- Search
| Ann Rehabil Med > Volume 42(6); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the association between progression of curvature of scoliosis, and correction for functional component in patients with juvenile idiopathic scoliosis (JIS).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed medical data of patients prescribed custom molded foot orthosis (FO) to correct inequality of RCSPA (resting calcaneal stance position angle), and chose 52 patients (26 females, 26 males) with Cobb angle ≥10° in radiology and uneven pelvic level at iliac crest by different RCSPA (≥3°) as a factor of functional scoliosis. They had different hump angle ≥5° in forward bending test, for idiopathic scoliosis component. Their mean age and mean period of wearing FO were 79.5±10.6 months and 18.6±0.70 months.
Results
Cobb angle was reduced from 22.03°±4.39° initially to 18.86°±7.53° after wearing FO. Pelvis height difference and RCSPA difference, were reduced from 1.07±0.25 cm initially to 0.60±0.36, and from 4.25°±0.71° initially to 1.71°±0.75° (p<0.01). Cobb angle improved most in 9 months. However, there was no significant improvement for those with more than 25° of Cobb angle initially. Mean Cobb angle improved in all age groups, but patients less than 6 years had clinically significant improvement of more than 5°.
Scoliosis is the most common spinal problem in children, and is defined as a lateral curvature of the spine with more than 10° in frontal plane [1]. However, it is much more complex, and involves transverse and sagittal plane components. Curves may progress in growing children, and cause significant problems [2,3].
There are generally two classifications of scoliosis. The first is structural scoliosis, due to spinal pathologies. The other is nonstructural scoliosis, due to other extra-spinal causes such as leg length difference, pelvic inequality, and paraspinal muscle tone asymmetry. Leg length inequality and muscle spasm, are common causes of nonstructural scoliosis [1].
The cause of idiopathic scoliosis is unknown, but there are probably various possible causes. Spinal deformity due to scoliosis can be defined, as a sign of a syndrome with a multifactorial etiology [4,5]. Idiopathic scoliosis caused by deformation of the spine, can also cause deformation to other parts of the body. Le Blanc et al. [6] have reported that body deformation associated with idiopathic scoliosis, can occur in the spine, as well as in the neck, shoulders, scapula, pelvis, and lower extremities and changes depending on growth. Nissinen et al. [7] have concluded that trunk asymmetry, posture, and growth can separately predict development of scoliosis.
In nonstructural scoliosis, the lower extremity and deformity of the pelvis can affect the spine. For example, when pelvic tilt occurs due to difference in leg length, the spine will curve to maintain body balance according to changes in the center of gravity [8]. Leg length discrepancy can be divided into functional and structural inequality. Functional inequality is mostly caused by asymmetrical pronation of the feet [9].
