side effects or a second-line agent for the patients who have failed to respond to current treatments. Future studies are necessary to further establish the role of BoNT-A in the treatment of the chronic shoulder pain condition.
References
1. Grey RG. The natural history of "idiopathic" frozen shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1978;60:564PMID: 670287.


2. Bunker TD, Anthony PP. The pathology of frozen shoulder: a dupuytren-like disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1995;77:677-683. PMID: 7559688.


3. Shah N, Lewis M. Shoulder adhesive capsulitis: systematic review of randomised trials using multiple corticosteroid injections. Br J Gen Pract 2007;57:662-667. PMID: 17688763.


5. Hand GC, Athanasou NA, Matthews T, Carr AJ. The pathology of frozen shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2007;89:928-932. PMID: 17673588.


6. Milgrom C, Novack V, Weil Y, Jaber S, Radeva-Petrova DR, Finestone A. Risk factors for idiopathic frozen shoulder. Isr Med Assoc J 2008;10:361-364. PMID: 18605360.

7. Tillander B, Franzen LE, Karlsson MH, Norlin R. Effect of steroid injections on the rotator cuff: an experimental study in rats. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 1999;8:271-274. PMID: 10389085.


8. Berardelli A, Gilo F, Curra A. In: Brin MF, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Effects of botulinum toxin type A on central nervous system function. editors. Scientific and therapeutic aspects of botulinum toxin. 2002.Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins; p.171-177.
9. Cui M, Khanijou S, Rubino J, Aoki KR. Subcutaneous administration of botulinum toxin a reduces formalin-induced pain. Pain 2004;107:125-133. PMID: 14715398.


10. Jeynes LC, Gauci CA. Evidence for the use of botulinum toxin in the chronic pain setting: a review of the literature. Pain Pract 2008;8:269-276. PMID: 18503628.


11. Knutson GA. The role of the gamma-motor system in increasing muscle tone and muscle pain syndromes: a review of the Johansson/Sojka hypothesis. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 2000;23:564-572. PMID: 11050614.


12. Mense S. Neurobiological basis for the use of botulinum toxin in pain therapy. J Neurol 2004;251(Suppl 1): I1-I7. PMID: 14991335.

13. Rosales RL, Arimura K, Takenaga S, Osame M. Extrafusal and intrafusal muscle effects in experimental botulinum toxin-A injection. Muscle Nerve 1996;19:488-496. PMID: 8622728.


14. Welch MJ, Purkiss JR, Foster KA. Sensitivity of embryonic rat dorsal root ganglia neurons to Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins. Toxicon 2000;38:245-258. PMID: 10665805.


15. Goyal N. Intra-articular knee joint Botox injection for chronic osteoarthritic pain. Anaesth Intensive Care 2008;36:123PMID: 18326148.
16. Mahowald ML, Singh JA, Dykstra D. Long term effects of intra-articular botulinum toxin A for refractory joint pain. Neurotox Res 2006;9:179-188. PMID: 16785116.


17. Singh JA, Mahowald ML. Intra-articular botulinum toxin A as an adjunctive therapy for refractory joint pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving biologics: a report of two cases. Joint Bone Spine 2009;76:190-194. PMID: 18952480.


18. Singh JA, Mahowald ML, Kushnaryov A, Goelz E, Dykstra D. Repeat injections of intra-articular botulinum toxin a for the treatment of chronic arthritis joint pain. J Clin Rheumatol 2009;15:35-38. PMID: 19131763.


19. Hernanz A, De Miguel E, Romera N, Perez-Ayala C, Gijon J, Arnalich F. Calcitonin gene-related peptide II, substance P and vasoactive intestinal peptide in plasma and synovial fluid from patients with inflammatory joint disease. Br J Rheumatol 1993;32:31-35. PMID: 7678534.


20. Buma P, Verschuren C, Versleyen D, Van der Kraan P, Oestreicher AB. Calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and GAP-43/B-50 immunoreactivity in the normal and arthrotic knee joint of the mouse. Histochemistry 1992;98:327-339. PMID: 1283163.


21. Alstergren P, Appelgren A, Appelgren B, Kopp S, Lundeberg T, Theodorsson E. Co-variation of neuropeptide Y, calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and neurokinin A in joint fluid from patients with temporomandibular joint arthritis. Arch Oral Biol 1995;40:127-135. PMID: 7540832.