Scoliosis can be classified according to the age of a child. Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis (JIS) is classically defined as scoliosis first diagnosed between ages 4 and 10, and incidence of juvenile scoliosis has been reported to range from 7% to 17% [10,11].
Treating juvenile idiopathic scoliosis takes a very lengthy time, due to lengthy period of growth to maturity in a child, and risk of progression of curvature. The natural progression of JIS is much more aggressive, than idiopathic scoliosis of adolescents [12,13]. Duval-Beaupere et al. [14] reported that patients with JIS had an annual increase in the curve of 4° to 7° Cobb before puberty.
There are many treatments for JIS, including observation, casting, orthosis, physical therapy, exercise, and surgery. Most studies have suggested that JIS can be first managed by observation for all mild curves (<20°). However, treatments should be considered if the curve shows progression, or if the patient has a family history of scoliosis. For patients with curves over 25°, treatments should be considered, due to high probability of progression. The goal of JIS management is to maintain the curve at low-angle value during the growth period to achieve minimal asymmetry [15].
If structural scoliosis and nonstructural scoliosis are present (i.e., if spinal pathologies and asymmetrical pronation of the feet are both accompanied), alignment of the spine will be affected by leg length, and pelvic height difference. It is difficult to find previous studies related to these two forms of scoliosis. However, depending on the degree of pelvic height difference and left and right positions, alignment of the spine may seem to improve or worsen. Our hypothesis is that spinal alignment could change, if factors that caused unstructured scoliosis were removed.
The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate the association between progression of curvature of scoliosis and correction for functional leg length discrepancy (a functional component of scoliosis), in patients with juvenile idiopathic scoliosis.
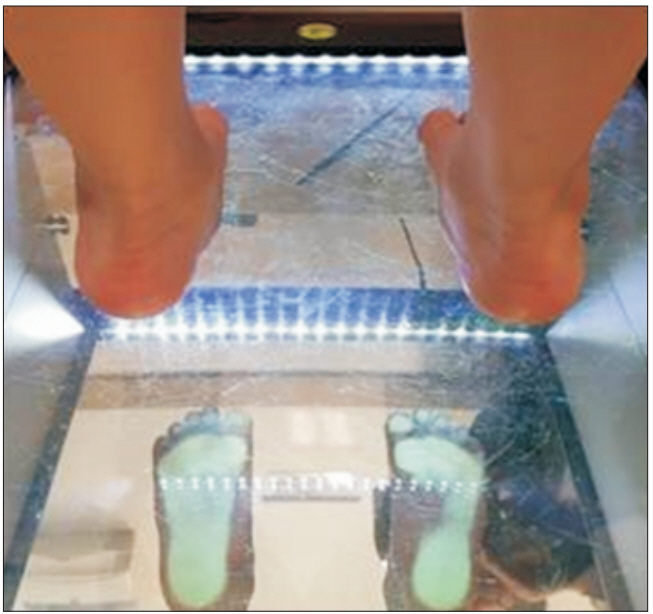
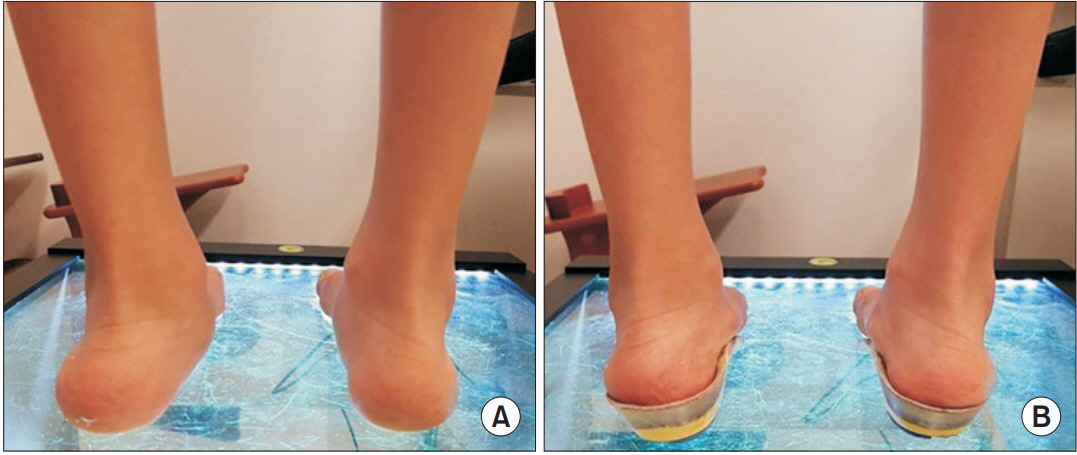
This was a retrospective study using data of 74 patients, with scoliosis managed with foot orthosis. Inclusion criteria were Cobb angle of more than 10° in simple radiographic findings, and hump angle of more than 5°, in the forward bending test [1]. Patients with nonstructural component with RCSPA (resting calcaneal stance position angle) differences >3°, and corresponding pelvic imbalance were selected. The difference in RCSPA was more than 2° at which functional scoliosis could be induced, but was conservatively set at more than 3° [16] (Fig. 1). Bisection of the posterior aspect of the calcaneus was conducted with patients, in prone position to get the RCSPA. A goniometer was used to record the angle of the bisection of the calcaneus, in relationship to the ground. In radiographic pictures, data of the plumb line of 2 cm or more in frontal plane were excluded, to obtain only data taken by the patient in the correct posture. Fifty-two patients met the criteria, and had 9-month and 18-month follow-ups.
JIS can be classified into early onset juvenile scoliosis (younger than age 6), and late onset juvenile scoliosis (older than age 6, but younger than age 10) [17]. Therefore, parameters were analyzed based on age 6.
Exclusion criteria were: presence of structural limb length discrepancy in femur and/or tibia, congenital malformation of the spine, neuromuscular scoliosis, and nervous system diseases.
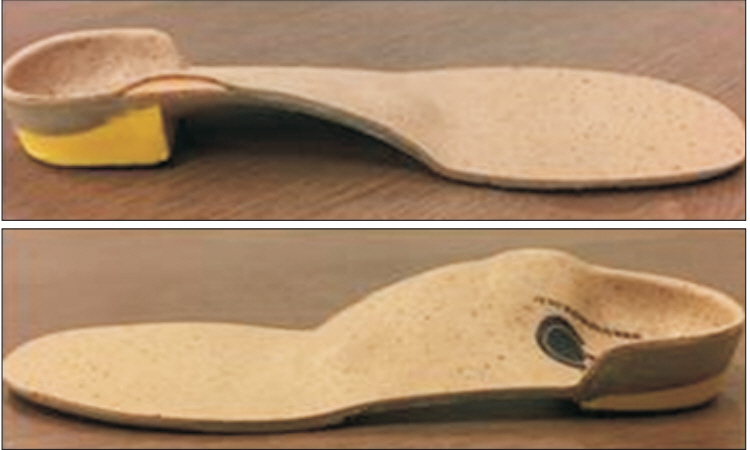
To correct foot pronation difference, foot orthosis (FO) were manufactured with inverted orthotic technique, to allow inversion of the hind foot and eversion of the forefoot, when the brace was worn. Negative casting was performed at subtalar joint neutral position. After gypsum was poured to make positive casting, artificial forward support was made for inversion of the hind foot. At this time, an inversion angle of 5° was given to 1° of RCSPA, to correct the difference between right and left. Based on this positive casting, a mold was made, and a polypropylene shell was made to match the mold. High-density ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) was used to make inversion hind foot. The brace was covered with vinyl (Fig. 2). No heel lift was applied, to directly correct pelvic height difference.
Patient underwent physical examination to assess if the right side and left side of RCSPA had been corrected (Fig. 3). After 2 weeks of FO wearing (at the second visit), height difference of the pelvis was observed on plain radiograph.
Patients were asked to wear FO for at least 2 hours a day, and visited our clinic every 3 months. Clinical tests including RCSPA were performed. Orthosis was corrected when necessary. Physical therapy and spinal orthosis were not performed, because caregivers did not want or could not do it. Hump angle was measured by forward bending test without foot orthosis.
Initial scanography included standing posture, and lateral X-ray taken without orthosis. Cobb angle and pelvis height difference were measured using standing X-ray, without orthosis at 9 months and 18 months to protect from radiation, and change of parameters were analyzed.
Initial Cobb angle at the time of idiopathic scoliosis diagnosis was divided into the following three groups: 10°–19° (n=20), 20°–24° (n=9), and >25° (n=23).
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Paired t-test was performed to compare mean values, and repeated ANOVA was used to analyze the difference among means of the Cobb angle and pelvic height differences.
Mean age of these patients was 79.5±10.6 months. There were 26 males and 26 females. Mean duration of foot orthosis was 18.56±0.70 months. Mean pelvic height difference was 1.07±0.25 cm. Mean Cobb angle was 22.03°±4.29°. Mean difference of RCSPA was 4.25°±0.71° (Table 1).
All patients had double curve scoliosis and distribution of major curve type, were right apex of thoracic curve from the first to the eighth spine (n=24), and left apex of thoracic curve below the ninth thoracic spine (n=28).
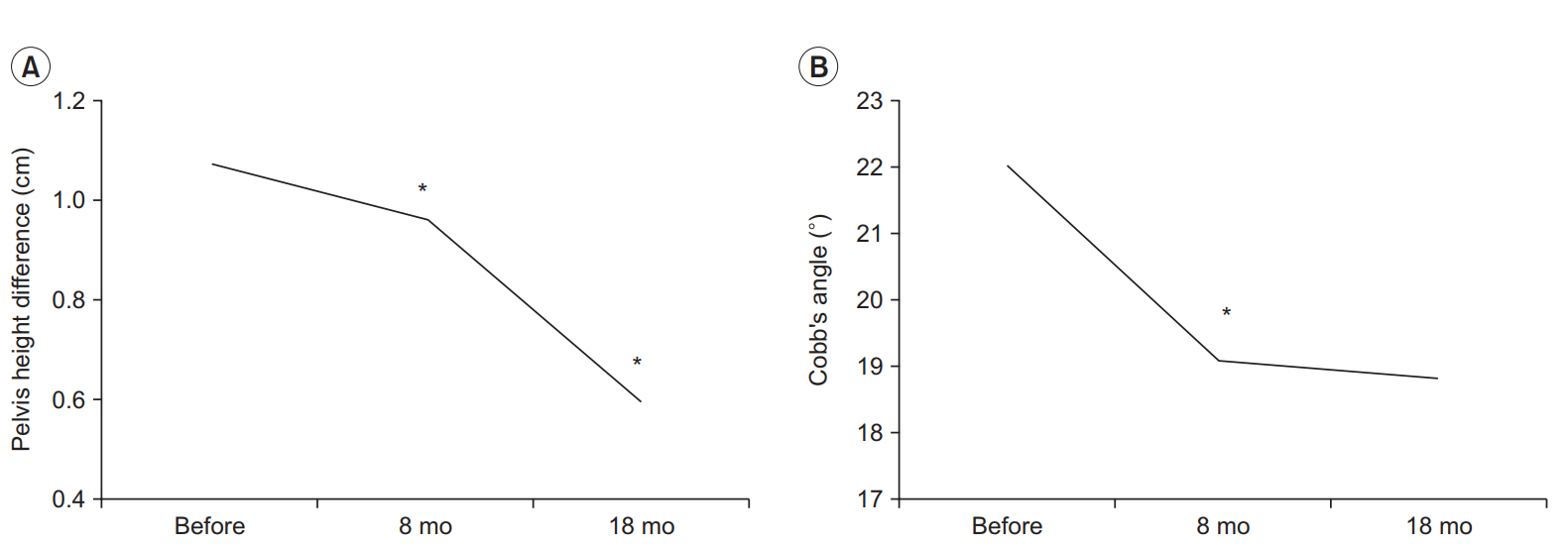
Average Cobb angle, RSCPA difference, height difference of the iliac crest, and hump angle difference decreased after wearing FO (p<0.05) (Table 2, Fig. 4).