22. Kido MA, Kiyoshima T, Kondo T, Ayasaka N, Moroi R, Terada Y, et al. Distribution of substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactive nerve fibers in the rat temporomandibular joint. J Dent Res 1993;72:592-598. PMID: 7680675.


23. Hanesch U, Heppelmann B, Schmidt RF. Substance P- and calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in primary afferent neurons of the cat's knee joint. Neuroscience 1991;45:185-193. PMID: 1721692.


24. Zhibo X, Miaobo Z. Botulinum toxin type A affects cell cycle distribution of fibroblasts derived from hypertrophic scar. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2008;61:1128-1129. PMID: 18555763.


25. Brue S, Valentin A, Forssblad M, Werner S, Mikkelsen C, Cerulli G. Idiopathic adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder: a review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2007;15:1048-1054. PMID: 17333122.


26. Ombregt L, Bisschop P, Veer HJ. A system of orthopaedic medicine. 2003.2nd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
27. Tveita EK, Ekeberg OM, Juel NG, Bautz-Holter E. Range of shoulder motion in patients with adhesive capsulitis; intra-tester reproducibility is acceptable for group comparisons. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2008;9:49PMID: 18405388.




28. Schaible HG, Ebersberger A, Von Banchet GS. Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2002;966:343-354. PMID: 12114291.


29. Namazi H, Torabi S. Novel use of botulinum toxin to ameliorate arthrofibrosis: an experimental study in rabbits. Toxicol Pathol 2007;35:715-718. PMID: 17763285.


30. Depalma AF. Loss of scapulohumeral motion (frozen shoulder). Ann Surg 1952;135:193-204. PMID: 14903846.



31. Kong KH, Neo JJ, Chua KS. A randomized controlled study of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of hemiplegic shoulder pain associated with spasticity. Clin Rehabil 2007;21:28-35. PMID: 17213238.


Fig.┬Ā1
Mean numeric rating scale (NRS) scores for the intra-articular TA and BoNT-A treatment groups. Both treatment groups showed a significant decrease in the NRS scores compared to baseline at week 8. BoNT-A, botulinum toxin type A (Dysport); TA, triamcinolone acetate. ŌĆĀSignificant difference (p<0.05) compared to the baseline value.
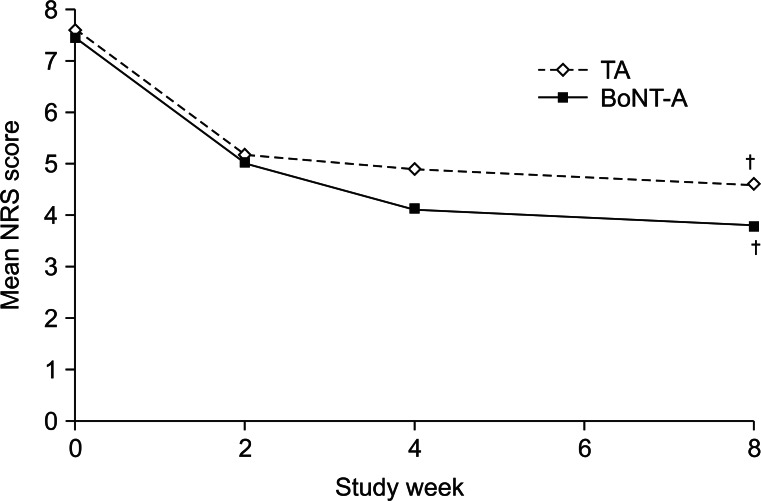
Fig.┬Ā2
Mean range of motion (ROM) assessments between the intra-articular TA group and the BoNT-A group. Both treatment groups produced significant improvements in the active shoulder abduction (A), flexion (B), the passive shoulder abduction (C), and external rotation (D) compared to baseline at week 8 (ŌĆĀp<0.05). Improvements in the range of the passive and active abduction (A, C) were significantly greater in the BoNT-A group than in the TA group. BoNT-A, botulinum toxin type A (Dysport); TA, triamcinolone acetate. ŌĆĀSignificant difference (p<0.05) compared to the baseline value. *Significant difference (p<0.05) compared to the BoNT-A group.