Pelvis height difference and Cobb angle were measured at 2 weeks with wearing FO. Difference in pelvis height was (p<0.05), decreased from 1.07±0.25 cm initially to 0.63±0.34 cm in wearing FO. Cobb angle also decreased from 22.03°±4.39° initially, to 20.42°±5.62° in wearing FO.
Cobb angle improved from 22.03°±4.39° before treatment, to 19.07°±6.88° after 9 months and to 18.86°±7.53° after 18 months. Parameters significantly changed in the first 9 months (p<0.05).
For those with apex of thoracic curve from the first to the eighth spine (n=24), Cobb angle decreased from 22.01°±4.36° before wearing FO to 18.23°±7.61° after wearing FO. Difference of RCSPA also decreased from 4.21°±0.88° to 1.75°±0.85°. Pelvis height difference also decreased from 1.02±1.99 cm to 0.54±0.24 cm (all p<0.05).
For those with apex of thoracic curve below the eighth thoracic spine (n=28), Cobb angle decreased from 22.05°±4.49° before wearing FO to 19.38°±7.57° after wearing FO. Difference of RCSPA decreased from 4.29°±0.53° to 1.68°±0.67°. Difference in pelvis height also decreased from 1.11±0.29 cm to 0.66±0.43 cm (all p<0.05) (Table 4).
A total of 41 patients were older than age 6, and 11 patients were younger than age 6. Cobb angle, RCSPA difference, pelvis height difference, and hump angle were all significantly (p<0.05) decreased in both groups, after wearing FO (Table 4). The mean Cobb angle was improved to 5.24°±4.60°.
Cobb angle, RCSPA difference, pelvis height difference, and hump angle were all significantly (p<0.05) decreased after wearing FO, in the groups with initial Cobb angle of 10°–19° and 20°–24°. However, Cobb angle and hump angle increased in the group with initial Cobb angle of more than 25° (Table 4).
There are various opinions about treatment, for juvenile idiopathic scoliosis. Conservative treatments include observation, specific exercises, and bracing. Conservative treatments for JIS are primarily focused on slowing or stopping the progression of curve, to avoid or delay spinal surgery [18], but these conservative management are controversial in JIS.
Bracing is the most effective non-surgical treatment of scoliosis. In management of JIS with bracing, Kahanovitz et al. [19] has reported that part-time bracing, is excellent for smaller curves. However, it has poor effect for patients with greater Cobb angles, and all of them eventually underwent surgery. Brace treatment should be maintained for a lengthy time, because it appears to be more effective in curves under 30° [18].
Wearing foot orthoses for controlling idiopathic scoliosis, has a problem in the spine, and remains controversial. This is based on a theory that good balance of the pelvis by foot orthosis can correct deformation of the spine. But previous study had reported that it was ineffective, because leg length inequality had poor correlation with lumbar scoliosis [20]. On the contrary, the studies [21,22] of the effect of foot orthosis on scoliosis indicated that foot orthosis for scoliosis was effective.
In the management of functional scoliosis with foot orthosis, modification of functional scoliosis obtained by eliminating the scoliotic factor, through the foot orthosis is reasonable. Yoon et al. [23] have reported that wearing FO, has limited effect of on RCSPA differences in patients with nonstructural scoliosis. In this study, however, pelvis inequality caused by RCSPA difference in functional scoliosis patients, was corrected using foot orthosis.
Nonstructural scoliosis involves change of spinal curvature by various factors. This is caused by an underlying condition such as a difference in leg length, pelvic inequality, and muscle spasms [1,24]. Functional scoliosis is treated by correcting the underlying problem. The spine does not need treatment. Correlation between leg length discrepancy due to RCSPA difference, and scoliosis has been reported. When RCSPA difference was more than 2° in standing posture, the medial arch of the foot collapsed, resulting in functionally lower limb length difference, and pelvic inequality, which can lead to scoliosis [16]. Therefore, we estimated that JIS patients with the RCSPA difference could have structural as well as functional components.
Patients who wore FO for correction of pelvic height differences, did not show progression of curvature in this study. Presumable mechanisms are that the first functional scoliosis component was resolved, leading to improvement of nonstructural scoliosis. Second, this can help reverse the vicious cycle of curve progression. Third, a similar mechanism to hitch exercise [25], which is a form of auto-correction to correct the asymmetry of the pelvis so that the spine can be self-corrected in the coronal plane, may have contributed to the correction of alignment of the spine.
Improvements of scoliosis were observed most prominently, within first 9 months after wearing the FO. It is possible to suppose that spinal curve improves when leg length is adjusted through functional component modification in unstructured scoliosis. In other words, in the case of idiopathic scoliosis with functional components of scoliosis, correcting these functional components may improve Cobb angle within one year.
Cobb angle improved in all groups, after observation of changes with age after wearing FO. In the younger age group, the Cobb angle improved more than 5°, although the precise cause was unknown. However, considering that scoliosis occurring in children younger than age 6 can progress to a larger curve as the child grows [12], it is advisable to modify functional components as early as possible, for patients with functional components.
Treatment result of FO was significantly better, for those with less Cobb angles (<25°) than that for those with Cobb angle greater than 25°. If Cobb angle is less than 25°, wearing FO seems to improve RCSPA, pelvis height difference, and Cobb angle. However, when Cobb angle was greater than 25°, only the differences in RCSPA and pelvis height improved, and there was no significant improvement in the Cobb angle. This may be due to the vicious cycle concept, regarding biomechanics of scoliosis progression described in a previous study [26]. Stokes and Burwell [26] have explained that ‘the vicious cycle’ is initiated by a triggering factor, that leads to wedged vertebrae. This will asymmetrically load the spine, which promotes asymmetric growth and curve progression. It cannot be certain that functional elements of JIS have caused structural deformity of the spine, but we can think of this mechanism as one of the reasons, for limited effectiveness of conservative treatment at above moderate Cobb angle (>25°). Results suggest that treatment with intervention is effective when Cobb angle is relatively low or moderate, and when the slope of the pelvis is caused by difference in RCSPA. Therefore, patients with JIS may benefit from early use of foot orthosis, when there is functional leg length discrepancy, due to RCSPA differences to help avoid large curves.
As a limitation of this study, natural progression or intervention of other factors by growth, was not determined in this study. In addition, efficiency of FO compared to exercise therapy or spinal orthosis was not performed, because there was no other group study. In addition, only 52 patients and limited follow-up data, were analyzed in this study. More cases and long-term study are needed to generalize our results. The progression of curve was evaluated by simple X-rays every 9 months. It was defined by change of more than 5° in Cobb angle. Minimum duration of follow-up has been suggested at 24 months after termination of treatment [27]. Although results were statistically significant in this study, Cobb angle did not decrease by more than 5°, after wearing FO. Therefore, more studies are needed in the future with larger sample size and longer follow-up.
Our conclusion from this study is that JIS patients may have functional components, and it is a good plan to identify factors that can cause functional scoliosis in JIS patients, to manage these functional factors. Foot orthosis are effective in correcting functional factors, such as pelvic inequality, caused by different RCSPA for patients with juvenile idiopathic scoliosis.
Fig. 4.
Changes in the angle of the spine, a 9-year-old wearing foot orthosis for 20 months. (A) Before and (B) after treatment.
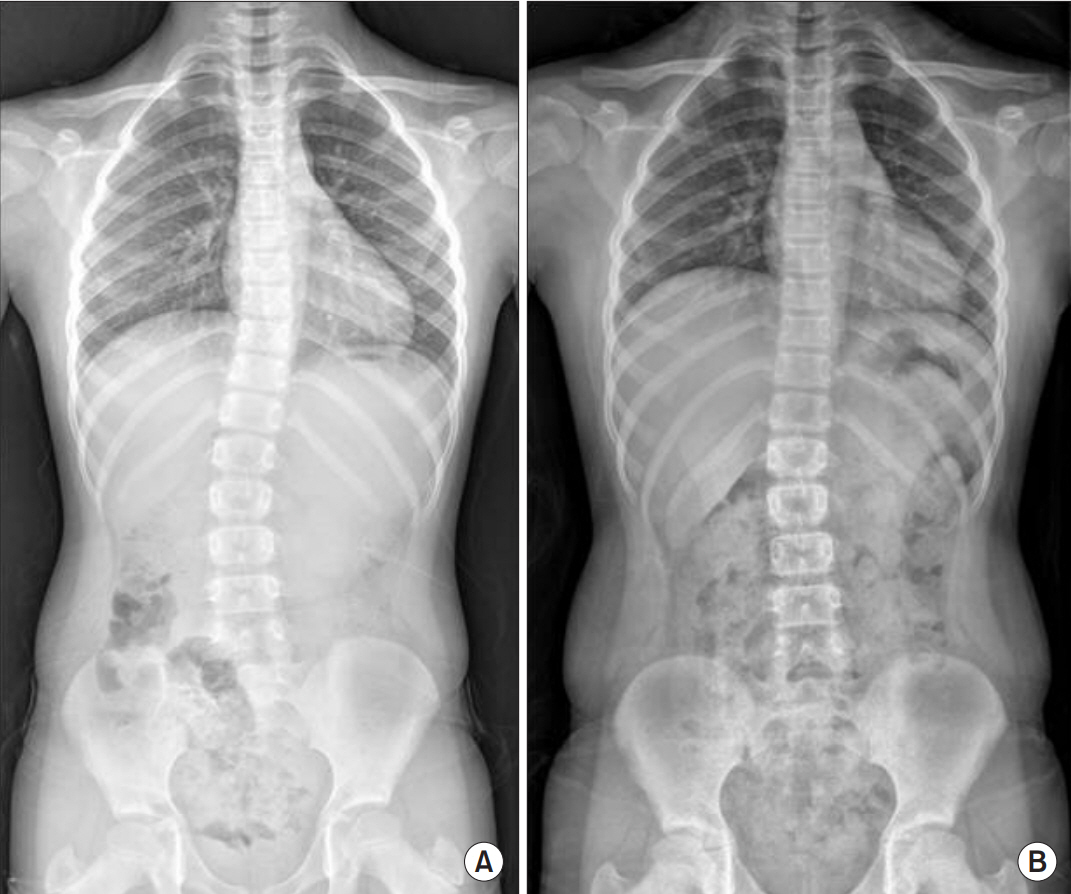
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics
| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (mo) | 79.5±10.6 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 26 |
| Female | 26 |
| Orthosis wearing duration (mo) | 18.56±0.70 |
| Pelvis height difference (cm) | 1.07±0.25 |
| Cobb angle (°) | 22.03±4.39 |
| RCSPA difference (°) | 4.25±0.71 |
Table 2.
Changes of parameters at before and after treatment (n=52)
Table 3.
Changes in parameters at the beginning of the treatment, after 8 months and 18 months follow-ups
Table 4.
Changes in parameters after treatment according to apex, age, and initial Cobb angle
REFERENCES
1. Staheli LT. Fundamentals of pediatric orthopedics. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003. p.91-106.
3. Negrini S, Donzelli S, Aulisa AG, Czaprowski D, Schreiber S, de Mauroy JC, et al. 2016 SOSORT guidelines: orthopaedic and rehabilitation treatment of idiopathic scoliosis during growth. Scoliosis Spinal Disord 2018;13:3.




4. Burwell RG, James NJ, Johnson F, Webb JK, Wilson YG. Standardised trunk asymmetry scores. A study of back contour in healthy school children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1983;65:452-63.


5. Brooks HL, Azen SP, Gerberg E, Brooks R, Chan L. Scoliosis: a prospective epidemiological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1975;57:968-72.


6. Le Blanc R, Labelle H, Poitras B, Rivard CH, Kratzenberg J. 3-D evaluation of posture in normal and scoliotic adolescents. Ann Chir 1996;50:631-6.

7. Nissinen M, Heliövaara M, Seitsamo J, Poussa M. Trunk asymmetry, posture, growth, and risk of scoliosis. A three-year follow-up of Finnish prepubertal school children. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1993;18:8-13.


8. McCaw ST, Bates BT. Biomechanical implications of mild leg length inequality. Br J Sports Med 1991;25:10-3.



9. Gill S. Postural disorders and musculoskeletal dysfunction: diagnosis, prevention and treatment. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2008. p.96-124.
10. Moe JH, Kettleson DN. Idiopathic scoliosis. Analysis of curve patterns and the preliminary results of Milwaukee-brace treatment in one hundred sixty-nine patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1970;52:1509-33.


11. Riseborough EJ, Wynne-Davies R. A genetic survey of idiopathic scoliosis in Boston, Massachusetts. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1973;55:974-82.


12. Mannherz RE, Betz RR, Clancy M, Steel HH. Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis followed to skeletal maturity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1988;13:1087-90.


14. Duval-Beaupere G, Dubousset J, Queneau P, Grossiord A. A unique theory on the course of scoliosis. Presse Med 1970;78:1141-6. passim.
15. Bialek M. Mild angle early onset idiopathic scoliosis children avoid progression under FITS method (Functional Individual Therapy of Scoliosis). Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e863.



16. Rothbart BA, Estabrook L. Excessive pronation: a major biomechanical determinant in the development of chondromalacia and pelvic lists. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 1988;11:373-9.

17. Coillard C, Circo AB, Rivard CH. SpineCor treatment for Juvenile Idiopathic Scoliosis: SOSORT award 2010 winner. Scoliosis 2010;5:25.




18. Aulisa AG, Guzzanti V, Marzetti E, Giordano M, Falciglia F, Aulisa L. Brace treatment in juvenile idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective study in accordance with the SRS criteria for bracing studies - SOSORT award 2013 winner. Scoliosis 2014;9:3.




19. Kahanovitz N, Levine DB, Lardone J. The part-time Milwaukee brace treatment of juvenile idiopathic scoliosis. Long-term follow-up. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1982;(167): 145-51.

20. Hoikka V, Ylikoski M, Tallroth K. Leg-length inequality has poor correlation with lumbar scoliosis. A radiological study of 100 patients with chronic low-back pain. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1989;108:173-5.


21. D’Amico M. Scoliosis and leg asymmetries: a reliable approach to assess wedge solutions efficacy. Stud Health Technol Inform 2002;88:285-9.

22. D’Amico M, Roncoletta P, Di Felice F, Porto D, Bellomo R, Saggini R. Leg length discrepancy in scoliotic patients. Stud Health Technol Inform 2012;176:146-50.

23. Yoon YS, Kang JY, Yoon SB, Choi JS, Choi JL, Yu KP, et al. Effect of the foot orthosis for children scoliosis caused by inequality of resting calcaneal stance position angle. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med 2010;34:66-73.
24. Raczkowski JW, Daniszewska B, Zolynski K. Functional scoliosis caused by leg length discrepancy. Arch Med Sci 2010;6:393-8.



25. Maruyama T, Takeshita K, Kitagawa T. Side-shift exercise and hitch exercise. Stud Health Technol Inform 2008;135:246-9.